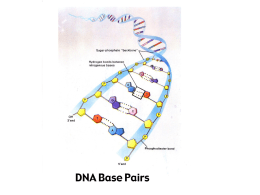
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1978 "for the discovery of restriction enzymes and their application to problems of molecular genetics" Werner Arber Daniel Nathans Hamilton O. Smith Biozentrum der Universität Basel, Switzerland Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD, USA Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD, USA b. 1929 b. 1928 d. 1999 b. 1931 1/3 of the prize Switzerland 1/3 of the prize USA 1/3 of the prize USA RESTRICTION ENZYMES • function : to “restrict” infection by phages • endonuclease site specific : each enzyme recognizes either 4 or 6 or 8 base pairs and cuts in correspondence of the recognized site Rescriction enzymes recognise palindromic sequences RESTRICTION ENZYMES •Endonuclease site specific : recognizes 4-6-8 base pairs and cut in correspondence of the recognized site. cleavage site symmetry Auto protection from cleavage Restriction maps DNA ligase Cloning is the process of creating an identical copy of an original organism or thing. A cloning in the biological sense, is a molecule, a single cell (like bacteria or yeast , eukariotes etc.) or a multi-cellular organism that has been directly copied from and is therefore genetically identical to another living organism. Molecular cloning refers to the procedure isolating a DNA sequence of interest and obtaining multiple copies of it in an organism. Cloning is frequently employed to amplify DNA fragments containing genes, an essential step in their subsequent analysis. Cloning of any DNA sequence involves the following four steps: amplification, ligation, transfection, and screening/selection. Cloning a cell means to derive a (clonal) population of cells from a single cell. This is an important in vitro procedure when the expansion of a single cell with certain characteristics is desired, for example in the production of gene-targeted ES cells. Most individuals began as a single cell and are therefore the result of clonal expansion in vivo. Cloning an organism means to create a new organism with the same genetic information as a cell from an existing one(identical). It is an asexual method of reproduction, where fertilization or inter-gamete contact does not take place. This form of reproduction is common among simple organisms such as bacteria. Dolly (1996) was the first mammal to have been successfully cloned from an adult cell. She was cloned at the Roslin Institute in Scotland and lived there until her death when she was 6. The name "Dolly" in honor of Dolly Parton, because it was a mammary cell that was cloned. The technique that was made famous by her birth is somatic cell nuclear transfer, in which a nonreproductive cell containing a nucleus is placed in a de-nucleated ovum (which then develops into a fetus). 1972 (October) Paul Berg and co-workers create the first recombinant DNA molecule (PNAS). Trasformazione = inserimento un DNA in un batterio o in un lievito Trasfezione = inserimento di un DNA In una cellula di eucarioti DNA viral vectors lamda (l) phage Advantages: • bigger insert with respect to plasmids (~20kb) • bacterial cell lysis (expression vector) Cloning DNA fragments 32-45 kb with cosmids Cloning DNA fragments 32-45 kb with cosmids YAC = yeast artificial chromosomes for 600 kb to 2 Mb inserts BAC = bacterial artificial chromosomes to insert ~ 300 kb. Genoteca genomica = collezione del DNA di un genoma di un organismo in frammenti clonati Quanti cloni indipendenti sono necessari per rappresentare un intero genoma? Un “array” ordinato permette di identificare un gene dal suo posizionamento nell “array”. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1975 "for their discoveries concerning the interaction between tumour viruses and the genetic material of the cell" David Baltimore Renato Dulbecco 1/3 of the prize USA 1/3 of the prize USA Massachusetts Institute Imperial Cancer Research University of Wisconsin of Technology (MIT) Fund Laboratory Madison, WI, USA Cambridge, MA, USA Kingdom b. 1938 Howard Martin Temin 1/3 of the prize USA London, United b. 1914 (in Catanzaro, Italy) b. 1934 Genoteca di cDNA I cDNA posono espressi in cellule batteriche se si usa un promotore batterico Identificazione di un clone specifico in una genoteca classica Ibridizzazione con sonde di DNA : Mediante anticorpi Per evidenziare la Proteina prodotta dal Vettore d’espressione. Polymarase Chain Reaction PCR The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1993 "for contributions to the developments of methods within DNA-based chemistry" "for his invention of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method" Kary B. Mullis 1/2 of the prize La Jolla, CA, USA b. 1944 "for his fundamental contributions to the establishment of oligonucleotide-based, sitedirected mutagenesis and its development for protein studies" Michael Smith 1/2 of the prize University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada b. 1932 (in Blackpool, United Kingdom) d. 2000 T > 950C Tm primers T > 950C T DNA pol.
Scaricare