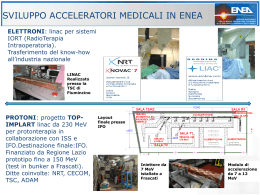
EURORIB'10 -Lamoura, Jura, France June 6th -11th 2010 First results of reactions induced by exotic beams in the region of 11Be with CHIMERA array L. Grassi – INFN, Sezione di Catania Università degli Studi di Catania OUTLINE Fragmentation beams at LNS Chimera characteristics and detection techniques Tagging system First experiments with 13C, 16O, 18O primary beams at 55 MeV/A Kinematical coincidence technique and its capabilities Preliminary and incoming results Fragmentation beams at INFN-LNS in Catania Production Target CHIMERA Detection Techniques 40Ar+Pety 20 MeV·A E (MeV) PSD Si Si CsI(Tl) PSD CsI Z=10 Z=6 Z=2 ΔE-E Rise Time (ns) TOF TOF-E 124Sn+64Ni DE (MeV) 35 MeV·A θ=10° TOF(channel) Z=10 Fragmentation Beams Tagging System Tagging System test with a-source At the entrance of the CHIMERA scattering chamber, we mounted a-source, MCP and DSSSS (16x16 strips, thickness 140 mm). The base of flight is 70 cm By using coincidences between MCP and one pixel in the silicon detector, we obtain a time resolution better than 500 psec Fragmentation beams on CHIMERA: - 12B setting primary beam 9Be target (1,5 mm thickness ) at 55 MeV/A 11Be 12B DE (MeV) DE (MeV) 13C 11Be 12Be 11B 10Be 10Be 9Be 9Li 7Li 8Li 6He 4He 10 kHz 8Li 7Li 4He TOF (ns) TOF (ns) 11Be 13B 12B 80 kHz Fragmentation beams on CHIMERA: 18O 18O primary beam magnet setting on 16C 11Be strip 140 mm thick 13B 11Be 3 kHz 10Be 7Li - 16O primary beams Fragmentation beams on CHIMERA: identification test DE(MeV) 11Be 10Be 8Li 6He DSSD MCP DE/TOF 1 charge 4 DE(ch) T (ns) 2 3 5 10 Si- CsI(Tl) DE-E Tel 66 4.1° Z=4 11 E (ch) 13C primary beam at 55 MeV/A mass kinematical coincidences technique DE (MeV) transfer reactions study induced on proton and deuteron targets Tagged beam Target p 11Be 12Be 10Be 11Be 7Li 4He 10Be p 8Li 6He d TOF (ns) CHIMERA 4p multidetector kinematical coincidence kinematical coincidence technique Method capability with the reaction 7Li+p at 52 MeV Df=180° p 7Li 7Li+p-->p' 140 120 Ep (MeV) 100 ds/dw (arb.un.) E7Li (MeV) Tel 117 (q=6.4°) Tel 117 (q=6.4°) Silicon energy silicon energy Tel 802 (q=58°) Silicon energy 80 0.47 MeV average 60 Tel 802 (q=58°) Silicon energy 40 20 0 116 118 120 122 124 q cm 126 128 130 kinematical coincidence technique It is very interesting to see the reaction p(7Li,7Be)n CHIMERA detects charge particles neutrons make some reactions inside CsI producing g, p, a Df=180° Tel 117 (q=6.4°) silicon energy Tel 624 (q=25.5°) CsI(Tl) energy DE(channel) Kinematical coincidences – preliminary results elastic 12B+d E(channel) Tel 38(3.1°) Target CD beam setting on 12B Coincidences between telescopes with Df=180° Tel 38(3.1°) - 870(66°) DE(channel) E(channel) E(channel) Tel 38(3.1°)-875(66°) Df=215° Kinematical coincidences – preliminary results 16C+d 16C+d Ring 2E(4.1°) coin with ring15 (74°) ring 14(66°) Ring 2I (3.1°) coin with ring 15(74°) ring 14 (66°) E(channel) 10Be+p Ring 2I (3.1°) coin with ring 15(74°) ring 14 (66°) E(channel) 16C excite state 1.7 MeV E(channel) Transfer reactions B. B. Back et al., PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS 104, 132501 (2010) 7,4 MeV/A 6,2 MeV/A Transfer reactions p(11Be, 10Be)d at 48 MeV/A d(10Be, 11Be)p at 58 MeV/A d(12B, 11Be) 3He at 47 MeV/A p(13B, 11Be) 4He at 52.4 MeV/A 35.3 MeV/A V. Lapoux et al, PHYSIC LETTERS B 658 (2008) 198-202 J.S. Winfield et al. Nuclear Physics A 683 (2001) 48–78 Angular distribution Elastic scattering (~ 50 MeV/A) CONCLUSION • Trough kinematical coincidence we’re going to study transfer reactions with light exotic beams • On June 2010 we’ll have also beam 9Li on 5.5 MeV/A by LNS-EXCYT facilities • Next improvement to detect particles at 0° • New experiments by using fragmentation beams at LNS (primary beam 36Ar to produce 32,33Ar neutron poor beams) • Exotic beams delivered by SPES at LNL. EXOCHIM collaboration F.AMORINIa, A.ANZALONEa, L.AUDITOREb, G.CARDELLAc, S.CAVALLAROa,d, M.B.CHATTERJEEe, E.DE FILIPPOc, E.GERACIc,d, L.GRASSIc,d, A.GRZESZCZUKi, P.GUAZZONIl, J.HANa, E.LA GUIDARAc,f, G.LANZALONEa,f, I.LOMBARDOa,d, S.LO NIGROc,d, D.LORIAb, C.MAIOLINOa, M. PAPAc ,A.PAGANOb, S.PIRRONEc, G.POLITIc,d, F.PORTOa,d, F.RIZZOa,d, E.ROSATOm, P.RUSSOTTOa,d, A.TRIFIRÒb, M.TRIMARCHIb, G.VERDEc, M.VIGILANTEm, L.ZETTAl (a) INFN - Lab. Nazionali del Sud, Catania, Italy; (b) INFN - Gruppo collegato di Messina and Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Messina, Italiy; (c) INFN - Sezione di Catania, Italy; (d) Dip. di Fisica e Astronomia, Università di Catania, Italy; (e) Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Kolkata, India; (f) CSFNSM, Catania, Italy;(g) Università Kore di Enna, Enna, Italy; (h) Institute de Physique Nucleaire d'Orsay, CNRS-IN2P3, Orsay Cedex, France; (i) Institute of Physics, University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland; (l) INFN - Sezione di Milano and Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Milano, Itally; (m) INFN - Sezione di Napoli and Dipartimento di Fisica Università Federico II, Napoli, Italy
Scaricare