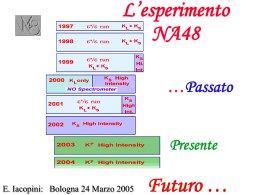
Argomenti della presentazione: Che cosa vuole misurare NA62 e perché Come intende procedere Enrico Iacopini Univ. di Firenze e INFN-FI Bologna, 21 settembre 2010 La misura L’esperimento NA62 si propone di misurare il BR del decadimento rar(issim)o K + (BRSM~0.8×10-10) con un’accuratezza del 10% Perché si vuole farlo ? La ragione è che questo decadimento costituisce un test inequivoco delle previsioni dello SM, dato che, in esso, il suo BR (con quello del decadimento “fratello” K L 0 ) può essere oggi calcolato con un grado di accuratezza, oggi non raggiungibile in altri processi FCNC (10%5%). E’ molto sensibile a contributi di Fisica oltre il MS (NP). Infatti, risultando sin8qC, esso é fortemente soppresso (BR ≈ 10-10) nel MS ed in caso di NP, contributi mediati, per esempio, da W-ini e Z-ini sono in grado di modificarlo sensibilmente… K→ nn : Teoria nello Standard Model 2 2 Im Re Re t t c B ( K nn ) 5 X SM 5 X SM ( Pc Pc ,u ) B ( K L0 Im t nn ) L 5 X SM Vus c Vcs*Vcd t Vts*Vtd 2 0 top contributions charm contribution X SM ( NLO) 1.464 0.041 3 2 Br ( K 0en ) 8 11 8 rK (5.165 0.025) 10 ( / 0.225) 2 2 sin 4 qW The hadronic matrix element is, in fact, measured (and isospin rotated) … Predizioni dello SM Standard Model BR(K++n n) (8.5 ± 0.7)×10-11 BR(KL0n n) (2.6 ± 0.4)×10-11 dove, per il decadimento carico che ci interessa, il break down dell’incertezza è il seguente: 25% incertezza sulla massa del charm (assunta 1.3 GeV); 45% incertezze su CKM e fattori di scala; 11% incertezze su s , mt; 19% incertezza dal Ke3 e dal contributo da quarks u e c (16%) k 6%; X SM 38%; Pc 17%; Pc 39% J.Brod, M. Gorbahn; arXiv:0805.4119v1 … e, a detta dei teorici del campo, una predizione addirittura meglio che ≈ 5% (7% nel caso del KL) sembra possibile in un futuro prossimo … Eventuali discordanze, dunque, sarebbero segno di NP … Impact of the proposed measurement on the Unitarity Triangle Oggi da K+ + n nbar (ρ,η) α K+→π+νν K0→π0νν γ (0,0) β (1,0) 100 events Mean=E787/949 BR(K+ → + n n ) = 1.73+1.15-1.05 × 10-10 Impact on possible NP Possibility to distinguish among several NP models (SUSY, MSSM with or without new sources of CPV or FV), 5-dim split fermions, topcolor, multi Higgs, light sgoldstino, extra-dimensions, ...) NA62 is the continuation of NA48, with an improved detector… NA48: ’/ 1997 ’/ 1998 ’/ 1999 no spectrometer KL ’/ NA48/1 KS lower inst. intensity NA48/1: KS NA48/2: K NA48/2: K Direct CP-Violation established Re ’/ = 14.7 ± 2.2 104 KTeV (2008) 19.2 ± 2.1 10-4 2000 + KL Rare Decays 2001 2002 2003 2004 First observation of K0S → 0 e+e- and K0S → 0 mm + KL Rare Decays • Search for Direct CP-Violation in charged kaon decays • scattering length: (a0-a2)m+= 0.268 0.017 NA48/3 P326 NA62 NA62 phase I Data taking: 2007 Results: end 2008 With the NA48 standard detector, perform a precision measurement (<0.5% accuracy) of the ratio RK (K e n e ) ( K m n m ) to check lepton universality and possibly observe signals of Physics beyonf the SM 5 RK(ex ) (2.486 0.013) 10 (40% dataset) RK(th) (2.477 0.001) 10 5 NA62 phase II 2005: First Proposal 2013-2015: data taking Perform the measurement of the BR (10% accuracy) of the very rare decay K nn Proposal to Measure the Rare Decay K n n at the CERN SPS CERN-SPSC-2005-013 SPSC-P-326 CERN-SPSC-2007-035 SPSC-M-760 NA62 Collaboration: Bern ITP, Birmingham, Bristol, CERN, Dubna, Ferrara, Fairfax, Florence, Frascati, Glasgow, IHEP, INR, Liverpool, Louvain, Mainz, Merced, Naples, Perugia, Pisa, Rome I, Rome II, San Luis Potosi, SLAC, Sofia, TRIUMF, Turin •Presented at the CERN SPSC in September 2005 •R&D endorsed by CERN Research Board on December 2005 •Test beams for R&D in 2006-2008 •Addendum to the Proposal in November 2007 •2008-2009: approval •2009-2011: construction •2012: commissioning •2013-2014: data taking NA48 present Beam line NA62 Data l’estrema piccolezza del BR della reazione, la misura si può fare solo se si riesce davvero ad “eliminare” il fondo ! (Jacques de La Palice …) … E come si fa ? Una bella somiglianza con Peter. Come hai fatto? Semplice. Prendi un grosso masso e togli via tutto quello che non somiglia a Peter Le linee guida per NA62 O(100) eventi K++ n n in 2 anni BR(SM) = 8×10-11 ~ 4.8×1012 K+ decays/y Accettanza ~15% Reiezione cinematica n qK n m2miss=(PKP)2 Veto e particle ID ~ max 15% di fondo Tecnica di decadimento del K in volo Fascio intenso di protoni dal SPS K di alta energia (PK = 75 GeV/c) Fascio non separato Cherenkov per K tagging: CEDAR K+: tracciatore del fascio (GTK:Si) : spettrometro magnetico (STraw-CHambers STCH) Veto g,0 : LKr + LAV + SAC Veto eventi multitraccia: STCH Separazione /m : MUD+RICH Il detector di NA62 ppp: Momentum: Duty cycle: Pulses/year: SM events/y: 3.3 x 1012 75 GeV/c 4.8/16.8 s 1.5 x105 50 NA62 future beam line Beam line TARGET NA62 future beam line Fondo con soglia cinematica 92% dei decadimenti del K+ Decay BR K+ mn (Km2) 0.634 K+ +0 (K2) 0.209 K+ ++K+ 00 0.073 n qK n m2miss=(PKP)2 K+ +0 determina, quanto al segnale, la divisione in due regioni utili Regione I: 0 < m2miss < 0.01 GeV2/c4 Regione II: 0.026 < m2miss < 0.068 GeV2/c4 Reiezione basata su Cinematica, Veto e Particle ID Fondo senza soglia cinematica 8% dei decadimenti del Decay n K+ qK n m2miss=(PKP)2 BR K+0en (Ke3) 0.049 K+0mn (Km3) 0.033 K+mn g (Km2g) 6.2×10-3 K+ 0 g 1.5×10-3 (2.75×10-4 PDG) K+ en (Ke4) 4.1×10-5 K+mn ( Km4) 1.4×10-5 Questo fondo attraversa la regione del segnale Reiezione basata solo su Veto e Particle ID Esempio di riduzione del fondo Quanto alla cinematica, si è assunto (mmiss)2 ~ 10-3 GeV2/c4 Resolution requirements: P < 1 % PK < 0.5% qK 50-60 μrad K+→ 0 (K2) K+→mn (Km2) Largest BR: 63.4% Need ~10-12 rejection factor • Kinematics: 10-5 • Muon Veto: 10-5 • Particle ID: 5×10-3 MUD RICH 2nd Largest BR: 20.9% Need ~3×10-12 rejection factor • Kinematics: 10-4 • 0 (2 Photon Veto): 3.5×10-8 Large angle: 12 ANTIs (10 < acceptance < 50 mrad) Medium angle: NA48 LKr (1 < acceptance < 10 mrad) Small angle: IRC SAC (acceptance < 1 mrad) Va bene eliminare il fondo, ma occorre che un po’ di segnale resti ! Selezione: 1 traccia ricostruita nel gigatracker e nelle straw 1 traccia vista nel RICH particle-ID e timing Traccia nell’accettanza del LKr e MUD particle-ID 5 < Zvertex<65 m dalla 3rd stazione del gigatracker definizione della regione fiduciale CDA<0.8 cm (s(CDA)~0.1 cm) rigetta eventi mal ricostruitai P < 35 GeV/c essenziale sia per vetare il +0 che per mantenere la separazione m/ del RICH a meglio dello 0.5% . Accettanza = 14.4% (3.5% Regione 1, 10.9% Regione 2) Efficienza di ricostruzione del gigatracker ~90%. Contributo principale: taglio su P (riduzione 50% dell’accettanza) Rapporto segnale/fondo Decay Mode Signal [acc=14.4%, flux = 4.8×1012 decay/year] K++0 [h0 = 2×10-8 (3.5×10-8) ] # events 55 evt/year 4.3% (7.5%) K+m+n 2.2% K+e++n 3% Other 3 – track decays 1.5% K++0g ~2% K+m+ng ~0.7% K+e+(m+) 0n, others negligible Expected background 13.5% (17%) … e veniamo ora alle caratteristiche che devono possedere i principali rivelatori di NA62 … Il fascio che useremo … m 2 BEAM A N T I1-12 M H A C U V R IC H M (CERN) 1 0 T A X A chrom at1 -1 SAC T arget Primary beam: 400 GeV/c primary from SPS A chrom atprotons 2 12 protons/sC 7 target 1.1 on C 2 x 10C 5 +75G K~ eV Secondary beam: V A C U U M 75C GeV/c (P/P ~ 1%) E D A R p//K (fraction of K ~6%) e+ component suppressed G IG A T R A C K E R Area at beam tracker 16 cm2 A N 0 Integrated average rate atTIbeam tracker 750 MHz N e 1atm IR C StrawC ham bers -2 0 Expected kaon decays per year 4.8x1012 (1y = 100d, 60% eff.) 50 150 100 200 Iron L K r 250 22 Zm K tagging m 2 CEDAR A N T I1-12 M (UK+USA) H A C U V R IC H M 1 T arget T A X A chrom at2 C 7 C 5 C 2 0 A chrom at1 C E D A R -1 +Upgraded K~ 75G eV version of the CEDAR built for the SPS secondary beams: V A C U U M H (3.6bar) instead of Nitrogen • Pressurized 2 • New photo detectors and electronics G IG A T R A C K E R SAC A differential Cherenkov counter for K tagging N e 1atm Vary gas pressure and diaphragm aperture A N T I0 to select Kaons: 80% eff, rej err = 1%IRC StrawC ham bers -2 Iron L K r 100 ps time resolution (30 pe; 1.5 x 10^9 pe/s) 0 50 100 150 200 250 23 Zm Il Gigatracker (GTK) 800 MHz beam Rate< 82MHz/cm2 200 ps time resolution <0.5 % X0 /station (CERN, TO, FE) A1÷A4: achromat dipole magnets to provide the momentum selection and recombination beam not to scale Layout of the beam on the horizontal plane The Beam momentum is derived from the hit coordinate in GTK2 with respect to GTK1 and GTK3 coordinates: 75 GeV/c -> 60 mm Layout di ciascuna stazione pixel matrix mechanical support chip 18000 pixels quadrati con lato di 300 mm • • • • • 200 mm Silicon sensor (>11 000 e/h mip) – Bump-bonding Read-out chip (0.13mm techology) – Thinned down to ~100 mm Beam surface ~ 14 cm2 ~125 mm Carbon fibre for cooling & support Fluences: 1.×1012 to 2.×1014 1MeVequiv n/cm2 vista frontale Risoluzioni necessarie: s(PK)/PK ~ 0.2% s(dX,Y/dZ) ~ 12 mrad (mmiss)2 ~ 10-3 GeV2/c4 Il tracking m 2 A N T I1-12 1 STRAW TRACKER M H A C U V R IC H M (CERN-Dubna) T arget T A X A chrom at2 C 7 C 5 vacuum SAC C 2 in +75G 4 straw chambers K~ eV 0 1 magnet (NA48 magnet, 256 MeV/c P kick) t V A C U U M 4 views per chamber (XYUV) A chrom at1 C E D A R 4 staggered layers of tubes per view long -1 9.6 mm Mylar tubes 2.1 m G IG A T R A C K E R Total X0 ~0.1% per view N e 1atm A N T I0 IR C Full length prototypes built in 2007 and 2010 -2 Tested in beam 0 50 100 StrawC ham bers 150 200 Iron L K r 250 26 Zm Photon Veto I 2 1 LARGE ANGLE VETO (LNF, NA, PI, RM1) A N T I1-12 M H A C U V R IC H M 12 rings in vacuum to cover 8.5 to 50 mrad OPAL lead glass T A Xin Frascati A chrom at2 T arget built Rings C 2 C 7 C 5 0 +75G K~ eV SAC m V A C U U M A chrom at1 C E D A R -1 N e 1atm G IG A T R A C K E R A N T I0 IR C StrawC ham bers -2 0 50 100 150 200 Iron L K r 250 27 Zm Photon Veto II (CERN-Sofia) m 2 LKR A N T I1-12 M H A C U V R IC H M Liquid Krypton Calorimeter 1 0 T A X SAC T arget Use the existing LKr from NA48 A chrom 2 Inefficiency foratdetecting g measured on data C 7 C 2 C 5 + -6 For Eg > 10 GeV K~ e <75 8x10 G eV V A C U U M A chrom at1 C E D A R IRC -1 G IG A T R A C K E R Intermediate RingANTI0 Calorimeter Radial coverage in front of LKr 7 cm < R < 14.5 cm -2 0 50 N e 1atm 100 SAC IR C StrawC ham bers Small Angle Calorimeter 150 200 24x24 cm Neutral particles escaping through the beam pipe Iron L K r 250 28 Zm The photon Veto system Medium angle (1-10 mrad): the “old” NA48 LKr Calorimeter • Rate: ~8.7 MHz (m) + ~4 MHz (g) + ~4 MHz () New Readout Costituisce il “cuore” del sistema dei veto: per decadimenti K+ 0 nella zona fiduciale (5<z<65m) e con E <35 GeV, i due fotoni del 0 sono, nell’82% dei casi, nell’accettanza del LKr e nel resto dei casi, quello di energia maggiore è nel LKr+SAC. Per questo è cruciale conoscere esattamente la sua inefficienza in funzione dell’energia del fotone (in NA48 LKr veniva usato come calorimetro e non come Veto …) /m rejection I m 2 RICH 0 -1 -2 M Purposes: • /m separation between 15 and 35 GeV/c X A chro m a~100 t2 T a•rg et TA Event time with resolution of ps C 7 C 2 C 5 +75G • L0 trigger signals K~ eV SAC 1 (FI, PG, CERN) A N T I1-12 H A C U V R IC H M V A C U U M FullAlength prototype built and tested at chrom at1 C E D A R CERN 0.5 radius G IG A T R A C K E R 2 x 1000 PMT A N T I0 18 mm pixel size Nhits ~ 17/event tevent ~ 70 ps [NIM A 593, 2008] 0 50 100 N e 1atm IR C StrawC ham bers 150 Per maggiori dettagli: vedi presentazione di R. Piandani 200 Iron L K r 250 30 Zm /m rejection II m 2 A N T I1-12 MUON VETO 1 M H A C U V R IC H M (Mainz-Protvino) T arget T A X A chrom at2 0 -1 MUV3: Fast trigger signals SAC MUV1 andC2MUV2:C5 C 7 +75G K~ eV Iron-scintillator sandwich calorimeters with 24 (MUV1) and 22 (MUV2) layers ofC V A U U M A c h r o m a t 1 C E D A R scintillator strips. N e 1atm G IG A T R A C K E R A N T I0 IR C StrawC ham bers -2 0 50 100 150 200 Iron L K r 250 31 Zm TDAQ A possible scheme…… Level L0 “hardware” L1-L2 “software” Input ~10 MHz 1 MHz Output 1 MHz O(KHz) Implementation Dedicated hardware TDAQ farm Actions RICH minimum multiplicity, Muon veto, LKr (g) veto L1 = single sub-detectors L2 = whole event •1track × m! × g! → 1 MHz L1 trigger input → PC farm Main work on possible solutions for the L0 hardware TELL-1 board (LHCb) based implementation for all non FADC sub detectors Design of a new 100 ps TDC daughter-card (RICH, Straws, MAMUD,…) Per maggiori dettagli: vedi presentazione di B. Angelucci Conclusioni NA62, studiando il decadimento ultrararo del K+ in pi nu nubar, particolarmente “pulito” dal punto di vista teorico, consentirà una verifica importante delle predizioni del MS, avendo altresì molto da dire su una possibile (nuova) fisica oltre il MS ! Lo studio dei mesoni strani K, in passato ha consentito di capire sempre più profondamente il flavour nelle particelle elementari ed in particolare la violazione di CP. Avranno davvero finito di sorprenderci ? K mesons Flavour Physics Il detector di NA62 STRAW Prototype results Dubna σ = 61 μm 5 hits for track σ = 136 μm/hit Magnet MNP33 ch 1 ch 2 (Ptkick = 260 MeV/c) ch 3 ch 4 (mmiss)2 ~ x,y,u,v 183 m from target x,y,u,v 10 m x,y,u,v 10 m x,y,u,v 15 m 10-3 GeV2/c4 The photon Veto system: the LKr Method II: brem photons, to cover the range 2 GeV < Eg< 10 GeV Kevlar window Magnet Photon beam g e- Electron beam (25 GeV/c) vacuum Bremsstrahlung Energy He Calorimeter Drift chambers Hodoscope Inefficiency 2 < Eg < 3.5 GeV (5.8 ± 1.3)×10-4 3.5 < Eg < 5 GeV (1.6 ± 0.4)×10-4 5 < Eg < 7.5 GeV (2.8 ± 1.6)×10-5 7.5 < Eg < 10 GeV <2×10-5 Eg > 10 GeV <1×10-5 Questi risultati garantiscono per il sistema dei Veto (LKr+SAC+LAV) una inefficienza di reiezione del 0 inferiore a 3×10-8. Dove siamo oggi con le misure del BR di K+ n n K+→+ nn : State of the art K+→+ nn : State of the art hep-ex/0403036 PRL93 (2004) AGS Stopped K ~0.1 % acceptance BR(K+ → + nn ) = 1.47+1.30-0.89 × 10-10 •Twice the SM, but only based on 3 events… Experiment concluded KL→0 nn : E391a BR(K0 → 0 nn ) < 6.7 × 10-8 (90%CL) arXiv:0712.4164v1 (27 Dec 2007) KL 0nn at J-Parc • Step by step approach – KEK E391a ~O(10-9) – J-Parc Step 1: » Move E391a detector to J-Parc » Search beyond the Grossman-Nir limit (3.5 standard model evts/3e7 sec) – Step 2: Optimize beamline and detector for >100 events
Scaricare