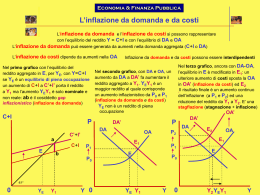
Soluzioni a problemi di inconsistenza dinamica della politica monetaria: DELEGATION (a soggetti indipendenti che hanno come interesse primario il controllo dell’inflazione) Le banche centrali devono essere politicamente e operativamente indipendenti dai governi (Grilli Masciandaro e Tabellini, 1991 - GMT) GMT political autonomy The ability of CB to select the final objectives of monetary policy Based on the following eight criteria: (1) governor is appointed without government involvement (2) governor is appointed for more than five years <= beta! (3) board of directors is appointed without government involvement (4) board is appointed for more than five years <= beta! (5) there is no mandatory participation of government representatives in the board (6) no government approval is required for formulation of monetary policy (7) central bank is legally obliged to pursue monetary stability as one of its primary objectives <= a! (8) there are legal provisions that strengthen the central bank’s position in the event of a conflict with the government GMT economic (operational) autonomy The ability of CB to select the instruments of monetary policy Based on the following eight criteria: (1) there is no automatic procedure for the government to obtain direct credit from the central bank (2) when available, direct credit facilities are extended to the government at market interest rates (3) this credit is temporary <= a! (4) and for a limited amount <= a! (5) the central bank does not participate in the primary market for public debt <= a! (6) the central bank is responsible for setting the policy rate (7) the central bank has no responsibility for overseeing the banking sector (two points) or shares responsibility (one point) L’indipendenza delle banche centrali a partire dalla fine degli anni Ottanta 4 GMT 91 Variabile dipendente: tasso di inflazione Esiste un tasso ottimale di inflazione? Costi dell’inflazione: • suole • distorsioni fiscali • illusione monetaria • variabilità dell’inflazione Benefici dell’inflazione: • signoraggio • possibilità di ottenere tassi reali negativi Trade off: inflazione ha benefici sulla crescita (effetti reali, sebbene temporanei e di breve periodo) ma può crearsi un circolo vizioso costoso da arrestare Credibilità = tying hands Taylor rule: it i * a( t *) b(ut u N ) Atre regole di politica monetaria utilizzate monetary targeting: ormai poco utilizzato, il problema è la volatilità della domanda di moneta interest rate targeting: gestisce meglio il problema della volatilità della domanda di moneta, no per TFP shocks inflation targeting: più utilizzato, più de facto che de jure output targeting: idea più recente, al momento scarsamente utilizzato (ma in parte incluso nella Taylor rule) 7 Esempio di uso distorto della politica monetaria Il motivo elettorale Elezioni Nixon 8 9 10
Scaricare