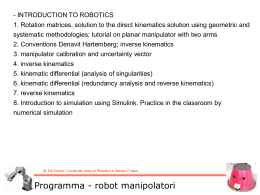
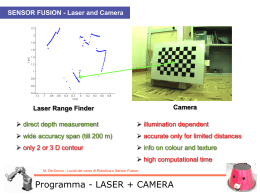
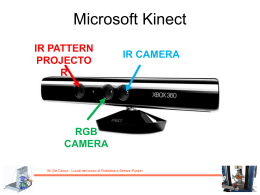
Kinematic model of a differential drive robot M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential kinematic configuration Velocity of the reference point: Angular velocity of the reference point: Kinematic configuration: M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics Simulink Scheme Matlab file: kinematicModel.m M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics Calculate the velocity of the right and left wheels in order to create this path: M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics Differential kinematic configuration Velocity of the reference point: Velocity of the two wheels 𝑅𝐶 = 2 𝑚 𝑚 𝑣 = 0.1 𝑠 𝑏 =1𝑚 M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics Simulink Scheme with Drives Dynamics Add two new Subsystems M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics Drives Dynamics The motor could be modelled with a Low Pass Filter 1 𝐻 𝑠 = 1 + 𝜏𝑠 𝜏 = time constant of the motor With a time of about 4-5 𝜏 the motor reaches the full speed. M. De Cecco - Lucidi del corso di Robotica e Sensor Fusion Differential drive robot kinematics
Scaricare