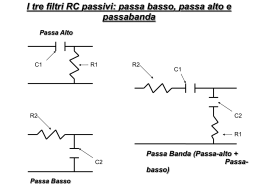
RIEPILOGO Filtri del secondo ordine e diagrammi di Bode SUMMARY Second order filters and Bode plots Filtri del secondo ordine » I filtri L-C e C-L sono filtri del secondo ordine. » L-C and C-L filters are the second-order filters. Caduta di tensione » I filtri L-C passa-basso sono impiegati soprattutto quando desideriamo limitare la caduta di tensione dovuta alla corrente continua che avverrebbe sulla resistenza in serie di un filtro R-C. » The L-C low-pass filters are used especially when we want to limit the voltage drop due to the current that would take place on series resistance of an R-C filter. Circuito risonante serie » Il filtro L-C passa-basso è un circuito risonante serie. Le espressioni del guadagno e della frequenza di risonanza sono: G ( j ) 20 j R L 2 0 2 0 1 LC » The L-C low-pass filter is a series resonant circuit. The expressions of the gain and resonance frequency are: G ( j ) 20 20 2 j R L 0 1 LC Coefficiente di risonanza » L’altezza e la forma del picco di risonanza sono determinati dal valore del coefficiente di risonanza Q. Per i nostri scopi l’usuale definizione di Q è il rapporto tra la frequenza di risonanza e l’ampiezza di banda presa quando la potenza si dimezza: f f Q 0 0 0 2 2 f B dove f0 è la frequenza di picco. » The height and shape of the resonance peak are determined by the value of the coefficient of resonance Q. For our purposes the usual definition of Q is the ratio between the resonance frequency and the bandwidth taken when the power is halved: f f Q 0 0 0 2 2 f B where f0 is the peak frequency. Connessione in cascata » I filtri del secondo ordine possono essere anche ottenuti connettendo in cascata due filtri del primo ordine. » The filters of the second order can be also obtained by connecting in cascade two filters of the first order. Pendenza della curva » Connettendo in cascata un numero n di filtri del primo ordine otteniamo un filtro di ordine n con una pendenza della curva di risposta pari a n ∙ 20 dB/decade. » Connecting in cascade a number n of filters of the first order we obtain a filter of order n with a slope of the response curve equal to n ∙ 20 dB/decade. Curva di risposta » La curva di risposta di un filtro passa-banda può essere immaginata come una curva derivante dal risultato della messa in cascata (il prodotto) di un passa-alto e di un passa-basso. » The response curve of a band-pass filter can be imagined as a curve derived from the result of the putting in cascade (the product) of a high-pass and a low-pass. Filtro passa-banda » Un circuito risonante R-L-C serie o parallelo può costituire un filtro passa-banda. In quelli serie otteniamo un passa banda quando l’uscita è presa ai capi del resistore, oppure un filtro respingi-banda quando l’uscita è presa ai capi delle serie L-C. » A series or parallel R-L-C resonant circuit can constitute a band-pass filter. In those series we get a band-pass when the output is taken across the resistor, or a bandreject filter when the output is taken across the L-C. Banda passante » Per la banda passante di un circuito risonante R-L-C, vale la relazione: f0 R B f2 f1 2L Q » For the bandwidth of a resonant circuit R-L-C, the following relation holds: f0 R B f2 f1 2L Q Teorema della risposta in frequenza » Il teorema della risposta in frequenza stabilisce che, per un sistema lineare avente funzione di trasferimento G(jω), se applichiamo al suo ingresso un segnale sinusoidale di pulsazione ω0, alla sua uscita a regime è presente un segnale sinusoidale avente: - stessa pulsazione; - ampiezza pari al prodotto del modulo del segnale per il modulo di G(jω) calcolata alla pulsazione ω0; - fase pari alla somma di quella del segnale d’ingresso con quella di G(jω) calcolata alla pulsazione ω0. » The frequency response theorem states that, for a linear system, whose transfer function is G(jω), if we apply a sinusoidal signal with pulse ω0 at its input, to its output in steady-state there is a sinusoidal signal having : - same pulsation; - amplitude equal to the product of the signal for the module of G(jω) calculated to the pulsation ω0; - phase equal to the sum of that of the input signal with that of G(jω) calculated to the pulsation ω0.
Scaricare