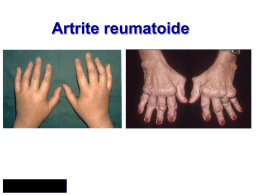
SANITA’ AZIENDA OSPEDALIERA "C. POMA" P.O. ”Destra Secchia" Pieve di Coriano (Mantova) Dipartimento di Riabilitazione S. C. di Riabilitazione Specialistica e Reumatologia Direttore: Giovanni Arioli Malattie Reumatiche e terapie attuali: quando, come e perchè Gestione della Disabilità nelle Malattie Reumatiche: coordinamento tra Reumatologi e Fisiatri ALoMAR Milano 10 Dicembre 2012 Giovanni Arioli Long-term health-enhancing physical activity in rheumatoid arthritis the PARA 2010 study. Nordgren B, Fridén C, Demmelmaier I, Bergström G, Opava CH BMC Public Health. 2012 Jun 1;12(1):397 BACKGROUND: People with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) suffer increased risk of disability and premature mortality. Health-enhancing physical activity (HEPA) could be one important factor to reduce this risk. Rising health care costs call for the development and evaluation of new modes of rehabilitation, including physical activity in settings outside the health care system. METHODS: This cohort study targets 450 patients with RA that do not currently meet HEPA recommendations, recruited from six hospitals reporting to the Swedish Rheumatology Quality Registers (SRQ). We have developed a two-year real-life intervention program including a minimum of twice-weekly circuit training, moderately intense physical activity the remaining days of the week and group meetings to support behavior change every other week. Our hypothesis is that increased physical activity and exercise will improve perceived health, reduce pain and fatigue, increase muscle function and aerobic capacity, impact psychosocial factors and prevent future cardiovascular events. Research questions regard outcomes, retention rates, dose-response matters and the exploration of responder characteristics. This protocol outlines recruitment procedure, design, assessment methods and the intervention program of the study. DISCUSSION: The PARA 2010 project is designed to expand the knowledge on HEPA in RA by a progressive approach regarding population, setting, intervention, time frames and outcome measures. To our knowledge this is the first long-term HEPA program based on Social Cognitive Theory, and performed in a real life environment to demonstrate if this new setting can promote increased and maintained physical activity in people with RA. Trial registration number ISRCTN25539102. Development and delivery of an exercise intervention for rheumatoid arthritis: strengthening and stretching for rheumatoid arthritis of the hand (SARAH) trial. Heine PJ et al. Physiotherapy. 2012 Jun;98(2):121-30. This paper describes the development and implementation of a hand exercise intervention for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as part of a large multi-centred randomised controlled trial in a U.K. National Health Service (NHS) setting. Participants are eligible if diagnosed with RA according to American College of Rheumatology criteria, have a history of disease activity, functional deficit or impairment in the hand and/or wrist, and have been on a stable medication regime for at least 3 months. The intervention development was informed by the current evidence base, published guidelines, clinician and expert opinion, and a pilot study. The exercise programme targets known, potentially modifiable physical impairments of the hand with 5 exercise sessions and a home exercise component over a 12 week period. The intervention will be provided to 240 participants along with usual care. A further 240 will receive usual care only as part of the control arm. Specific details of the treatments delivered are described. Splinting and hand exercise for three common hand deformities in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical perspective. Porter BJ, Brittain A. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012 Mar;24(2):215-21. PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Hand deformities (ulnar drift, swan neck and boutonniere) are prevalent in rheumatoid arthritis and develop early in the disease process. These deformities cause significant functional impairment and impact quality of life. This review will provide a clinical perspective using the most recent evidence regarding the role of splinting and hand exercise in their management. The pathomechanics and functional consequences of these deformities are also described. RECENT FINDINGS: Patients tend to under-report their hand problems and are often reluctant to seek treatment for their deformities. There is limited evidence to support or refute the role of splinting and hand exercises in their management. Clinical experience suggests splinting and hand exercise are most beneficial when prescribed for early, flexible deformities. SUMMARY: More research is required to guide clinicians on the most effective approach to the management of these three hand deformities. It is imperative that clinicians assess for and recognize these deformities in order to ensure timely and appropriate treatment. Until more evidence becomes available, an evidenced-informed approach is recommended. Efficacy of resistance exercises in rheumatoid arthritis: metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials Baillet A, Vaillant M, Guinot M, Juvin R, Gaudin P. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 Mar;51(3):519-27. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the efficacy of resistance exercises in RA patients. CONCLUSION: Resistance exercise in RA is safe, and the improvement in most outcomes was statistically significant and possibly clinically relevant for RA disability. Rapporti fra Reumatologi e Fisiatri • Come dovrebbe essere il rapporto fra Reumatologi e Fisiatri ??? • Confidenziale ? • Conflittuale ? • Cordiale ? Rapporti fra Reumatologi e Fisiatri • Come dovrebbe essere il rapporto fra Reumatologi e Fisiatri ??? • Collaborazione ? • Interazione ? • Integrazione ? • Sinergico Competenze e Profili • Definizione del concetto di Disabilità in ambito reumatologico • Definizione della specifica attività professionale • Individuazione degli ambiti di competenza • Condivisione dei percorsi assistenziali interazione ed integrazione gestionale Condivisione dei Percorsi Assistenziali • Definizione degli obiettivi gestionali comuni • Condivisione delle problematiche relative alla scelte terapeutiche • Condivisione degli strumenti di valutazione e monitoraggio degli “outcome” terapeutici Utilizzo scale di valutazione della Disabilità e Qualità della vita STRUMENTI DI VALUTAZIONE DELLA DISABILITA’ E QUALITA’ DELLA VITA SPECIFICI GENERICI PROFILI SANITARI GENERICI SCALE DI VALUTAZIONE DELL’UTILITA’ AIMS AIMS2 MACTAR/PET FSI HAQ MOS-SF36 SIP NHP MHIQ EUROQoL Rating scale SG TTO QWB Measures of work disability and productivity in Rheumatoid Arthritis • Rheumatoid Arthritis Specific Work Productivity Survey (WPS-RA), • Workplace Activity Limitations Scale (WALS), • Work Instability Scale for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA-WIS), • Work Limitations Questionnaire (WLQ), • Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire (WPAI). Tang K, Beaton DE, Boonen A, Gignac MA, Bombardier C. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Nov;63 Suppl 11:S337-49. Measurement properties of physical function scales validated for use in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of the literature. Oude Voshaar MA, ten Klooster PM, Taal E, van de Laar MA. Health Qual Life Outcomes.2011 Nov 7;9:99. Based on this literature review, the disease-specificHAQ and the generic SF-36 can currently be most confidently recommended to measure PF in RA for most research purposes. The HAQ, however, was frequently associated with considerable ceiling effects, while the SF-36 has limited content coverage. Alternative scales that might be better suited for specific research purposes are identified along with future directions for research. LA DISABILITA' NELLE MALATTIE REUMATICHE DISABILITA’: DEFINIZIONE PERDITA DI UNA FUNZIONE RIDUZIONE DELL’ABILITÀ NELL’EFFETTUARE LE NORMALI ATTIVITÀ DELLA VITA QUOTIDIANA (ADL) DISABILITA’ NELLE MALATTIE REUMATICHE (MR) La disabilità nelle MR condiziona la comparsa di un’invalidità che si manifesta nel: • 37,2% dei casi di Artrite Reumatoide • 40% dei casi di Spondilite Anchilosante 50% dei casi di Connettivite AR: EVOLUZIONE E DISABILITA’ Kirwan JR. Conceptual issues in scoring radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Mar;26(3):720-5. DISABILITY EVOLUTION DISEASE ACTIVITY Short Term Time DISABILITY JOINT DAMAGE Long Term Smolen J. 2006 The relationship between joint damage and functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Bombardier C, Barbieri M, Parthan A, Zack DJ, Walker V, Macarios D, Smolen JS. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Jun;71(6):836-44. Epub 2011 Nov 29. While many of the studies did not include multivariate analysis with confounder adjustment, the published evidence indicates a link between joint damage and functional disability and that an increase in joint damage is associated with an increase in disability over time. Treatments to limit progressive joint damage may lead to better joint function and improved patient outcome with less disability. Disabilità in ambito reumatologico • Non è solo un problema del reumatologo o del fisiatra, ma dovrebbero essere coinvolti anche altri specialisti e operatori: Ortopedico,Dermatologo, Oculista, Fisioterapista, Terapista occupazionale, Infermiere Professionale, Psicologo ed altri operatori che, per competenza ed ambito professionale, dovrebbero intervenire durante le varie fasi del processo assistenziale DISABILITA’ NELLE MR: NON SOLO UN PROBLEMA MEDICO DEVONO ESSERE CONSIDERATE 1. Le istanze delle Persone con “disabilità”, delle loro Famiglie e delle Associazioni 2. L’evoluzione del bisogno di salute in rapporto alla “disabilità” (dati demografici ed epidemiologici) 3. L’evoluzione del concetto di “disabilità” (orientamenti culturali e di politica sanitaria) 4. Le istanze politico-economiche e gestionali nei confronti della sfida “disabilità” Tutto questo ci conferma che le MR NON sono solo un problema medico… DISABILITA’ E ARTRITE REUMATOIDE (AR) • L'ARTRITE REUMATOIDE, rappresenta, tra i REUMATISMI CRONICI INFIAMMATORI, una delle patologie più gravi ed invalidanti 37,2% dei casi, entro la prima decade di malattia INDAGINE CENSIS - ANMAR-SIR 2008 Un’indagine CENSIS - ANMAR-SIR 2008 sull’attività lavorativa dei pazienti con AR ha permesso di rilevare che: • più di un malato di AR su 5, riferiva modificazioni del suo profilo lavorativo • venivano segnalate ripetute assenze dal lavoro per malattia, dal 35,0% dei soggetti under 44 anni e dal 43,6% dei soggetti tra i 44-65 anni (periodo riferito all’ultimo mese precedente la rilevazione) DISABILITA’ NELLE MR/AR FATTORI FISICI direttamente correlati ai danni della patologia di base FATTORI INDIPENDENTI DALLA MALATTIA (speranze, aspirazioni, conoscenze ed esperienze precedenti) DISABILITA’ NELLE MR/AR Alterazione delle strutture articolari determinata dal PROCESSO INFIAMMATORIO Dolore Danno Anatomico Articolare DISABILITA’ NELLE FASI EVOLUTE DI UNA MR (AR) DANNO ANATOMICO INVETERATO Perdita della funzione articolare Ipotrofia muscolare ASSENZA DI MOVIMENTO DANNO SECONDARIO MUSCOLOSCHELETRICO Ipotrofia ed ipostenia muscolare (sarcopenia) Demineralizzazione ossea (osteoporosi) Instabilità articolare ASSENZA DI MOVIMENTO DANNO SECONDARIO NEUROFISIOLOGICO Alterazione degli schemi motori (prensione, cammino…) DISABILITA’ NELLE FASI EVOLUTE DI UNA MR (AR) Perdita progressiva delle funzioni necessarie all’espletamento delle attività della vita quotidiana (ADL), del ruolo sociale e riduzione della qualità della vita (health-related QoL) Rupp I. et al Scand J Rheumatology 2006 QUALE DISABILITA’ NELLA EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (ERA) ? DISABILITA’ NELLA ERA • The impact of RA can be devastating • Up to 50% of patients with ERA will be unable to do their job after 3 years of disease Bykerk VP. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2011 Mar;23(2):17984. Bykerk VP, Hazes JM: Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69:473– 475. Felts W & Yelin E J Rheumatol 1989 DISABILITA’ NELLE FASI DI ESORDIO DI UNA MR (ERA) La disabilità non è la conseguenza dei danni e delle deformità articolari, ma viene condizionata dall’inibizione del movimento determinata dal Dolore Reumatologo Altri Operatori Fisiatra PROGRAMMA TERAPEUTICO • PROGRAMMA RIABILITATIVO – FKT • Mobilizzazione • Esercizi aerobici – TERAPIA FISICA • EDUCAZIONE DEL PAZIENTE – Presa di coscienza della malattia – Economia articolare – Home training/educazione gestuale • ADDESTRAMENTO ALL’USO DI AUSILI ED ORTESI Diagramma di flusso gestionale Gestione del Paziente Reumatico Fase della valutazione clinica e diagnostica (Reumatologo) Fase della definizione del programma terapeutico-riab. (Reumat. e Fisiatra) Fase della gestione terap. cronica e riabilitativa (Reumat. e Fisiatra) Conclusioni • La gestione di una malattia reumatica richiede una stretta e costante collaborazione sinergica tra Reumatologo e Fisiatra • Dovrebbero essere definiti ruoli e le specifiche competenze di entrambe le figure • Dovrebbero essere condivisi gli obiettivi terapeutici e soprattutto, dovrebbero essere utilizzati gli stessi strumenti per valutare Disabilità e Qualità della vita • Infine, dovrebbero essere definiti “insieme” tutti i possibili programmi terapeutici individuali VI Congresso Internazionale Multidisciplinare Approccio Clinico e Riabilitativo in Reumatologia Percorsi Diagnostici e Terapeutici: le Nuove Frontiere Mantova 6-8 Giugno 2013 GRAZIE E vissero insieme felici…!!!
Scaricare