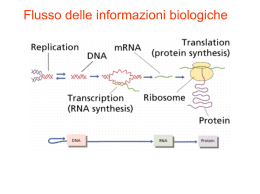
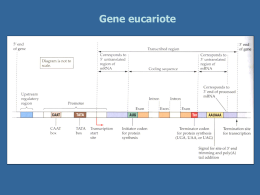
Meccanismi di Regolazione dell’espressione genica Fase Nucleare •Scelta del gene che deve essere espresso •Maturazione dell’RNA •Trasferimento Nucleo Citoplasma Fase Citoplasmatica •Sintesi delle catene polipeptidiche •Modificazioni post-traduzionali •Trasferimento delle proteine nelle sedi di competenza Unione di ribonucleotidi monofosfato per formare una catena polinucleotidica I precursori della sintesi sono i nucleotidi trifosfato. L’energia che occorre per la formazione del legame fosfodiesterico è data dall’eliminazione del pirofosfato per idrolisi del legame. ATP ATP = Adenosin Trifosfato ADP = Adenosin Difosfato ADP Classes of prokaryotic RNA • ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 16S (small ribosomal subunit) 23S (large ribosomal subunit) 5S (large ribosomal subunit) • transfer RNA (tRNA) • messenger RNA (mRNA) Structure of prokaryotic messenger RNA 5’ Shine-Dalgarno sequence PuPuPuPuPuPuPuPu initiation AUG translated region 3’ AAU termination The Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence base-pairs with a pyrimidine-rich sequence in 16S rRNA to facilitate the initiation of protein synthesis Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs • ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) • transfer RNA (tRNA) • messenger RNA (mRNA) • heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) (precursors of mRNA) • small nuclear RNA (snRNA) U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, U8, U9, U10... • small cytoplasmic RNA (scRNA) 7SL RNA What are the enzymes responsible for the synthesis of these RNAs? The human RNA polymerases Polymerase Location Product RNA polymerase I nucleolus 18S, 28S, 5.8S rRNA RNA polymerase II nucleoplasm hnRNA/mRNA, U1, U2, U4, U5 snRNA RNA polymerase III nucleoplasm tRNA, 5S RNA, U6 snRNA, 7SL RNA mitochondrial RNA polymerase mitochondrion all mitochondrial R _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Sensitivity of the nuclear RNA polymerases to a-amanitin1 RNA pol I RNA pol II RNA pol III 1 cyclic resistant high sensitivity (binds with K = 10-8 M) low sensitivity (binds with K = 10-6 M) octapeptide from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides Structure of eukaryotic mRNA Cap 5’ 7mGppp initiation 5’ untranslated region AUG translated region UGA termination 3’ untranslated region polyadenylation signal AAUAAA (A)~200 3’ poly(A) tail • all mRNAs have a 5’ cap and all mRNAs (with the exception of the histone mRNAs) contain a poly(A) tail • the 5’ cap and 3’ poly(A) tail prevent mRNA degradation • loss of the cap and poly(A) tail results in mRNA degradation b). Gene structure promoter region exons (filled and unfilled boxed regions) +1 introns (between exons) transcribed region mRNA structure 5’ 3’ translated region Legame al promotore della RNA polimerasi Apertura della doppia elica Inizio della sintesi Allungamento Terminazione closed promoter complex RNA polymerase open promoter complex initiation elongation termination RNA product Transcription Direzione della sintesi Filamento senso Filamento antisenso Sequence elements within a typical eukaryotic gene1 1 based on the thymidine kinase gene octamer transcription element +1 promoter ATTTGCAT GC CAAT GC TATA -130 -95 -80 -50 -25 TATA box (TATAAAA) • located approximately 25-30 bp upstream of the +1 start site • determines the exact start site (not in all promoters) • binds the TATA binding protein (TBP) which is a subunit of TFIID GC box (CCGCCC) • binds Sp1 (Specificity factor 1) CAAT box (GGCCAATCT) • binds CTF (CAAT box transcription factor) Octamer (ATTTGCAT) • binds OTF (Octamer transcription factor) Proteins regulating eukaryotic mRNA synthesis General transcription factors • TFIID (a multisubunit protein) binds to the TATA box to begin the assembly of the transcription apparatus • the TATA binding protein (TBP) directly binds the TATA box • TBP associated factors (TAFs) bind to TBP • TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH1, TFIIJ assemble with TFIID RNA polymerase II binds the promoter region via the TFII’s Transcription factors binding to other promoter elements and transcription elements interact with proteins at the promoter and further stabilize (or inhibit) formation of a functional preinitiation complex 1TFIIH is also involved in phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II, DNA repair (Cockayne syndrome mutations), and cell cycle regulation Nome TF2D TBP + TAF Alias Chromosoma TAF1 250 Xq13.1 TAF1L 250like 9p21.1 TAF2 150 8q24.12 TAF3 140 10p15.1 TAF4 135 20q13.33 TAF4B 105 18q11.2 TAF5 100 10q24-10q25.2 TAF6 80 7q22.1 TAF6L 11q12.3 TAF7 55 5q31 TAF7L 50 Xq22.1 TAF8 43 6p21.1 TAF9 32 5q11.2-5q13.1 TAF10 30 11p15.3 TAF11 28 6p21.31 TAF12 20-15 1p35.3 TAF13 18 1p13.3 TAF15 68 17q11.1-q11.2 GTF 2 Binding of the general transcription factors E F TAFs TFIID B H TBP A J -25 +1 • TFIID (a multisubunit protein) binds to the TATA box to begin the assembly of the transcription apparatus • the TATA binding protein (TBP) directly binds the TATA box • TBP associated factors (TAFs) bind to TBP • TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH, TFIIJ assemble with TFIID Binding of RNA polymerase II E F TFIID B H TBP A J RNA pol II • RNA polymerase II (a multisubunit protein) binds to the promoter region by interacting with the TFII’s • TFs recruit histone acetylase to the promoter Steps in mRNA processing (hnRNA is the precursor of mRNA) • capping (occurs co-transcriptionally) • cleavage and polyadenylation (forms the 3’ end) • splicing (occurs in the nucleus prior to transport) exon 1 intron 1 exon 2 Transcription of pre-mRNA and capping at the 5’ end cap Cleavage of the 3’ end and polyadenylation cap cap poly(A) Splicing to remove intron sequences cap poly(A) Transport of mature mRNA to the cytoplasm Polyadenylation • cleavage of the primary transcript occurs approximately 10-30 nucleotides 3’-ward of the AAUAAA consensus site • polyadenylation catalyzed by poly(A) polymerase • approximately 200 adenylate residues are added cleavage AAUAAA mGpppNmpNm AAUAAA mGpppNmpNm A A A polyadenylation A A A 3’ • poly(A) is associated with poly(A) binding protein (PBP) • function of poly(A) tail is to stabilize mRNA Splicing Rimozione di un introne attraverso due reazioni sequenziali di trasferimento di fosfato, note come transesterificazioni. Queste uniscono due esoni rimuovendo l’introne come un “cappio” GENE PREDICTION GeneScan GrailEXP Promoter 2.0 Omiga 2.0 GeneMark F GENE SH Recognition of splice sites • invariant GU and AG dinucleotides at intron ends • donor (upstream) and acceptor (downstream) splice sites are within conserved consensus sequences donor (5’) splice site branch site acceptor (3’) splice site G/GUAAGU..................…A.......…YYYYYNYAG/G U1 U2 •small nuclear RNA (snRNA) U1 recognizes the donor splice site sequence (base-pairing interaction) • U2 snRNA binds to the branch site (base-pairing interaction) Y= U or C for pyrimidine; N= any nucleotide Chemistry of mRNA splicing • two cleavage-ligation reactions • transesterification reactions - exchange of one phosphodiester bond for another - not catalyzed by traditional enzymes • branch site adenosine forms 2’, 5’ phosphodiester bond with guanosine at 5’ end of intron intron 1 Pre-mRNA 2’OH-A 5’ exon 1 G-p-G-U - A-G-p-G branch site adenosine exon 2 First clevage-ligation (transesterification) reaction 3’ intron 1 Step 2: binding of U4, U5, U6 U2 U4 U6 2’OH-A exon 1 5’ U5 G-p-G-U - exon 2 A-G-p-G 3’ U1 Step 3: U1 is released, then U4 is released intron 1 2’OH-A U6 exon 1 5’ G-p-G-U - U5 U2 exon 2 A-G-p-G 3’ Step 4: U6 binds the 5’ splice site and the two splicing reactions occur, catalyzed by U2 and U6 snRNPs intron 1 2’OH-A U2 U6 U-G-5’-p-2’-A A mRNA 5’ 3’ G-A G-p-G U5 3’ • ligation of exons releases lariat RNA (intron) intron 1 Splicing intermediate U-G-5’-p-2’-A A 5’ exon 1 exon 2 G-OH O 3’ A-G-p-G A - 3’ Second clevage-ligation reaction intron 1 Lariat U-G-5’-p-2’-A A Spliced mRNA exon 1 5’ 3’ G-A exon 2 G-p-G 3’ Trans-splicing Nei protozoi e in un nematode Differenti molecole di mRNA dallo stesso gene Splicing alternativo Uso di promotori alternativi Uso di segnali di poliadenilazione alternativi “Enhancers” Nei geni degli eucarioti gli enhancers possono distare dalla regione codificante anche più di 50 Kb.
Scaricare