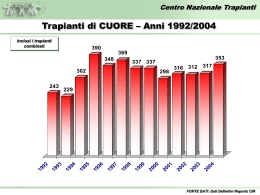
Santi Cosmo e Damiano Erano entrambi medici, nati in Arabia nel III secolo d.c. L’iconografia eccelsiastica li rende protagonisti del tentativo di trapiantare la gamba di un moro a un cristiano 1831 Mary Shelley Publishes Frankenstein …describes a morally and physically superior creature constructed with parts from graveyards; this creature turns to violence only when his fictional creator rejects him. This is the first positive and negative depiction in literature of the use of organs and parts from dead people. 1902, the French surgeon Alexis Carrel, Nobel Prize for medicine in 1912, develops the technique of vascular anastomosis for the suture of blood vessels. Joseph Murray and the medical team at Boston's Peter Bent Brigham Hospital perform the first long-term successful organ (kidney) transplant, Dec 23 1954. Richard Herrick received a kidney from his identical twin. T.E. Starzl performed in Denver, Co, USA the first successful liver transplant procedure 1963 Christiaan Barnard performed the first human heart transplant, in Cape TownSouth Africa Dec. 3, 1967 TRASPLANTS IN THE WORD KIDNEY PANCREAS KIDNEY-PANCREAS LIVER LRLT HEART CUORE-LUNG LUNG BONE MARROW 447.182 19.695 8.823 112.299 3.291 49.829 2.266 8.842 82.780 UNOS 2004 LONGEST SURVIVAL WITH WORKING TRANSPLANT KIDNEY LIVER BONE MARROW HEART PANCREAS KIDNEY-PANCREAS HEART-LUNG LUNG 35 anni 28 anni 29 anni 23 anni 15 anni 16 anni 13 anni 13 anni UNOS 2004 DEFINITION OF DEATH THE DEATH OF AN INDIVIDUAL IS IDENTIFIED BY THE IRREVERSIBLE CESSATION OF ALL THE ENCEPHALIC FUNCTIONS (CORTEX AND TRUNK) (art. 1 Legge 23/12/93 n. 578) POTENTIAL DONOR PRIMARY BRAIN PATHOLOGIES WITH POSSIBLE FATAL OUTCOME • Cerebro-vascular accidents • Cranioencephalic traumas • Post-anoxia cerebral damages Intensive Care DEATH DIAGNOSIS CONVOCATION OF THE MEDICAL COLLEGE (Art. 5 D.M. 409/1977) • Forensic expert/ pathologist or a doctor commisioned by Direzione Sanitaria • Anesthesist / Intensive Care expert • EEG expert neurologist/ neurosurgeon DEATH DIAGNOSIS INSTRUMENT CHECKS (D.M. 22/8/94 n. 582) • 30’ EEG is required every 2 h for 3 times ( absence of electric activity, spontaneous or induced) • X-ray brain angiography ( abcence of flux) DEATH DIAGNOSIS OBSERVATION TIME (D.M. 22/8/94 n. 582) • Adults and children > 5 anni 6 hours • Chidren 1 - 5 years 12 hours • Children < 1 year 24 hours ACTUAL DONOR TWO PREREQUISITE CONDITIONS • Not opposition/ consent of the family • Overall and specific organ suitability REALTIONSHIP WITH THE FAMILY THE PROPOSAL FOR DONATION IS MADE AFTER THE COMMUNICATION OF DEATH • The family cannot interfere in the course of death verification • The will of the deceased and the will of the family must be made clear • The talk must explain clearly the timing and procedure of consent or opposition RELATIONSHIP WITH THE FAMILY The Intensive Care expert must safeguard the relationship with the family as much as possible, supply all the information as clearly as possible and explain the possibility of donation without influencing the family discretionary power. THE NEW TRANSPLANT LAW (Legge n.91, 1-3-99) ANONIMITY • The donor’s and the recipient’s personal data must remain anonymous • The harvest must be performed with the due respect for the deceased THE NEW TRANSPLANT LAW (Legge n.91, 1-3-99) PENALTIEA FOR TRAFFICKERS • Arrest and heavy fines for organ traffickers. Disqualification from the medical profession for the doctors ORGANIZATIONAL ASPECTS (donor-recipient) – – – – – Suitability of the donor: Tests for the evaluation of organ functionality Serology ( transmissible diseases) Instrument exams (exclusion of tumors in the donor) Specialistic counselling Possible biopsies for the organ evaluation (liver, marginal kidneys) Managment of the recipient ( call, transport) Transplants in Italy CNT (Roma) NITp AIRT OCST SICILIA TRANSPLANT OPERATIVE SCHEDULE Repert about donor from I.C. to NITp Alert of transplant center Selection and call of the recipient Transport activation: harvest team and recipient Harvest and conservation of the organs Transplant (within ~ 10 hours from report) Heart 6h LIver 12 h Pancreas 20 h Kidney 36 h Donation & Transplantation Process Society Potential Donor Detection Brain Death Confirmation Org. Proc. Experts Transplant Family Consent Organ Storage Organ Removal Legal Confirmation Brain Death Transplant Teams Organizational Aspects Donor Management Legal Consent Donor Evaluation Safety-Quality Network T.I. Interregional Reference Centers Regional Reference Centers Componenti CNT Database Experts ( couselling during harvesting procedure) Video Conferenza National Transplant Center Istituto Superiore di Sanità *Dati preliminari al 31 luglio 2009 Confronto Donatori Utilizzati PMP 2008 vs 2009* Anno 2008 19,2 + 6,77% Anno 2009* 20,5 FONTE DATI: Dati Reports CIR *Dati preliminari al 31 luglio 2009 Confronto Numero Donatori Utilizzati 2008 vs 2009* Anno 2008 1094 +11,7%** **Il maggiore aumento % riscontrato sul numero assoluto delle donazioni rispetto all’incremento % del PMP è dovuto all’adozione della nuova popolazione Anno 2009* 1222 *Dati preliminari al 31 luglio 2009 Attività donazione per regione – Anno 2009* % Opposizioni alla donazione REGIONE 2009* 2008* diff Prov. Auton. Bolzano 0,0% 0,0% 0,0% Prov. Auton. Trento 0,0% 0,0% 0,0% Friuli Venezia Giulia 12,5% 25,0% -12,5% Umbria 20,0% 22,2% -2,2% Lombardia 21,2% 25,5% -4,2% Sardegna 23,1% 34,7% -11,6% Basilicata 25,0% 47,6% -22,6% Emilia Romagna 25,9% 33,3% -7,4% Toscana 27,3% 31,9% -4,6% Marche 28,6% 36,2% -7,6% ITALIA 29,2% 32,6% -3,4% Veneto 30,1% 21,6% 8,5% Puglia 30,3% 35,0% -4,7% Lazio 30,3% 27,8% 2,5% Liguria 31,0% 28,0% 3,0% Campania 33,6% 46,8% -13,1% Piemonte - Valle d'Aosta 35,9% 28,6% 7,3% Sicilia 46,3% 51,8% -5,5% Calabria 47,1% 38,3% 8,7% Abruzzo - Molise 56,0% 44,6% 11,4% FONTE DATI: Dati Reports CIR Donatori % opposizione – Anni 2002/2008 29,9 27,7 29,4 29,4 31,0 32,7 27,5 473 558 601 575 574 683 749 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 FONTE DATI: Dati Reports CIR Incremento percentuale delle opposizioni ultimo triennio 32,7 + 11,2 % 29,4 2005 2008 Incremento percentuale trapianti eseguiti ultimo triennio 3177 - 8,2 % 2005 2916 2008 Incremento percentuale pazienti iscritti in lista ultimo triennio 9790 8988 2005 + 8,9 % 2008 *Dati SIT 17 Febbraio 2009 Liste di Attesa al 31 Dicembre 2008* Incluse tutte le combinazioni Rene Fegato Cuore 9.175 7.069 Pazienti Tempo medio di attesa dei pazienti in lista % mortalità in lista Iscrizioni 1.544 1.535 Pazienti Iscrizioni 731 738 Pazienti Iscrizioni 3,11 anni 2,04 anni 2,19 anni 1,53 % 6,18 % 9,72% FONTE DATI: Dati Sistema Informativo Trapianti *Dati definitivi al 31 Dicembre 2008 Trapianto di FEGATO – Attività per centro trapianti Incluse tutte le combinazioni 2008* 100 75 50 25 Torino Pisa Bologna Pa ISMETT Padova Bergamo Modena Milano-Ni Na Cardarelli Milano-Pol Genova S. Mart. Ancona Udine Milano Tumori Rm S. Camillo Rm Cattolica Cagliari Rm Sapienza Rm S.Eugenio Bari Verona Rm B. Gesù 136 105 82 73 70 60 59 50 44 37 34 30 30 27 27 25 25 24 23 19 13 3 FONTE DATI: Dati Reports CIR OLTx Università degli Studi di Udine Clinica chirurgica Centro Nazionale Trapianti Sopravvivenza dei pazienti trapiantati 100 Sopravvivenza % p = 0,0001 80 74 % 60 40 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 Anni 5 Centro Nazionale Trapianti Sopravvivenza dei pazienti entrati in lista d’attesa e non trapiantati 100 Sopravvivenza % 80 60 p = 0,0001 31,2 % 40 20 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 Mesi 36 SOPRAVVIVENZA TRAPIANTI DI FEGATO Udine vs registro Europeo Udine ELTR 1 anno 80% 79% 5 anni 70% 69% 18 Ottobre 2003 TRAPIANTI:A GENOVA IMPIANTATO FEGATO DA DONATRICE DI 97 ANNI (ANSA) - GENOVA, 18 OTT - Il fegato di una paziente di 97, morta giovedi scorso in seguito ad un incidente stradale a Savona, e' stato impiantato in una donna di 64 anni. L' intervento, della durata di 8 ore, e' stato eseguito a Genova presso il Centro Trapianti d' Organo dell' Ospedale San Martino nella notte tra il 16 e il 17 ottobre. La donatrice, una genovese di 97 anni, risulta essere il donatore piu' anziano segnalato dalla letteratura internazionale. CONDIZIONI DEL PAZIENTE TRAPIANTATO DI FEGATO A 5 ANNI Scadente 9,2 % Eccellente 90,8 % Organ procurement Organ procurement Organ procurement Liver Transplantation in Europe Indications in 33845 Cirrhosis 01/1988 - 12/2005 Primary Biliary : 3761 11% Unknown causes : 2689 8% Others : 439 1% Virus related : 13973 41% Secondary Biliary : 378 1% > 60% HCV Autoimmune : 1462 4% Alcoholic : 11143 33% ELTR 12/2005 Primary Indications of Liver Transplantation in 14359 Virus related Cirrhosis in Europe 01/1988 - 06/2006 Virus BCD : 117 Other virus : 102 1% Virus BC : 590 1% 4% Virus B : 3469 Virus BD : 974 24% 7% Virus C : 9107 63% ELTR 12/2005 Liver Transplantation in Europe Indications in 7318 Hepato-Biliary Cancers 01/1988 - 12/2005 Cholangiocellular carcinoma : 227 3% Metastases : 403 6% Carcinoma biliary tract : 209 3% Others : 508 7% Hepatocellular carcinoma : 5971 82% ELTR Indications of Liver Transplantation in 177912/2005 Other liver diseases in Europe 01/1988 - 12/2005 Polycystic diseases : 424 24% Other liver diseases (unspecified): 523 29% Budd Chiari : 567 32% Parasitic diseases : 54 3% Benign liver tumors : 211 12% Emergency • • • • • Fulminating Hepatitis PNF within 10 days since OLTx Hepatectomy for trauma with complete loss of function Acute deficiency in Wilson’s disease HAT within 15 days since OLTx UNOS Priority Criteria Accepted indications for liver trasplant Emergency Not emergency Hepatic trauma Advancfed liver chronic disease Fulminating hepatitis Hereditary mataboic liver disease Primary non function Primary liver tumors Fulminating Wilson Benign tumors or polycystic liver Keeffe EB. In: Transplantation of the liver. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Ed 2001, mod. Controindications for liver transplant Relative Absolute alcohol or drugs abuse Extraepatic tumors Portal thrombosis Out of control infections Previous biliary surgery Advanced cardiopulmonary diseases Old age ( > 65 aa) Major psychiatric diseases Keeffe EB. In: Transplantation of the liver. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Ed 2001, mod. MILAN CRITERIA Solitary lesion < 5 cm or < 3 lesions with diameter < 3 cm, no major vessel invasion and no extrahepatic involvement NEWS CRITERI MINIMI PER INDIRIZZARE IL PAZIENTE AL CENTRO TRAPIANTI 1. Sopravvivenza stimata senza trapianto ad 1 anno 90% 2. MELD score >15 3. Child-Pugh score 7 (Child-Pugh class B or C) 4. Sanguinamento da varici esofagee o singolo episodio di PBS indipendentemente dal punteggio di ChildPugh Lucey et al. Liver Transpl Surg, 1997 PUNTEGGIO DI CHILD-PUGH Punti: 1 2 3 Albumina, g/l >35 28-35 <28 Prolung. PT, sec <3’’ 4-6’’ >6’’ Bilirubina, mg/dl <2 2-3 >3 Encefalopatia PS assente I-II III-IV Ascite assente + ++ Il candidato ideale per OLT ha CP-score 8-10 Pugh et al. Br J Surg 1973 Il modello MELD c l i c c a s u l p u l s a n t e p e r c a l c o Il MELD (Mayo End stage Liver Disease) è un particolare sistema a punteggio che è stato proposto dalla Mayo Clinic (Rochester, Minnesota, USA) per valutare la sopravvivenza dei pazienti con la cirrosi ed un'insufficienza epatica terminale. Si basa sulla determinazione dei valori di bilirubina, di INR (indice della coagulazione del paziente) e di creatinina (indice della funzione dei reni). Tanto più alto è il punteggio ottenuto, tanto più gravi sono le condizioni cliniche del paziente. La formula per il calcolo è: 3.8*loge(bilirubina [mg/dL]) + 11.2*loge(INR) + 9.6*loge(creatinina [mg/dL]) Liver transplantation in HIV-infected recipients in HAART era in Italy: inclusion criteria “Eligible” subjects: – No history of AIDS defining illness in the previous two years – CD4 >200 or >100 if intolerant to ARVs – HIV RNA undetectable, or intolerant to ARVs but post-transplant HIV suppression is expected “Ineligible” subjects: – Did not meet 1 or more criteria above UDINE, (2004-2009) 26/418 OLT 17% of the overall activity of the center Traditional types of liver transplant in adults and children Cadarveric donor Whole liver Living donor Split liver Classic split Enlarged split Split liver OLTx Surgical Incision Traditional technique Piggy-Back technique Split sinistro pediatrico Split destro adulto Trapianto di fegato da donatore vivente LRLT Trapianto di fegato da donatore vivente INDICAZIONI ADULTO LRLT 4% 8% FHF P=0.05 58% 60% Cirrosi HCC ReOLT 22% 10% 0.8% P< 0.0001 LRLT P< 0.0001 10% Intero da cadavere 15% 13% Altre 0% 20% 40% 60% Patient Survival according to the Year of Liver Transplantation (%) 100 88 85 80 77 82 65 60 61 64 52 46 40 34 20 0 21 0 1 2 <85 : 513 95-99 : 18044 3 4 5 18 6 7 85-89 : 4117 2000-2004 : 22573 8 9 10 Yrs 90-94 : 11984 >2004 : 6157 ELTR Evolution of Recipient Age 12/2005 05/1968 - 12/2005 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 6880 82 84 86 0 to 2 : 2633 88 90 92 2 to 15 : 3598 45 to 60 : 27864 94 96 98 2000 15 to 45 : 17860 >= 60 : 9561 2002 2004 Patient Survival according to Adult Recipient Age 01/1988 - 06/2006 100 (%) 81 80 74 70 78 69 60 63 59 62 52 45 40 < 60 yrs : 45262 20 p Log Rank = 0.001 >=60 yrs : 9867 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Yrs ELTR Soppravvivenza SPLIT versus LRLT e OLT (%) 100 79 80 75 77 65 60 66 64 58 54 49 40 Intero da cadavere Living donor Split liver 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 anni ELTR Graft Survival according to Donor Age in Europe 12/2005 01/1988 - 12/2005 (%) 100 Total Log Rank test p = 0.0001 <55 years : 46061 55-65 years : 7607 75 80 >=65 years : 4763 68 72 60 64 57 57 61 53 48 53 41 40 41 32 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Yrs AFTER OLTx Immunological complications Rejection Infections ... Immunosuppression Surgical complications Hypertension Diabetes Dyslilipidemia Obesity Osteoporosis “De novo” tumors ... Vascular Biliary ... Relapse Infectious complications Bacterial Viral Mycotic • • • • Bacterial infections of the biliary tract Cholangitis Peritonitis Abdominal absidations Medical complications • • • • • • • • D.M. Iperlipemia Obesity Osteoporosis Cardiovascular complications Neuropsychiatric complications IRA IRC REJECTION ACUTE REJECTION Within 5 days to 6 weeks after OLTx Inflammatory process involving the biliary ducts and the vascular endothelium • • • • • • • fever jaundice Hepatomegalia low bile production pale bile increase of ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubine increase WBC and eosinophily • • • BIOPSY RAI SCORE STEROIDS CRONIC REJECTION 60-90 days after OLTx or later After an acute rejection not solved After recurrent episodes of acute rejection Without acute episodes, probably related to an inadeguate immunosuppressive therapy • Not specific symptoms vs cholestasis HAT or HAS!!! Duttopenia • • IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE THERAPY Re OLTx De novo tumors after liver transplantation The risk of malignancy is a well recognized event in transplanmt recipients. Besides skin cancer, Kaposi’s sarcoma and lymphoproliferative disorder, in close contact with immunosuppression, many cancers of solid organ are described Causes of death after organ transplant N. = 321 (autopsies) 10% 8% 12% 6% 64% Infections Hepatic insuff. MOF Respiratory insuff Cardiovascular Torbenson et al. Mod Pathol; 1998
Scaricare