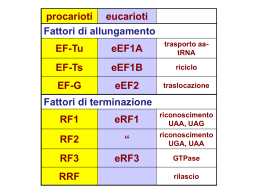
Regolazione della traduzione •generale •specifica Initiation Factor Activity eIF-1 Fidelity of AUG codon recognition eIF-1A Facilitate Met-tRNAiMet binding to small subunit eIF-2 Ternary complex formation eIF-2B (GEF) GTP/GDP exchange during eIF-2 recycling eIF-3 (10 subunits) Ribosome subunit antiassociation, binding to 40S subunit eIF-4F (4E, 4A, 4G) mRNA binding to 40S, ATPase-dependent RNA helicase activity eIF-4A ATPase-dependent RNA helicase eIF-4E 5' cap recognition eIF-4G Scaffold for of eIF-4E and -4A in the eIF-4F complex eIF-4B Stimulates helicase, binds simultaneously with eIF-4F eIF-4H Similar to eIF4B eIF-5 Release of eIF-2 and eIF-3, ribosome-dependent GTPase eIF5B Subunit joining eIF-6 Ribosome subunit antiassociation Via delle MAP chinasi stress Chinasi di eIF2a Figure 3. Stress-Responsive eIF2 Kinases Inhibit General Translation yet Stimulate Expression of a Special Class of Genes (A) Architecture of the four eIF2 Ser-51 kinases. The conserved kinase domains (KD) are depicted in green. The two hemebinding sites in HRI are marked in red. The dsRNA binding domains (dsRBD) in PKR are shown in blue. The N-terminal half of PERK resembles the corresponding domain of the ER stress-responsive IRE1 kinase. Also indicated are signal peptide (SP) and transmembrane (TM) domain of PERK. The regulatory histidyl-tRNA synthetase (HisRS) domain in GCN2 is shown in purple. The locations of the N-terminal GCN1 binding domain (blue), charged region (+/-), and pseudokinase domain (KD), as well as the C-terminal ribosome binding and dimerization domain (RB/DD) in GCN2 are also indicated. The activating condition or ligand for each kinase and the known sources of the kinases are also indicated. Azione delle chinasi di eIF2a Stress-Responsive eIF2 Kinases Inhibit General Translation yet Stimulate Expression of a Special Class of Genes (B) Stress response pathway for regulation of translation by eIF2 phosphorylation. The eIF2 kinases phosphorylate eIF2 leading to inhibition of eIF2B (red bar). This results in low levels of ternary complex (gray arrow) resulting in reduced general translation (gray arrow) and increased translation of GCN4, ATF4, or certain isoforms of C/EBP (black arrow). Increased production of the transcription factors GCN4, ATF4, or C/EBP results in increased expression of their target genes. Regolazione eIF2a Fosforilazione su ser 51 in risposta a stress da parte di 4 chinasi: PKR, GCN2, PERK, HRI La fosforilazione impedisce il riciclo da parte di eIF2B La traduzione di alcuni mRNA è stimolata da bassi livelli di eIF2a attivo Molti virus hanno sistemi per impedire la fosforilazione di eIF2a eIF4F Regolazione eIF4E Fosforilazione su ser 209 da parte di Mnk1 (e Mnk2) correlata con attivazione Mnk interagiscono con eIF4G e sono attivate dalla via delle MAP chinasi eIF4E è inibito dall’interazione con 4E-BP (1, 2 e 3) 4E-BP sono inibite da fosforilazione dipendente dalla via di mTOR
Scaricare