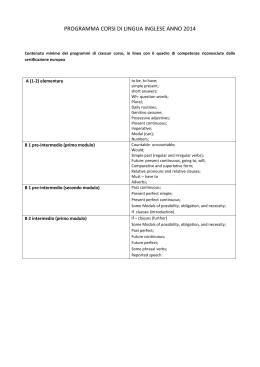
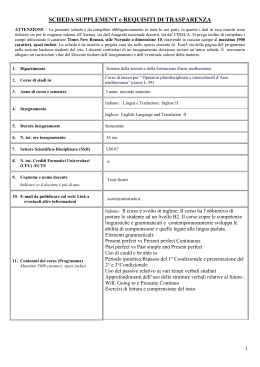
Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 1 CAPITOLO 1.2 : LA CONIUGAZIONE DEI VERBI 1.2.1 - LA CONIUGAZIONE DEI VERBI ITALIANI La coniugazione di un verbo è l’insieme ordinato delle varie forme che un verbo può assumere per indicare la persona, il numero, il modo, il tempo e l’aspetto dell’azione o dello stato che esprime. 1.2.2 -La coniugazioni dei verbi ausiliari I verbi ausiliari Essere e Avere presentano una coniugazione del tutto anomala rispetto agli nitri verbi della lingua italiana. Diamo in questa pagina la coniugazione del verbo essere e alla pagina seguente la coniugazione del verbo avere, che è necessario conoscere per formare i tempi composti degli altri verbi. 1.2.3. Verbo ausiliare ESSERE: Presente Io sono Tu sei Egli è Noi siamo Voi siete Essi sono Passato remoto Io fui Tu fosti Egli fu Noi fummo Voi foste Essi furono Indicativo Passato prossimo Imperfetto Io sono stato Io ero Tu sei stato Tu eri Egli è stato Egli era Noi siamo stato Noi eravamo Voi siete stato Voi eravate Essi sono stato Essi erano Trapassarto remoto Futuro semplice Io fui stato Io sarò Tu fosti stato Tu sarai Egli fu stato Egli sarà Noi fummo stato Noi saremo Voi foste stato Voi sarete Essi furono stato Essi saranno Presente Che io sia Che tu sia Che egli sia Che noi siamo Che voi siate Che essi siano Passato Che io sia stato Che tu sia stato Che egli sia stato Che noi siamo stato Che voi siate stato Che essi siano stato Condizionale Presente Io sarei Tu saresti Egli sarebbe Noi saremmo Voi sareste Essi sarebbero Passato Io sarei stato Tu saresti stato Egli sarebbe stato Noi saremmo stato Voi sareste stato Essi sarebbero stato Infinito Presente essere Passato essere stato SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Congiuntivo Imperfetto Che io fossi Che tu fossi Che egli fosse Che noi fossimo Che voi foste Che essi fossero Trapassato Prossimo Io ero stato Tu eri stato Egli era stato Noi eravamo stato Voi eravate stato Essi erano stato Futuro anteriore Io sarò stato Tu sarai stato Egli sarà stato Noi saremo stati Voi sarete stati Essi saranno stati Trapassato Che io fossi stato Che tu fossi stato Che egli fosse stato Che noi fossimo stati Che voi foste stati Che essi fossero stati Imperativo Presente -----sii tu sia egli siamo noi siate voi siano essi Participio Presente Passato ènte stato Gerundio Presente Passato essendo essendo stato - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 2 1.2.4 - Verbo ausiliare AVERE: Presente Io ho Tu hai Egli ha Noi abbiamo Voi avete Essi hanno Passato remoto Io ebbi Tu avesti Egli ebbe Noi avemmo Voi aveste Essi ebbero Indicativo Passato prossimo Imperfetto Io ho avuto Io avevo Tu hai avuto Tu avevi Egli ha avuto Egli aveva Noi abbiamo avuto Noi avevamo Voi avete avuto Voi avevate Essi hanno avuto Essi avevano Trapassarto remoto Futuro semplice Io ebbi avuto Io avrò Tu avesti avuto Tu avrai Egli ebbe avuto Egli avrà Noi avemmo avuto Noi avremo Voi aveste avuto Voi avrete Essi ebbero avuto Essi avranno Trapassato Prossimo Io avevo avuto Tu avevi avuto Egli aveva avuto Noi avevamo avuto Voi avevate avuto Essi avevano avuto Futuro anteriore Io avrò avuto Tu avrai avuto Egli avrà avuto Noi avremo avuto Voi avrete avuto Essi avranno avuto Presente Che io abbia Che tu abbia Che egli abbia Che noi abbiamo Che voi abbiate Che essi abbiano Congiuntivo Passato Imperfetto Che io abbia avuto Che io avessi Che tu abbia avuto Che tu avessi Che egli abbia avuto Che egli avesse Che noi abbiamo avuto Che noi avessimo Che voi abbiate avuto Che voi aveste Che essi abbiano avuto Che essi avessero Trapassato Che io avessi avuto Che tu avessi avuto Che egli avesse avuto Che noi avessimo avuto Che voi aveste avuto Che essi avessero avuto Presente Io avrei Tu avresti Egli avrebbe Noi avremmo Voi avreste Essi avrebbero Condizionale Passato Io avrei avuto Tu avresti avuto Egli avrebbe avuto Noi avremmo avuto Voi avreste avuto Essi avrebbero avuto Infinito Presente avere Passato avere avuto Imperativo Presente -----abbi tu abbia egli abbiamo noi abbiate voi abbiano essi Participio Presente Passato avente avuto Gerundio Presente Passato avendo avendo avuto 1.2.5 – La Coniugazione dei verbi regolari ed irregolari: La lingua italiana presenta tre coniugazioni verbali, cioè tre grandi sistemi di forme verbali che raggruppano tutti i verbi della lingua. Infatti, i verbi della nostra lingua si dividono in tre gruppi, a seconda della terminazione dell’infinito presente o, meglio, a seconda della vocale tematica che li caratterizza all’infinito presente: - i verbi che all’infinito presente terminano in -are e, quindi, sono caratterizzati dalla vocale tematica -a-, appartengono alla 1a coniugazione: amare; - i verbi che all’infinito presente terminano in -ere e, quindi, sono caratterizzati dalla vocale tematica -e-, appartengono alla 2a coniugazione: temere; - i verbi che all’infinito presente terminano in -ire e, quindi, sono caratterizzati dalla vocale tematica -i-, appartengono alla 3a coniugazione: sentire. SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 3 La maggior parte dei verbi che appartengono alla stessa coniugazione presenta le stesse desinenze. Perciò, dato un modello per ciascuna delle tre coniugazioni, basta applicare alla radice di ogni verbo le varie desinenze della sua coniugazione per avere tutte le sue forme. Tutti i verbi che si comportano in questo modo — e cioè, come abbiamo detto, la grande maggioranza dei verbi — sono detti regolari. Esistono, però, per ogni coniugazione, dei verbi che si discostano dal modello e sono detti verbi irregolari. 1.2.6 – La coniugazione attiva La 1a coniugazione: La 1a coniugazione (che contiene tutti i verbi in -are) è la coniugazione che risulta più ricca di verbi. Diamo qui di seguito la coniugazione del verbo amare, come modello di flessione dei verbi della 1a coniugazione. 1.2.7 – Verbo regolare AMARE : Indicativo Presente Passato prossimo Imperfetto Trapassato Prossimo Io amo Io ho amato Io amavo Io avevo amato Tu ami Tu hai amato Tu amavi Tu avevi amato Egli ama Egli ha amato Egli amava Egli aveva amato Noi amiamo Noi abbiamo amato Noi amavamo Noi avevamo amato Voi amate Voi avete amato Voi amavate Voi avevate amato Essi amano Essi hanno amato Essi amavano Essi avevano amato Passato remoto Trapassarto remoto Futuro semplice Futuro anteriore Io amai Io ebbi amato Io amerò Io avrò amato Tu amasti Tu avesti amato Tu amerai Tu avrai amato Egli amò Egli ebbe amato Egli amerà Egli avrà amato Noi amammo Noi avemmo amato Noi ameremo Noi avremo amato Voi aamaste Voi aveste amato Voi amerete Voi avrete amato Essi amarono Essi ebbero amato Essi ameranno Essi avranno amato Congiuntivo Passato Imperfetto Che io abbia amato Che io amassi Che tu abbia amato Che tu amassi Che egli abbia amato Che egli amasse Che noi abbiamo amato Che noi amassimo Che voi abbiate amato Che voi amaste Che essi abbiano amato Che essi amassero Presente Che io ami Che tu ami Che egli ami Che noi amiamo Che voi amiate Che essi amino Presente Io amerei Tu ameresti Egli amerebbe Noi ameremmo Voi amereste Essi amerebbero Presente avere Condizionale Passato Io avrei amato Tu avresti amato Egli avrebbe amato Noi avremmo amato Voi avreste amato Essi avrebbero amato Infinito Passato avere avuto SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Presente avente Trapassato Che io avessi amato Che tu avessi amato Che egli avesse amato Che noi avessimo amato Che voi aveste amato Che essi avessero amato Imperativo Presente -----ama (tu) ami (egli) amiamo (noi) amate (voi) amino (essi) Participio Passato avuto Presente avendo Gerundio Passato avendo avuto - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 4 La 2a coniugazione. La 2a coniugazione (verbi in -ere) comprende pochi verbi, per lo più irregolari. Alcuni di essi presentano la desinenza dell’infinito accentata (vedére, temére) , altri, invece, non accentata (rìdere, lèggere). Infatti, nella 2 coniugazione italiana sono confluiti sia i verbi della 2a coniugazione latina che terminavano in -ẽre, con la vocale tematica e lunga e quindi accentata (vid-ẽre → “vedére”), sia i verbi della 3a coniugazione latina che terminavano in -ẽre , con la vocale e breve e quindi non accentata (1ég-ĕre → “léggere”). Tranne questa differenza di accenti all’infinito presente, i due tipi di verbi hanno la medesima coniugazione. Appartengono alla 2a coniugazione anche i verbi in - arre (trarre e composti), -orre (porre e composti) e -urre (condurre, dedurre), che nascono dalla contrazione di verbi latini della 3a coniugazione in -ẽre : tráhẽre→ “trarre”; pónẽre → “porre”; condúẽre →“condurre”. Questi verbi, comunque, sono irregolari e li troveremo, perciò, tra gli irregolari della 2a coniugazione. Diamo qui di seguito, come modello della flessione dei verbi regolari della 2a coniugazione, la coniugazione del verbo Temere. 1.2.8 - Verbo regolare TEMERE : Indicativo Presente Passato prossimo Imperfetto Trapassato Prossimo Io temo Io ho temuto Io temevo Io avevo temuto Tu temi Tu hai temuto Tu temevi Tu avevi temuto Egli tema Egli ha temuto Egli temeva Egli aveva temuto Noi temiamo Noi abbiamo temuto Noi temevamo Noi avevamo temuto Voi temete Voi avete temuto Voi temevate Voi avevate temuto Essi temonono Essi hanno temuto Essi temevano Essi avevano temuto Passato remoto Trapassato remoto Futuro semplice Futuro anteriore Io temei (temetti) Io ebbi temuto Io temerò Io avrò temuto Tu temesti Tu avesti temuto Tu temerai Tu avrai temuto Egli temè (temette) Egli ebbe temuto Egli temerà Egli avrà temuto Noi tememmo Noi avemmo temuto Noi temeremo Noi avremo temuto Voi temeste Voi aveste temuto Voi temerete Voi avrete temuto Essi temerono Essi ebbero temuto Essi temeranno Essi avranno temuto (temettero) Congiuntivo Passato Imperfetto Che io abbia temuto Che io temessi Che tu abbia temuto Che tu temessi Che egli abbia temuto Che egli temesse Che noi abbiamo temuto Che noi temessimo Che voi abbiate temuto Che voi temeste Che essi abbiano temuto Che essi temessero Presente Che io tema Che tu tema Che egli tema Che noi temiamo Che voi temiate Che essi temano Presente Io temerei Tu temeresti Egli temerebbe Noi temeremmo Voi temereste Essi temerebbero Presente temere Condizionale Passato Io avrei temuto Tu avresti temuto Egli avrebbe temuto Noi avremmo temuto Voi avreste temuto Essi avrebbero temuto Infinito Passato avere temuto SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Presente temente Trapassato Che io avessi temuto Che tu avessi temuto Che egli avesse temuto Che noi avessimo temuto Che voi aveste temuto Che essi avessero temuto Imperativo Presente -----temi tu tema egli temiamo noi temete voi temano essi Participio Passato temuto Presente temendo Gerundio Passato avendo temuto - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 5 La 3° coniugazione. La 3 coniugazione (verbi in -ire) è una coniugazione particolarmente ricca di forme. Diamo qui di seguito, come modello della flessione dei verbi della 3a coniugazione, la coniugazione del verbo sentire. 1.2.9 - Verbo regolare SENTIRE : Indicativo Imperfetto Io sentivo Tu sentivi Egli sentiva Noi sentivamo Voi sentivate Essi sentivano Futuro semplice Io sentirò Tu sentirai Egli sentirà Noi sentiremo Voi sentirete Essi sentiranno Presente Io sento Tu senti Egli sente Noi sentiamo Voi sentite Essi sentono Passato remoto Io sentii Tu sentisti Egli sentì Noi sentimmo Voi sentiste Essi sentirono Passato prossimo Io ho sentito Tu hai sentito Egli ha sentito Noi abbiamo sentito Voi avete sentito Essi hanno sentito Trapassato remoto Io ebbi sentito Tu avesti sentito Egli ebbe sentito Noi avemmo sentito Voi aveste sentito Essi ebbero sentito Presente Che io senta Che tu senta Che egli senta Che noi sentiamo Che voi sentiate Che essi sentano Congiuntivo Passato Imperfetto Che io abbia sentito Che io sentissi Che tu abbia sentito Che tu sentissi Che egli abbia sentito Che egli sentisse Che noi abbiamo sentito Che noi sentissimo Che voi abbiate sentito Che voi sentiste Che essi abbiano sentito Che essi sentissero Condizionale Presente Passato Io sentirei Io avrei sentito Tu sentiresti Tu avresti sentito Egli sentirebbe Egli avrebbe sentito Noi sentiremmo Noi avremmo sentito Voi sentireste Voi avreste sentito Essi sentirebbero Essi avrebbero sentito Infinito Presente sentire Passato avere sentito SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Trapassato Prossimo Io avevo sentito Tu avevi sentito Egli aveva sentito Noi avevamo sentito Voi avevate sentito Essi avevano sentito Futuro anteriore Io avrò sentito Tu avrai sentito Egli avrà sentito Noi avremo sentito Voi avrete sentito Essi avranno sentito Trapassato Che io avessi sentito Che tu avessi sentito Che egli avesse sentito Che noi avessimo sentito Che voi aveste sentito Che essi avessero sentito Imperativo Presente -----senti tu senta egli sentiamo noi sentite voi sentano essi Participio Presente Passato sentente sentito (senziente) Gerundio Presente Passato sentendo avendo sentitoto - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 6 1.2.10 -THE ENGLISH VERBS CONJUGATION 1.2.11 - AUXILIARY VERBS: TO BE AND TO HAVE CONJUGATION: MOODS : Indicative ; Conjunctive; Conditional ; Imperative ; Infinitive ; Participle . Indicative : Tenses : Simple present ; Present perfect ; Simple Past , Past Perfect ; Simple Future ; Future Perfect ; Conjunctive : Tenses : Simple present ; Present perfect ; Simple Past Conditional : Tenses : Present ; Past Imperative : Tense : Present Infinitive : Tenses :Present ; Perfect Participle : Tenses : Present; Participle past Gerundio : Tenses : Present; Perfect 1.2.12 - AUXILIARY VERB : To be ; pass. was ; p.p. been Simple present I am You are He/She/It is We are You are They are Indicative Mood Present perfect Pass.Prossimo I have been sono stato You have been sei stato He/...has been é stato we have been siamo stati you have been siete stati they have been sono stati Presente Io sono Tu sei Egli/Ella/Esso é Noi siamo Voi siete Essi sono Past Perfect Trapass.Pros.e Remoto I had been ero-fui/stato You had been eri-fosti/stato He/She/It had been era-fu/stato We had been eravamo-fummo/ stati You had been ervate-foste/stati They had been erano-furono/stati Simple Future Futuro Semplice I will/shall be sarò You will be sarai He/She/It will be sarà We will/shall be saremo You will be sarete They will be saranno Simple Past Imperf.e P.Remoto I was Io ero - fui you were Tu eri - fosti He/She/It was Egli/... era - fu We were Noi eravamo - fummo You were Voi eravate - foste They were Essi erano - fùrono Future Perfect Futuro Anteriore I will/shall have been sarò stato You will have been sarai stato He/She/It will have been sarà stato We will/shall have been saremo stati You will have been sarete stati They will have been saranno stati The Conjunctivce Mood is → hardly ever used Modo Congiuntivo → Quasi mai usato Simple present Presente Simple Past Imperfetto Past Perfect Trapassato That I be che Io sia If I were se io Fossi If I had been se io fossi stato That You be che Tu sia If you were se tu fossi If you had been se tu fossi stato That He/She/It be che Egli /…sia If He/She/It were se Egli / If He/.. had been se Egli/…fosse That We be che Noi siamo Ella fosse stato You are che Voi siate If We were se noi fòssimo If We had been se noi fòssimo stati That They be che Essi siano If you were se voi foste If you had been se voi foste stati If they were se essi If they had been se essi fòssero fòssero sdtati Conditional Mood – Present Tense I wuold /should be sarei You would be saresti He/She/It would be sarebbe we would/shouls be saremmo You would be sareste They would be sarebbero Infinitive Mood Present : to be Perfect : to have been SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Conditional Mood Past tense I wuold /should have been sarei stato You would have been saresti stato He/… would have been sarebbe stato we would/shouls have been saremmo stati You would have been sareste stati They would have been sarebbero stati Participle Mood Participle Present : being Participle Past : been Imperative Mood Present be sii tu be sia egli be siamo noi be siate voi be siano essi Gerund Mood Present : being Perfect : having been - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 7 1.2.13 AUXILIARY VERB : To have ; pass. had ; p.p. had Indicative Mood Simple present Presente I have Io ho You have Tu hai He/She/It has Egli/Ella/Esso ha We have Noi abbiamo You have Voi avete They have Essi hanno Present perfect Pass.Prossimo I have had ho avuto you have had hai avuto He/She/It has had ha avuto we have had abbiamo avuto you have had avete avuto they have had hanno avuto Past Perfect Trapass.Pros.e Remoto I had had avevo avuto-ebbi avuto you had had avevi avuto He/She/It had had aveva avuto We had had avevamo avuto you had had avevate avuto they had had avevano avuto Simple Future Futuro Semplice I will/shall have avrò You will have avrai He/She/It will have avrà We will/shall have avremo You will have avrete They will have avranno The Conjunctivce Mood is → Simple present Presente That I have che Io abbia That You have che Tu abbia That He/... have che Egli/… abbia That We have che Noi abbiamo That You have che Voi abbiate That They have che Essi abbiano Simple Past Imperf.e P.Remoto I had avevo - ebbi You had avevi - avesti He/She/It had aveva - ebbe We had avevamo - avemmo You had avevate - aveste they had avevano - ebbero Future Perfect Futuro Anteriore I will/shall have had avrò avuto You will have had avrai avuto He/She/It will have had avrà avuto We will/shall have had avremo avuto You will have had avrete avuto They will have had avranno avuto hardly ever used Modo Congiuntivo → Quasi mai usato Simple Past Imperfetto Past Perfect Trapassato If I had se io avessi If I had had se avessi avuto If you had se tu avessi If you had had se avessi avuto If He/.. had se Egli/ avesse If He/.. had had se avesse avuto If We had se noi avessimo If We had had se avessimo avuto If you had se voi aveste If you had had se voi aveste avuto If they had se essi avessero If they had had se essi avessero " Conditional Mood - Present Tense I wuold/should have avrei You would have avresti He/She/It would have avrebbe we would/shouls have avremmo You would have avreste They would have avrebbero Infinitive Mood Present : to have Avere Perfect : to have had Avere avuto Present Continuous: to be having Perfect Contin: to have been having Conditional Mood - Past tense I wuold/should have had avrei avuto You would have had avresti avuto He/… would have had avrebbe avuto we would/shouls have had avremmo avuto You would have had avreste avuto They would have had avrebbero avuto Participle Mood Participle Present : having Avente Participle Past : had Avuto Imperat. M.- Pres. be abbi tu be abbia egli be abbiamo noi be abbiate voi be abbiano essi Gerund Mood Present : having Avendo Perfect : having had Avendo avuto 1.2.14 - REGULAR VERBS: CONJUGATION: MOODS : Indicative ; Conjunctive; Conditional ; Imperative ; Infinitive ; Participle . Indicative : Tenses : Simple present ; Present perfect ; Simple Past , Past Perfect ; Simple Future ; Future Perfect ; Present Continuous ; Pres. perfect contin.; Past Contin.; Past Perfect Contin.; Future Contin.; Future Perfect Contin. Conjunctive : Tenses : Simple present ; Present perfect ; Simple Past Conditional : Tenses : Present ; Past Imperative : Tense : Present Infinitive : Tenses :Present ; Perfect Participle : Tenses : Present; Participle past Gerundio : Tenses : Present; Perfect SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 8 2.15 - REGULAR VERB : To study; pass. studied; p.p. studied Indicative Mood Simple present Presente I study Io studio You study Tu studi He/She/It studies Egli/Ella..studia We study Noi studiamo You study Voi studiate They study Essi studiano Past Perfect Trap.Pros.e Remoto I had studied avevo-ebbi studiato You had " avevi - avesti studiato He/..had " aveva - ebbe studiato We had studied avevamo studiato You had " avevate studiato They had " avevano studiato Present Continuous Presente continuo I am studying Io sto studiando you are studying Tu stai " He/she/it is studying Egli sta " We are studying Noi stiamo " You are studying Voi state " they are studying Essi stanno " Past Perfect Continuous Trapassato Continuo I had been studying Io ero stato studiante You had been studiyng H/She/It had been studiyng We had been studiyng You had been studiyng They had been studiyng Present perfect Pass.Prossimo Simple Past Imperf.e P.Remoto I have studied ho studiato you have studied hai studiato He/.. has studied ha studiato we have " abbiamo studiato you have " avete studiato they have " hanno stud. Simple Future Futuro Semplice I will/shall study studierò You will study studierai He/She/It will study studierà We will/shall study studieremo You will study studirete They will study studieranno Present perfect continuous Passato prossimo continuo I have been studying Io sono stato studiante you have been studying he/she/it has been studying We have been studying you have been studying they have been studying I studied studiavo - studiai you studied sudiavi - studiasti He/.. " studiava - studiò We " studiavamo-studiammo You " studiavate-studiaste they " studiavano- studiarono Future Perfect Futuro Anteriore I will/shall have studied avrò stud. You will have studied avrai stud. He/.. will have " avrà studiato We will/shall have " avremo stud. You will have studied avrete stud. They will have " avranno studiato Past continuous Passato continuo I was studying Io ero studiante you were studying he/she/it was studying We were studying you were studying they were studying Future Continuous Futuro Continuo I will be studying Io sarò studiante You will be studying He/She/It will be studying We will be studying You will be studying they will be studying Future Perfect Continuous Futuro Anteriore Continuo I will have been studying Io sarò stato studiante You will have been studying He/She/It will have been studying We will have been studying You will have been studying they will have been studying The Conjunctivce Mood is → hardly ever used Modo Congiuntivo → Quasi mai usato Simple present Presente Simple Past Imperfetto Past Perfect Trapassato That I study che Io studi If I studied se io studiassi If I had studied se avessi stud. That You study che Tu studi If you studied se tu studiassi If You had " se avessi studiato That He/... study che Egli/ studi If He/... " se Egli studiasse If He/.had " se avesse studiato That We study che Noi studiamo If We " se noi studiassimo If We had " se avessimo studiato That You study che Voi studiate If you studied se voi studiaste If you had " se aveste studiato That They study che Essi studino If they " se essi studiassero If they had " se avessero studiato Conditional Mood – Present Tense I would/should study studierei You would study studieresti He/She/It would study studierebbe we would/should study studieremmo You would study studiereste They would study studierebbero Infinitive Mood Present : to study studiare Perfect : to have studied Present Contin.: to be studying Perfect Cont.:to have been studyintg SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 Conditional Mood - Past tense Imperat. Present I would/should have studied avrei studiat You would have avresti studiato He/… would have avremmo " You would have avreste studiato They would have avrebbero studiato study studia tu study studi egli study studiamo noi study studiate voi study studino essi Participle Mood Participle Present : studying Participle Past : studied Gerund Mood Present : studying Perfect : having studied - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 - Maritime English for Deck and Engine Ratings – Inglese marittimo per comuni di Coperta e Macchina 9 2.16 – VERBO CAN SEZIONE 1 : Capitolo 1.2 - F.V. SCARDINA & SONS - 91100 Trapani - Edizione 2012 -
Scaricare