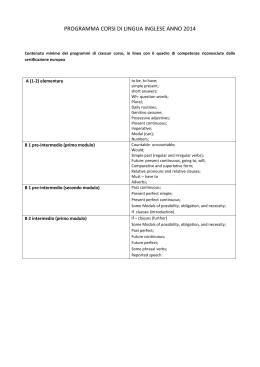
INGLESE – 2 LEZIONE ARGOMENTI: RIPASSO DELLA LEZIONE PRECEDENTE; PRESENT PERFECT. APPUNTI: RIPASSO DELLA LEZIONE PRECEDENTE PRESENT SIMPLE (Fatti concreti che si svolgono in ogni tempo: passato, presente e futuro) L’acqua bolle a 100° C / Water boils at 100° C PRESENT CONTINUOUS (Sarebbe il gerundio in italiano) Soggetto + Verbo essere + Forma ing Io sto scrivendo / I’m writing PAST SIMPLE (Un evento concluso nel passato) Nel 1995 sono andato a Parigi / In 1995 I went to Paris To go / Went / Gone (Verbo irregolare) To start / Started / Started (Verbo regolare, si aggiunge -ed) SIMPLE PAST CONTINUOUS (Un evento che accadde in passato che è stato interrotto) Mi stavo facendo la doccia quando improvvisamente qualcuno è entrato in casa mia (fare la doccia in inglese si dice: to have a shower) / I was having a shower when suddently someone entered my house PRESENT PERFECT Si forma cosi: Soggetto + Have (verbo avere) + Past Participle (terza colonna del paradigma) Corrisponde al passato prossimo in italiano In italiano si usa il verbo essere Sono andato Lei è andata In inglese si usa il verbo avere I have gone She has gone Si usa il PRESENT PERFECT quando si descrive un’azione avvenuta nel passato senza specificare quando! Se specifico quando è avvenuta si usa il SIMPLE PAST! Nel 1914 iniziò la prima guerra mondiale e finì tre anni dopo Dirò: The 1st world war broke out in 1914 and ended three years later (quindi ho usato il SIMPLE PAST) Ho visto questo film / I’ve seen this film (PRESENT PERFECT) Ho visto questo fim domenica scorsa / I saw this film last Sunday (SIMPLE PAST) Si usa il PRESENT PERFECT anche per raccontare delle esperienze della propria vita! (Solo se non specifico quando, altrimenti si usa il SIMPLE PAST) Ho visto dei gorilla in Africa / I’ve seen gorillas in Africa (PRESENT PERFECT) Nel 2002 ho visto dei gorilla in Africa / In 2002 I sow gorillas in Africa (SIMPLE PAST) Come si formano alcune domande MAI in inglese si dice NEVER ma nelle domande diventa EVER Sei mai stato a New York? Si, ci sono stato / No, non ci sono stato / Si, ci sono stato nel 98 Have you ever been to New York? (Si usa il participio passato del verbo essere) Yes, I’ve been (to New York) No, I haven’t / No, I have never been there Yes, I have been there I’ve been to Paris (Sono stato a Parigi nel senso che sono andato e tornato) But I’m back now He has gone to Paris but He’s not back yet (E’ andato a Parigi ma non è ancora tornato) Si usa il PRESENT PERFECT anche quando si parla di una azione ad esempio svolta nella mattinata che si è conclusa ma la ricordiamo sempre durante il mattino. Questa mattina ho fatto colazione con il mio capo (SE LO DICO DURANTE LA MATTINATA) In this morning I’ve had breckfast with my boss (PRESENT PERFECT) Se questa frase la diciamo alla sera sarà: In this morning I had breckfast with my boss (SIMPLE PAST) Si usa il PRESENT PERFECT anche quando si parla di azioni iniziate nel passato che continuano nel presente Ho mangiato la pizza tre volte in questo mese / I’ve eaten pizza three times this month Quando si usano FOR e SINCE FOR (Indica un periodo di tempo) Per tre settimane / For three weeks SINCE (Indica un momento preciso, quando ha avuto inizio) Non vedo Tom da martedì / I haven’t seen Tom since tuesday Per dieci minuti / For ten minutes Non vedo Tom da tre mesi / I haven’t seen Tom for three months Quando si usano JUST, ALREADY e YET Appena = Just Già = Already Si collocano tra soggetto e participio passato Ancora = Yet Si usa nelle frasi negative e interrogative Si colloca dopo il soggetto e il Present Perfect Ho appena finito / I have just finished Non sono ancora andato / I haven’t gone yet Ho già letto quel libro / I have already read* that La posta non è ancora arrivata / book The post hasn’t arrived yet Hai già trovato un lavoro? / Have you found a job yet? No, non ancora / No, I haven’t found a job yet No, non ancora / No, not yet *Il verbo leggere (to read) si scrive nello stesso modo ma si legge diversamente: Si scrive: (read ---- read ---- read) Ma si legge: (rid ---- red ---- red) Alte frasi con le regole che abbiamo appena analizzato Have you written to John yet? Yes, I’ve written, I’ ve just finished a letter Are you caming home? No, not yet I’ve just (already) finished my italian homework, but I haven’t finished maths yet Can I speak to Tim? No, I’m sorry, He has gone to London. He’ll be back tomorrow / Yes, He has been to Paris but he came back yesterday What is that book about? I don’t know, I haven’t read it yet
Scaricare