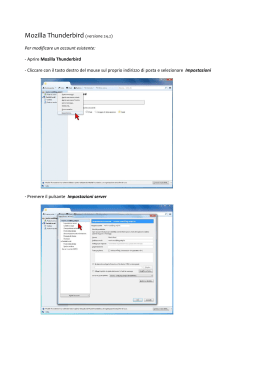
Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale 1. General Information / Informazioni generali Page / Pagina 1 2. Form A (Identification of the Beneficial Owner) / Formulario A (Identificazione del Avente diritto economico) Page / Pagina 4 3. Declaration of status / Dichiarazione di status Page / Pagina 5 4. Signature Card / Cartellino delle firme Page / Pagina 6 5. UNICEF Donation / Donazione all’UNICEF Page / Pagina 7 IN ADDITION TO THE APPLICATION, please enclose + Notarized copy of passport or identity card (with photo and signature). The copy must be fully legible and the photograph clear and identifiable. Copia autenticata del passaporto o della carta d’identità (corredata di foto e firma). La copia deve essere perfettamente leggibile e la foto chiara e identificabile. + Authentication of signature by a public notary (if not features on the Passport or Identity card) Firma autenticata da un notaio (se non riportata sul passaporto o la carta d’identità). + Utility Bill (ex. electricity, telephone, etc.) or a notarized proof of residence La bolletta di un’utenza (es. elettricità, telefono, ecc.) o un documento autenticato comprovante il domicilio. If you are Not the beneficial owner of the funds to be deposited as per page 4 of this agreement, please enclose Se Lei NON è l'avente diritto economico dei fondi che verranno depositati, in base a quanto indicato alla pagina 4 del presente contratto, La preghiamo di allegare For each person listed as beneficial owner on page 4 / Per ciascuna persona indicata come avente diritto economico alla pagina 4. + Notarized copy of passport or identity card (with photo and signature). The copy must be fully legible and the photograph clear and identifiable. Copia autenticata del passaporto o della carta d’identità (corredata di foto e firma). La copia deve essere perfettamente leggibile e la foto chiara e identificabile. + Utility Bill(s) (ex. electricity, telephone, etc.) or a notarized proof of residence for that person La/e bolletta/e di un’utenza (es. elettricità, telefono, ecc.) o un documento autenticato comprovante il domicilio di quella persona For each company listed as beneficial owner on page 4 / Per ciascuna società indicata come avente diritto economico alla pagina 4. + Extract of Commercial Register (in original or notarized copy) / Estratto del Registro delle imprese (in originale o copia autenticata). + Or, if the company is registered in a common law country / Ovvero, se la società è registrata in un paese dove vige la common law: - Certificate of Incorporation (in original or notarized copy) / Certificato di costituzione (in originale o copia autenticata). - Certificate of Good Standing (if Certificate of Incorporation is older than 12 months; in original or notarized copy) / Certificato di vigenza (se il Certificato di costituzione è stato rilasciato da oltre 12 mesi; in originale o copia autenticata) - Memorandum & Articles of Association (in original or notarized copy) / Lo Statuto della società (in originale o copia autenticata). - Certificate of Incumbency or other official document (made by an official State authority) listing the directors in charge (all in original or notarized copies). / Attestazione di titolarità o altro documento ufficiale (rilasciato da un’autorità statale) nel quale siano elencati gli amministratori in carica (in originale o in copia autenticata). M I G BANK Ltd. Tel +41 32 722 81 00 14, rte des Gouttes d’Or Fax +41 32 722 81 01 D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 CH-2008 Neuchâtel [email protected] Index & List of Documents to Enclose / Indice ed elenco dei documenti da allegare AGREEMENT INDEX / INDICE DEL CONTRATTO Switzerland www.migbank.com | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Please complete the application form below. If you have any questions about the application, please contact the Customer Desk. Fields marked with a “*” are mandatory. La preghiamo di compilare il modulo che segue. Per qualsiasi quesito relativo alla richiesta di apertura del conto, La invitiamo a contattare il Servizio Clienti. I campi contrassegnati con “*” sono obbligatori. Family name* / Cognome*: First name* / Nome*: Date of Birth (Day / Month / Year)* / Data di nascita (Giorno / Mese / Anno)*: Passport or identity document number : / Numero del passaporto o della carta d’identità : Nationality* / Nazionalità*: Place of birth / Luogo di nascita: Residence Address / Domicilio : Street & Number* / Via e numero civico*: City* / Città: Postal code* / Codice postale*: Country* / Paese*: Contact details / Recapiti : E-mail* / E-mail*: à NOTE : Please enter your Country Code followed by City Code, then the phone number. NOTA: Inserire il Prefisso internazionale seguito dal Prefisso della città, quindi il numero di telefono. Day Phone Number* / Numero di telefono diurno*: Mobile Phone / Telefono cellulare: Alternative Phone / Numero di telefono alternativo: Fax Number / Numero di fax: Other Personal Information / Altri dati personali : Occupation* / Occupazione : 1. General Information / Informazioni generali PERSONAL INFORMATION / DATI PERSONALI Company */ Società : Language for correspondence* / Lingua per la corrispondenza*: Marital Status / Stato civile: Type of account / TIPO DI CONTO I wish to open an account in accordance with the General Business Conditions and Safe Custody Regulations of the Bank. Desidero aprire un conto in conformità con le Condizioni commerciali e il Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito della Banca. Online Trading / TRADING ON-LINE I wish to have access to one or more terminals, including terminal access through the Bank internet browser, for the electronic transmission of orders and/or transactions, for my accounts with M I G BANK. Desidero avere acceso a uno o più terminali, ivi incluso l’accesso al terminale tramite il browser Internet della Banca, per la trasmissione degli ordini e/o le transazioni, per i miei conti presso M I G BANK. D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 1/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Unless otherwise directed, amounts deposits will be converted in the currency selected below / Salvo altrimenti indicato, gli importi depositati saranno convertiti nella valuta di seguito indicata Type of currency* / Tipo di valuta* USD EUR GBP CHF JPY AUD CAD Estimated initial deposit* / Deposito iniziale stimato*: Estimated total deposit within one year* / Deposito totale stimato entro 1 anno*: Planned Investment (please check the appropriate boxes) / INVESTIMENTO PREVISTO (spuntare le caselle rilevanti) CFD Contratti differenziali Forex Forex Commodities Prodotti di base Futures/Options Future/Prodotti di baseopzioni Bonds/Shares Obbligazioni/ azioni Funds Fondi Product experience (please check the appropriate boxes, all these fields are mandatory) ESPERIENZA DEI PRODOTTI (spuntare le caselle rilevanti, tutti i campi sono obbligatori) Nr. of Years N. di anni Forex Forex CFD Contratti differenziali Commodities Prodotti di basei Futures/Options Future/Prodotti di baseopzioni less than 1 meno di 1 anno 1-3 years 1-3 anni Bonds/Shares Obbligazioni/ azioni Funds Fondi 1. General Information / Informazioni generali Base currency / VALUTA BASE more than 3 più di tre anni DO YOU ALREADY HAVE AN ACCOUNT AT M I G BANK ? È GIÀ TITOLARE DI UN CONTO PRESSO M I G BANK? c No / No c Yes, account number / Sì, conto numero: DID YOU OPEN A DEMO ACCOUNT WITH M I G BANK? HA ATTIVATO UN CONTO DIMOSTRATIVO CON M I G BANK? c No / No c Yes, account number / Sì, conto numero: WERE YOU CONTACTED BY A MEMBER OF M I G BANK’S TEAM? È STATO CONTATTATO DA UN MEMBRO DELLA SQUADRA DI M I G BANK? c No / No c Yes, by Mr./Mrs./ Sì, dal/la Sig./Sig.ra : HAVE YOU BEEN INTRODUCED TO M I G BANK BY SOMEBODY ? È STATO PRESENTATO A M I G BANK DA QUALCUNO? c No / No D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 c Yes, introduced by / Sì, presentato da: 2/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Origin of money to invest (Select as many as apply, min. 1 choice) Provenienza del denaro da investire (selezionare tutte le opzioni rilevanti, minimo 1 scelta) c Savings Risparmi c c Gift Donazione c Earned income/pension Reddito da lavoro/pensione c Inheritance Eredità c Financial markets earnings Reddito da investimenti Other (please specify) : Altro (specificare): do you have an important public function ? / SVOLGE UN’IMPORTANTE FUNZIONE PUBBLICA? Do you hold any prominent public office (e.g. head of state or government; senior politician, high-ranking official in the public administration, the judiciary, the armed forces or political party; senior executive officer of a state-owned enterprise of national importance)? Or do you have close family, or personal or business relations with any such person? Or does any person likely to be involved in the client relationship or anyone close to them hold such office? Riveste un importante incarico pubblico (ad es., capo di Stato o di governo; autorevole esponente politico; funzionario di alto rango nella pubblica amministrazione, nella magistratura, nelle forze armate o in un partito politico; alto dirigente di un’azienda di proprietà statale di importanza nazionale)? Oppure ha stretti rapporti familiari, personali o professionali con una persona che riveste un tale incarico? Oppure una persona che potrebbe essere coinvolta nella relazione con il cliente o altra persona a questa vicina riveste un simile incarico? c No / No c Yes, please describe / Sì, descrivere: 1. General Information / Informazioni generali CLIENT FINANCIAL INFORMATION / INFORMAZIONI FINANZIARIE SUL CLIENTE General Conditions and Contract documents / CONDIZIONI GENERALI E DOCUMENTI CONTRATTUALI By signing below, you hereby agree that you have received, read, understood, consented and accepted any and all of the General Business Conditions and Safe Custody Regulations. You confirm you have received, read, understood, consented and accepted the “Special risks in securities trading” brochure. Firmando nello spazio sottostante, Lei dichiara di aver ricevuto, letto, compreso, approvato e accettato tutte le Condizioni commerciali e il Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito della Banca. Conferma altresì di aver ricevuto, letto, compreso, approvato e accettato l’opuscolo dal titolo “Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari”. Place / Luogo Signature / Firma Date / Data D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 3/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Verification of the Beneficial Owner / VERIFICA DELl’Avente diritto economico According to the Swiss regulation the Bank must identify the economical beneficial owner(s) of the assets deposited on the account. If you are the beneficial owner of the assets, please check the first box to confirm that you are the beneficial owner and then sign at the bottom of the page. If you are not the beneficial owner, please check the second box and fill in all the requested information. Please also provide us with a notarized copy of the passport or company documents of this person(s) or company(ies). In conformità con la normativa svizzera, la Banca è tenuta a identificare l'/gli avente/i diritto economico dei fondi depositati sul conto. Se Lei è l'avente diritto economico dei fondi, La preghiamo di spuntare la prima casella per confermare che Lei è l'avente diritto economico e quindi di firmare in fondo alla pagina. Se Lei non è l'avente diritto economico, La preghiamo di spuntare la seconda casella e di compilare le informazioni richieste. La invitiamo anche a fornirci una copia autenticata del passaporto o dei documenti societari di questa/e persona/e o società. The contracting partner hereby declares La parte contraente con la presente dichiara c That the contracting partner is the beneficial owner of the assets deposited with M I G BANK Che la parte contraente è l'avente diritto economico dei fondi depositati presso M I G BANK OR / OPPURE c That the beneficial owner(s) of the assets deposited with M I G BANK is(are) (write below) : Che l'/gli avente/i diritto economico dei fondi depositati presso M I G BANK è/sono (scrivere nello spazio sottostante): Family name / First name or Company name Date of birth or incorporation (D / M / Y) Nationality or country of incorporation Address Country Cognome / nome o ragione sociale: Data di nascita o di costituzione (G / M / A) Nazionalità o Paese di costituzione Indirizzo Nazione The contracting partner(s) undertake(s) to automatically inform M I G BANK of any changes. 2. Form A (Identification of the Beneficial Owner) / Formulario A (Identificazione dell’avente diritto economico) Please note that this form will not be accepted if it contains any alterations / Si noti che questo modulo non verrà accettato se contiene alterazioni La/e parte/i contraente/i si impegna/no ad informare prontamente M I G BANK di qualsiasi variazione intervenuta. It is a criminal offence to deliberately provide false information on this item (Art. 251 of the Swiss Penal Code, document forgery; penalty : imprisonment for up to five years or a fine). Il rilascio di dichiarazioni mendaci su questo punto costituisce reato penale (Art. 251 del Codice penale svizzero, contraffazione di documenti; sanzione: detenzione fino a cinque anni o contravvenzione). Translation of documents is provided for the added convenience of the Client. In the event of conflict between the original English text and any translation or any other agreement between the Bank and the Client, the English version shall take precedence. La traduzione dei documenti è per comodità di lettura. In caso di conflitto tra la versione originale inglese in corso e qualsiasi altra versione tradotta, la versione inglese sarà quella valida e prevarrà sulle altre. Place / Luogo Signature / Firma Date / Data D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 4/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Your answer to this field to this field is mandatory / La compilazione di questo campo è obbligatoria The account holder is a “non-US person”, i.e. not a US citizen (be it by single, dual or multiple nationality), does not have “resident alien” status (for example by holding a “Green Card” or having carried out frequent visits to the USA in the current year and the previous two years). c Il titolare del conto è un “soggetto non statunitense”, cioè non è un cittadino degli Stati Uniti (con nazionalità singola, doppia o multipla) e non gode dello status di “straniero residente” (per esempio, per il fatto di detenere una “Green Card” o di aver effettuato visite frequenti negli Stati Uniti nell’anno in corso e nei due anni precedenti). The account holder is a “US person”, i.e. a US citizen (single, dual or multiple nationality) or that he holds the “resident alien” status (for example by holding a “Green Card” or having carried out frequent visits to the USA in the current year and the previous two years). The account holder accepts that the Bank, due to legal and fiscal reasons, prohibits the access to any US securities (in particular access to the US stock markets and US securities listed on other stock markets) as well as other investments considered US relevant. c Il titolare del conto è un “soggetto statunitense”, cioè è un cittadino degli Stati Uniti (con nazionalità singola, doppia o multipla) o gode dello status di “straniero residente” (per esempio, per il fatto di detenere una “Green Card” o di aver effettuato visite frequenti negli Stati Uniti nell’anno in corso e nei due anni precedenti). Il titolare del conto accetta che la Banca, per ragioni legali e fiscali, proibisca l’accesso a tutti i valori mobiliari statunitensi (in particolare, l’accesso ai mercati azionari degli Stati Uniti e ai titoli statunitensi quotati in altri listini), nonché ad altri investimenti considerati rilevanti negli Stati Uniti. Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined the information on this item and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct and complete. / Sotto giuramento dichiaro di aver esaminato l’informazione su questo punto e che, al meglio delle mie conoscente e informazioni, tale informazione è veritiera, corretta e completa. Taxation of savings income from the EUropean union TASSAZIONE DEI REDDITI DA RISPARMIO DALL’UNIONE EUROPEA This point applies only to EU citizens and residents. / Il seguente punto si applica soltanto ai cittadini e ai residenti dell’Unione europea. The account holder has been informed of the Agreement between Switzerland and the European Union which requires the Bank either to apply a withholding tax on relevant interest payments or to communicate all payments of such interests to the relevant authorities. Il titolare del conto è stato informato dell’Accordo vigente tra la Svizzera e l’Unione europea che impone alla Banca di operare una ritenuta fiscale alla fonte sugli interessi corrisposti oppure di comunicare tutti i pagamenti di tali interessi alle autorità rilevanti. 3. Declaration of status / Dichiarazione di status Declaration of status of “non-US person” or “US person” DICHIARAZIONE DELLO STATUS DI “SOGGETTO NON STATUNITENSE” O “SOGGETTO STATUNITENSE” I authorize the Bank to transmit such information (complete identity, account number, details of interest paid) to the relevant tax authorities in my country of residence. c c Autorizzo la Banca a trasmettere tali informazioni (dati personali completi, numero di conto, dettagli degli interessi corrisposti) alle autorità fiscali rilevanti nel mio paese di residenza. I authorize the Bank to apply the withholding tax rather than informing to the relevant tax authorities in my country of residence. Autorizzo la Banca ad operare una ritenuta fiscale alla fonte anziché informare le autorità fiscali rilevanti nel mio paese di residenza. Translation of documents is provided for the added convenience of the Client. In the event of conflict between the original English text and any translation or any other agreement between the Bank and the Client, the English version shall take precedence. La traduzione dei documenti è per comodità di lettura. In caso di conflitto tra la versione originale inglese in corso e qualsiasi altra versione tradotta, la versione inglese sarà quella valida e prevarrà sulle altre. Place / Luogo Signature / Firma Date / Data D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 5/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Family name / Cognome: First name / Nome: Nationality / Nazionalità: Date of Birth (Day / Month / Year) / Data di nascita (giorno / mese / anno): Please sign in both boxes below / Apporre una firma in ciascuno dei due riquadri sottostanti D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 4. Signature Card / Cartellino delle firme SIGNATURE SPECIMEN / SPECIMEN DELLA FIRMA 6/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale Client name / NOME CLIENTE Family name / Cognome: First name / Nome: M I G and UNICEF / M I G E UNICEF Since January 1st 2007, M I G BANK collaborates with UNICEF to support its role as the World’s driving force for the well-being of children. M I G BANK backs this initiative by donating a percentage of its profits to UNICEF projects. Dal 1° gennaio 2007 M I G BANK collabora con l’UNICEF per sostenere il suo ruolo determinante nella promozione del benessere dei bambini a livello mondiale. M I G BANK sostiene questa iniziativa donando una percentuale dei suoi profitti ai progetti dell’UNICEF. We encourage you to join us in this program by selecting the donation of your choice La incoraggiamo ad unirsi a noi in questo programma, selezionando la donazione di Sua scelta: c c c I wish to donate USD 25.- to UNICEF and therefore instruct M I G bank to withdraw the donation from my account upon receipt of the first deposit in my account in order to credit UNICEF Desidero donare 25,00 USD all’UNICEF e pertanto autorizzo M I G BANK a prelevare la donazione dal mio conto non appena vi sarà effettuato il primo deposito, al fine di accreditarla all’UNICEF I wish to donate USD ____________ to UNICEF and therefore instruct M I G BANK to withdraw the donation from c my account upon receipt of the first deposit in my account in order to credit UNICEF Desidero donare ____________ USD all’UNICEF e pertanto autorizzo M I G BANK a prelevare la donazione dal mio conto non appena vi sarà effettuato il primo deposito, al fine di accreditarla all’UNICEF I do not wish to donate to UNICEF 5. UNICEF Donation / Donazione all’UNICEF Please note that it is not mandatory to return this form Si noti che la compilazione del presente modulo non è obbligatoria Non desidero effettuare alcuna donazione all’UNICEF D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 7/08 | Page Pagina Individual Bank Account Application Richiesta di apertura conto individuale UNICEF is the United Nations Children’s Fund created with the purpose in mind to work with others to overcome the obstacles that poverty, violence, disease and discrimination place in a child’s path. It works in 190 countries through country programmes and National Committees. It advocates for measures to give children the best start in life, because proper care at the youngest age forms the strongest foundation for a person’s future. It promotes girls’ education – ensuring that they complete primary education as a minimum – because it benefits all children, both girls and boys. Girls who are educated grow up to become better thinkers, better citizens, and better parents to their own children. It acts so that all children are immunized against common childhood diseases, and are well nourished, because it is wrong for a child to suffer or die from a preventable illness. It works to prevent the spread of HIV / AIDS among young people because it is right to keep them from harm and enable them to protect others. It helps children and families affected by HIV / AIDS to live their lives with dignity. It involves everyone in creating protective environments for children. It is present to relieve suffering during emergencies, and wherever children are threatened, because no child should be exposed to violence, abuse or exploitation. UNICEF upholds the Convention on the Rights of the Child. It works to assure equality for those who are discriminated against, girls and women in particular. It works for the Millennium Development Goals and is part of the Global Movement for Children – a broad coalition dedicated to improving the life of every child. Through this movement, and events such as the United Nations Special Session on Children, it encourages young people to speak out and participate in the decisions that affect their lives. Please refer to www.unicef.org should you be interested in further understanding. L’UNICEF è il Fondo per l’infanzia delle Nazioni Unite creato allo scopo di collaborare con altri alla rimozione degli ostacoli che la povertà, la violenza, le malattie e la discriminazione pongono sul cammino di un bambino. L’UNICEF lavora in 190 paesi attraverso programmi e comitati nazionali,sostenendo la necessità di misure per assicurare ai bambini un ottimo inizio nella vita, poiché una cura adeguata nella più tenera età crea le fondamenta più robuste per il futuro di una persona. L’UNICEF promuove l’istruzione delle bambine, facendo in modo che riescano a completare come minimo l’istruzione primaria, poiché questo va a beneficio di tutti, maschietti e femminucce. Le bambine che acquisiscono un’istruzione diventano donne più consapevoli, cittadine più attive e madri migliori per i loro figli. L’UNICEF lavora per far sì che tutti i bambini vengano vaccinati contro le più comuni malattie dell’infanzia e che siano ben nutriti, perché non è giusto che un bambino soffra o muoia a causa di una malattia prevenibile. L’UNICEF è anche impegnato a combattere la diffusione dell’HIV/AIDS tra i giovani, poiché è bene proteggerli da questo male e consentire loro di proteggere gli altri; inoltre, aiuta i bambini e le famiglie colpiti da HIV/AIDS a condurre una vita dignitosa. L’UNICEF coinvolge tutti nella creazione di un ambiente protettivo per i bambini. È presente per alleviare le sofferenze durante le emergenze e ovunque l’infanzia sia minacciata, perché nessun bambino deve essere esposto alla violenza, agli abusi o allo sfruttamento. 5. UNICEF Donation / Donazione all’UNICEF Who is unicef / Cos’è l’UNICEF? L’UNICEF sostiene la Convenzione internazionale sui diritti dell’infanzia, e si batte per assicurare l’uguaglianza per coloro che sono vittime di discriminazione, in particolare le donne e le bambine. Lavora per realizzare gli Obiettivi di sviluppo del millennio e fa parte del Movimento globale per l’infanzia, una vasta coalizione dedita a migliorare la vita di ogni bambino. Tramite questo movimento ed eventi come la Sessione speciale delle Nazioni unite sull’infanzia, l’UNICEF incoraggia i giovani a far sentire la propria voce ed a partecipare alle decisione che influenzano le loro vite. Si rimanda al sito dell’UNICEF (www.unicef.org) per ulteriori approfondimenti. Translation of documents is provided for the added convenience of the Client. In the event of conflict between the original English text and any translation or any other agreement between the Bank and the Client, the English version shall take precedence. La traduzione dei documenti è per comodità di lettura. In caso di conflitto tra la versione originale inglese in corso e qualsiasi altra versione tradotta, la versione inglese sarà quella valida e prevarrà sulle altre. Place / Luogo Donor’s Signature / Firma del donatore Date / Data D-CLIENT-01-01-EN_IT_v1.1 8/08 | Page Pagina General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito This document contains important information regarding the terms and conditions applicable to an account holder (i.e. contractual partner) hereinafter referred to as the “Client” of M I G Bank (the “Bank”). The access to and the use of an account and the Bank’s services are subject to the Client’s compliance with all terms and conditions set forth hereinafter. Il presente documento contiene informazioni importanti relative ai termini e alle condizioni applicabili al titolare di un conto (ovvero controparte contrattuale), di seguito indicato come il “Cliente” di M I G Bank (la “Banca”). L’accesso ad un conto e ai servizi della banca, nonché il loro uso, sono soggetti al rispetto, da parte del Cliente, di tutti i termini e le condizioni definiti in seguito. The Client understands and acknowledges that the Bank may modify, alter or change the terms and conditions set forth herein by posting such modifications or changes online or by other communication deemed appropriate by the Bank. Il Cliente intende e riconosce che la Banca può apportare modifiche, variazioni o emendamenti ai termini e alle condizioni contenuti nel presente documento, mediante la loro pubblicazione online o altra modalità di comunicazione ritenuta adeguata dalla Banca. Neither the information nor any opinion expressed in the Bank web site and/or the Bank contractual or other documentation constitutes a solicitation, an offer or a recommendation of the Bank to buy or sell any currencies or to engage in financial investments or transactions, or in any other transaction. Le informazioni e le opinioni espresse nel sito web e/o nella documentazione contrattuale o di altro tipo della Banca non costituiscono un sollecito, un’offerta o una raccomandazione della Banca ad acquistare o a vendere valute o ad effettuare investimenti o transazioni finanziarie di qualsiasi altro tipo. The present General Business Conditions (the “Conditions”) and Safe Custody Regulations (the “Regulations”, hereinafter collectively referred to as the “Conditions and Regulations”) govern the relationship between the Client and the Bank (together with the Client hereinafter collectively referred to as the “Parties”). Le presenti Condizioni commerciali (le “Condizioni”) e il Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito (il “Regolamento”, in seguito collettivamente definiti “le Condizioni e il Regolamento”) disciplinano il rapporto tra il Cliente e la Banca (in seguito definiti congiuntamente le “Parti”). I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 1. Services 1. SERVIZI Bank’s services include Banking transactions (see 2.1) and technical installation to enable the Client to conduct Banking transactions via the Internet (see 2.2) through the Bank’s website (http://migBank. com) or through (www.migbank.com). I servizi della Banca comprendono le transazioni bancarie (si veda il punto 2.1) e l’installazione tecnica che consente al Cliente di effettuare transazioni bancarie via Internet (si veda il punto 2.2) tramite il sito web della Banca (http://migbank.com oppure www.migbank.com). The Client acknowledges that the only liable source of information about the Bank and its services is the official website of the Bank and the official marketing material released by the Bank. The Client takes good notice that the Bank does not endorse any information about the Bank nor its services that may be contained on any other website or any other marketing material. Il Cliente riconosce che l’unica fonte attendibile di informazioni riguardo alla Banca e ai suoi servizi è costituita dal sito web officiale della Banca e dal materiale promozionale ufficiale pubblicato dalla Banca. Il Cliente prende formalmente atto che la Banca non approva alcuna informazione relativa alla Banca né ai suoi servizi che possa essere contenuta in altri siti web o in altro materiale promozionale. 2.1 Banking transactions 2.1 TRANSAZIONI BANCARIE 2.1.1 Transactions 2.1.1 TRANSAZIONI Transactions shall include, but are not limited to : Le transazioni includeranno, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo: a) Spot and forward foreign currency contracts; b) Foreign currency rollover transactions; c) All related currency transactions; d) Precious metals trading; e) Current account; f) CFD’s on indices and CFD’s on commodities; g) Fiduciary deposits. h) Fiduciary transactions; i) Equity trading j) Futures; k) Funds; l) Options; In addition, some investments shall be governed by special agreement between the Client and the Bank. Transactions may involve margins where the Client is required to deposit cash or other assets to secure performance of the Client’s obligations under the transaction. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 a) i contratti a pronti e a termine su valute; b) le opzioni OTC su valute; c) le transazioni differite in valuta; d) tutte le transazioni in valuta correlate; e) le transazioni su metalli preziosi; f) i contratti per differenza; g) le operazioni su conto corrente; General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito INTRODUCTION / INTRODUZIONE h) le transazioni fiduciarie; i) la compravendita di azioni; j) i contratti future; k) i fondi; l) le opzioni. Inoltre, alcuni investimenti saranno disciplinati da accordi particolari stipulati tra il Cliente e la Banca. Le transazioni potranno richiedere il versamento di margini, nel qual caso il Cliente dovrà depositare fondi liquidi o altre attività a garanzia dell’adempimento degli obblighi derivanti dalle transazioni. 1/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito 2.1.2 Risk awarness 2.1.2 CONSAPEVOLEZZA DEL RISCHIO The Client is aware and accepts the risks resulting from foreign exchange transactions and all related transactions. Risk of loss in trading foreign exchange can be substantial. Before entering into transactions, the Client acknowledges that he/she has fully understood : Il Cliente conosce ed accetta i rischi insiti nelle transazioni in valuta estera e in tutte le operazioni correlate. Nelle operazioni in valuta il rischio di perdita può essere cospicuo. Prima di concludere una transazione, il Cliente dichiara di avere pienamente compreso: + The nature and fundamentals of the transactions and the market underlying such transactions; + la natura e i concetti fondamentali delle transazioni e del mercato sottostante le medesime; + The extent of the economic risk to which the Client is exposed as a result of such transactions (and determine that such risk is suitable for the Client in light of its specific experience in relation to the transaction and its financial objectives, circumstances and resources); + la portata del rischio economico a cui il Cliente è esposto in conseguenza di tali transazioni (avendo stabilito altresì l’adeguatezza di tale rischio per sé stesso alla luce della propria specifica esperienza relativamente alla transazione, nonché dei propri obiettivi finanziari, delle proprie circostanze e delle proprie risorse personali); + The legal terms and conditions for such transactions. + I termini e le condizioni legali di tali transazioni. The Client should also be aware of the following : Il Cliente deve essere altresì consapevole di quanto in seguito specificato: + The Client understands the terms and conditions of the transactions to be undertaken, including, without limitation : + Il Cliente comprende i termini e le condizioni delle transazioni da effettuare, inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo: - The terms as to price, term, expiration date, restrictions on exercing an OTC option and of the terms material to the transactions; - The circumstances under which the Client may become obliged to make or take delivery of a leveraged foreign exchange transactions or options transaction. - le condizioni relative a prezzo, durata, data di scadenza e limitazioni all’esercizio di un’opzione OTC, nonché i termini sostanziali per le transazioni; - tutti i termini che descrivono i fattori di rischio, quali volatilità, liquidità e così via; - le circostanze nelle quali il Cliente può essere obbligato ad effettuare o ad accettare la consegna del sottostante nel caso di transazioni in valuta con effetto leva o transazioni su opzioni. + The high degree of leverage that is often obtainable in foreign exchange and precious metals trading can work against the Client as well as for the Client, due to fluctuating market conditions. Trading in such instruments can lead to large losses as well as gains in response to a small market movement. + L’elevato effetto leva spesso ottenibile nella compravendita di valuta estera e di metalli preziosi può agire sia a vantaggio che a svantaggio del Cliente, in seguito al variare delle condizioni di mercato. La negoziazione di tali strumenti può comportare sia realizzi che perdite di cospicua entità in conseguenza di un modesto movimento del mercato. If the market moves against the Client, he/she may not only sustain a total loss of its initial margin deposit, and any additional funds deposited with the Bank to maintain its position, but the Client may also incur further liability to the Bank. The Client may be called upon to “top-up” its margin by substantial amounts at short notice to maintain its position, failing which the Bank may have to liquidate its position at a loss and the Client would be liable for any resulting loss. Qualora l’andamento del mercato sia sfavorevole al Cliente, questi potrebbe non soltanto subire la perdita del deposito dei margini inizialmente versato e di tutti i fondi addizionali depositati presso la Banca per mantenere la propria posizione, ma maturare altresì ulteriori passività verso la Banca. Il Cliente potrebbe essere sollecitato a “integrare” il proprio margine mediante il versamento di importi ingenti con un breve preavviso, al fine di mantenere la sua posizione; in mancanza di tale copertura, la Banca potrebbe essere costretta a liquidare la posizione realizzando una perdita, che graverebbe esclusivamente sul Cliente. - Any terms describing risk factors, such as volatility, liquidity, and so on; and Under certain market conditions the Client may find it difficult or impossible to liquidate a position, to assess a fair price or assess risk exposure. This can happen, for example, where the market for a transaction is illiquid or where there is a failure in electronic or telecommunications systems, or where there is the occurrence of an event commonly known as “Force Majeure Event”. Placing contingent orders, such as “stop-loss” orders, will not necessarily limit losses to the intended amounts, as it may be impossible to execute such orders under certain market conditions. When placing a stop order or stop loss order, the Client must be aware that in certain market conditions the Client may be filled at a different price than initially requested. Because the prices and characteristics of over-the-counter transactions are individually negotiated and there is no central source for obtaining prices, there are inefficiencies in transaction pricing. The Bank consequently cannot and do not warrant that prices or the prices the Bank secures for the Client are or will at any time be the best prices available to the Client. + Transactions in options involve a high degree of risk and are not suitable for many members of the public. Such transactions should be entered into only by persons who have read, understood and familiarized themselves with the type of options, style of exercise, the nature and extent of rights and obligations and the associated risks. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 In determinate condizioni di mercato il Cliente potrebbe ostacolato o impossibilitato a liquidare una posizione, a stabilire un prezzo equo o a valutare l’esposizione al rischio. Ciò può accadere, ad esempio, in caso di illiquidità del mercato per un certo tipo di transazione, o di guasto ai sistemi elettronici o di telecomunicazione, o al verificarsi di un evento comunemente noto come “Causa di Forza Maggiore”. L’impartizione di ordini limitativi, ad esempio di tipo “stop-loss”, non garantisce la limitazione delle perdite all’importo previsto, poiché in determinate condizioni di mercato l’esecuzione di tali ordini potrebbe risultare impossibile. Nell’impartire un ordine con limite di prezzo o un ordine “stop-loss”, il Cliente deve essere consapevole che in talune condizioni di mercato l’ordine potrebbe essere eseguito ad un prezzo diverso da quello inizialmente richiesto. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Poiché i prezzi e le caratteristiche delle operazioni fuori borsa vengono negoziati singolarmente e non esiste un organismo centrale di rilevamento dei prezzi, possono sussistere inefficienze nella fissazione dei prezzi delle transazioni. Di conseguenza, la Banca non può garantire e non garantisce che i prezzi genericamente intesi o quelli assicurati dalla Banca al Cliente siano o saranno sempre i migliori disponibili. + Le transazioni su opzioni comportano un elevato grado di rischio e pertanto non sono adatte a molti investitori privati. Tali operazioni devono essere concluse solo da soggetti che abbiano letto, compreso e acquisito dimestichezza con il tipo di opzioni, le modalità di esercizio, la natura e la portata dei diritti e degli obblighi, nonché i rischi associati. 2/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito The Client acknowledges that many transactions will be affected subject to, and in accordance with, Market Rules. In particular, the Client acknowledges that Market Rules usually contain wide powers in an emergency or otherwise undesirable situation, and the Client agrees that if any market or other organization takes any action which affects a transaction then the Bank may take any action which it, in its discretion, considers desirable in the interests of the Client and/or the Bank. The Bank shall not be liable for any loss suffered by the Client as a result of the acts or omissions of any market or organization or any action reasonably taken by the Bank as a result of such acts or omissions. The Bank may, in its reasonable opinion, determine that an emergency or an exceptional market condition exists (“Force Majeure”) and in due course, will take reasonable steps to inform the Client. Il Cliente riconosce che numerose operazioni sono condizionate e soggette alle Regole del Mercato. In particolare, il Cliente riconosce che di norma le Regole del Mercato prevedono ampi poteri in casi di emergenza o in altre situazioni avverse e, qualora un mercato o un’altra organizzazione eserciti un’azione tale da influire su un’operazione, accetta che la Banca possa prendere qualsiasi misura che a propria discrezione consideri opportuna nell’interesse del Cliente e/o della Banca. La Banca non sarà responsabile di alcuna perdita subita dal Cliente in seguito ad azioni o omissioni di qualsiasi mercato o organizzazione o di qualsiasi azione ragionevolmente intrapresa dalla Banca in seguito a tali azioni o omissioni. La Banca può, a suo ragionevole giudizio, stabilire che sussiste una condizione di emergenza o di mercato eccezionale (“Forza Maggiore”) e prendere a tempo debito misure ragionevoli per informarne il Cliente. A Force Majeure Event shall include, but is not limited to, the following : Un Evento di Forza Maggiore includerà, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, i casi di seguito elencati: a) any act, event or occurrence (including, without limitation, any interruption of power supply or electronic or communication equipment failure, strike, riot or civil commotion) which, in the Bank opinion, prevents it from maintaining an orderly market in one or more of the currencies in respect of which the Bank ordinarily allows the Client to enter into transactions; b) the suspension or closure of any market or the abandonment or failure of any event upon which the Bank bases, or to which it in any way relates, its quote, or the imposition of limits or special or unusual terms on the trading in any such market or on any such event; or c) the occurrence of an excessive movement in the level of any rate and/or corresponding market. a) qualsiasi atto, evento o circostanza (inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, i guasti e le interruzioni dell’alimentazione di apparecchiature elettroniche o di comunicazione, gli scioperi, le agitazioni o le insurrezioni popolari) che, a giudizio della Banca, le impediscano di mantenere un mercato disciplinato in una o più delle valute in cui la Banca consente normalmente al Cliente di effettuare transazioni; b) la sospensione o la chiusura di qualsiasi mercato, o l’abbandono o il mancato verificarsi di qualsiasi evento su cui la Banca basi, o a cui siano in qualche modo correlate, le sue quotazioni, oppure l’imposizione di limiti o di termini speciali o inusuali sul trading in qualsivoglia di questi mercati o per qualsivoglia di tali eventi; oppure c) il verificarsi di una variazione eccessiva del livello di qualsiasi tasso di cambio e/o del mercato corrispondente. 2.1.3 Streamline dealing 2.1.3 NEGOZIAZIONE A FLUSSO CONTINUO The Bank offers streamline dealing and fixed spreads for all Foreign Exchange transactions. Streamline dealing does not guarantee that requotes will not be given and the client accepts to receive a re-quote on the requested price prior to a trade being confirmed. Re-quotes are given if the requested price is not favorable to the Bank and in case of re-quote, the Client is free to accept the new quote and the Bank shall remain harmless of any damages or costs arising thereof. The Bank shall remain harmless of any damages or costs arising thereof. In certain market conditions and upon Bank’s sole discretion, the Bank may change the quoted prices and/or spreads in the online trading platform and the Bank shall remain harmless of any damages or costs arising thereof. La Banca consente di eseguire negoziazioni a flusso continuo e di avvalersi di spread fissi per tutte le operazioni in valuta estera. La negoziazione a flusso continuo non è esente da riquotazioni; pertanto il Cliente accetta di ricevere una riquotazione del prezzo richiesto prima della conferma di una transazione. Le riquotazioni vengono fornite se il prezzo richiesto non è favorevole alla Banca; in tal caso, il Cliente è libero di accettare la nuova quotazione e la Banca sarà comunque sollevata da qualsiasi danno o costo da questo derivante. In talune condizioni di mercato e a propria insindacabile discrezione, la Banca potrà modificare i prezzi quotati e/o gli spread nella piattaforma di trading online, rimanendo sollevata da qualsiasi danno o costo da questo derivante. The Client is informed that the Bank does not accept clients using scalping methods. In particular, the Bank reserves the right to close all open positions of such clients and to close their account(s). The Bank also offers a mechanical trade system (MTS, also called “Expert Advisor”) linked up to a plot. This system does not only inform about a possible entry and exit points but can also generate orders automatically on behalf of the Bank’s Client and direct them to the trade server. This system is enabled by default. The use of this system is at the Client’s risk. The Bank does thus not guarantee the result of the use of this system and the Bank shall remain harmless of any damages or costs arising thereof. The Bank may at its sole discretion de-activate this feature if the Client is deemed to be using this feature for abusive purposes. Trailing Stop features are enabled by default. The Client acknowledges being fully aware of how this feature works. The use of this feature is at the Client’s risk. The Bank does thus not guarantee the result of the use of this feature and the Bank shall remain harmless of any damage or costs arising thereof. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Il Cliente prende atto che la Banca non accetta che i clienti ricorrano a metodi di “scalping”. In particolare, la Banca si riserva il diritto di chiudere tutte le posizioni aperte di tali clienti e il/i relativo/i conto/i. La Banca rende inoltre disponibile un sistema di trading meccanico (altresì denominato “Expert Advisor”), collegato ad un diagramma, che non solo segnala i possibili punti di ingresso e uscita, ma può anche generare automaticamente gli ordini per conto del Cliente, inviandoli al server di trading. Questo sistema è attivo per impostazione predefinita e il Cliente lo utilizza a proprio rischio. La Banca non garantisce i risultati ottenuti mediante questo sistema e sarà sollevata da qualsiasi danno o costo da questo derivante. La Banca può a sua esclusiva discrezione disattivare questa funzionalità qualora ritenga che il Cliente la utilizzi per scopi illeciti. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Le funzioni di Trailing Stop sono attive per impostazione predefinita. Il Cliente dichiara di avere piena conoscenza del funzionamento di questa funzione e la utilizza a proprio rischio. La Banca non garantisce i risultati ottenuti mediante questa funzione e sarà sollevata da qualsiasi danno o costo da questo derivante. 3/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito The Client may request to have his account not be charged or given any swap fees for open positions. Such request is made separately from the Client and the Client thereby agrees to pay any additional fees or costs as the Bank specifies from time to time for handling such account. If the Bank finds that a client is using such account for abusive purposes, the Bank may, at its sole discretion, decide to close all open positions for such an account and deduct or add any swap fees for all the transactions currently and/or previously made with the Client and decline from accepting any further request from the Client to be exempted from swap fees. Il Cliente può chiedere che il suo conto non sia soggetto ad addebiti o a commissioni di swap per le posizioni aperte. Tale richiesta viene effettuata separatamente dal Cliente, il quale di conseguenza accetta di pagare tutte le commissioni o i costi aggiuntivi che la Banca indicherà di volta in volta per la gestione di tale conto. Qualora la Banca ritenga che un cliente utilizzi tale conto per scopi illeciti, essa potrà, a propria insindacabile discrezione, decidere di chiudere tutte le posizioni aperte relative al conto in questione e dedurre o applicare tutte le commissioni di swap per tutte le transazioni attualmente e/o precedentemente effettuate con il Cliente e rifiutarsi di accettare qualsiasi ulteriore richiesta, da parte del Cliente, di essere esentato dalle commissioni di swap. 2.1.4 Instructions / Communications The Client may give the Bank oral or written instructions. The Client is authorized to grant, a power of attorney without right of substitution to a third person in order to represent him/her in any business with the Bank. To that effect, the Client undertakes to use the Bank’s standard form that may be downloaded on its website http://migbank.com and must be sent duly completed and signed to the Bank. The Bank shall be entitled to act upon the oral or written instructions of any person so authorized, notwithstanding that the person is not, in fact, so authorized. For these purposes, written instructions may be given by letter, facsimile, or via the Internet or other electronic means of communication and oral instructions in person or by telephone. The Bank shall not be obliged to confirm such instructions. Any instruction in writing shall set out the names and specimen signatures of the Client or person so authorized. The Client accepts that the Bank is entitled, though not obliged, to ask for personal data in order to establish its identity with greater certainty. The Bank shall not incur any liability as a result of refusing to execute any order(s) issued by a person whose identity it considers not to have been sufficiently established. Once an instruction has been given by, or on behalf of the Client, it cannot be rescinded, withdrawn or amended without the Bank express consent. The Bank may at its absolute discretion refuse any dealing instruction given by, or on behalf of, the Client without giving any reason or being liable for any loss occasioned thereby. The Client shall promptly (and within the limits imposed by the Bank) give any instructions the Bank may request from the Client in respect of any transaction or proposed transaction. If the Client does not provide such instructions promptly, the Bank may, in its absolute discretion, take such steps at the Client’s cost as the Bank considers appropriate for its own protection or for the protection of the Client. If the Client does not provide the Bank with notice of its intention to exercise an OTC option at the time stipulated by the Bank, the Bank may treat the option as abandoned by the Client and, if so, will notify the Client. If the Bank does not receive instructions from the Client to settle any open transactions by the close of the business day two days prior to value date of the said transactions, is hereby authorized (but not obliged) to rollover all said transactions to the next value date traded. During market holidays and weekends pre-announced by the Bank, the Bank does not execute orders for clients. The Client agrees to indemnify and hold the Bank harmless for and against any damages or losses it may incur as a result of instructions transmitted by any of the above means. Communications may be made to the Client at such address, telephone, facsimile or email address notified from time to time to the Bank for this purpose. Any communication by telephone, facsimile or email shall be deemed to have been made or (as the case may be) delivered when dispatched. Any communication by letter shall be deemed to have been made forty-eight hours after being sent to it at that address by prepaid first-class post in the case of an address in Switzerland, or, in the case of an address outside Switzerland, six business days after being sent D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 2.1.4 DISPOSIZIONI / COMUNICAZIONI l Cliente può impartire alla Banca disposizioni verbali o scritte. Il Cliente è autorizzato a conferire una procura senza facoltà di sostituzione ad una terza persona che lo rappresenti in tutti i rapporti con la Banca. A tale effetto, il Cliente si impegna ad usare il modulo della Banca, scaricabile dal sito web http://migbank.com, che deve essere inviato alla Banca debitamente compilato e firmato. La Banca avrà diritto ad agire sulla base delle disposizioni verbali o scritte di qualsiasi persona in siffatto modo autorizzata, nonostante essa non sia di fatto autorizzata. A tal fine, le disposizioni scritte potranno essere inviate per lettera, fax o Internet o altri mezzi elettronici di comunicazione, oppure impartite verbalmente di persona o per telefono. La Banca non sarà obbligata a confermare tali istruzioni. Qualsiasi disposizione inviata per iscritto dovrà riportare i nomi e le firme, come da specimen, del Cliente o della persona debitamente autorizzata. Il Cliente accetta che la Banca si avvalga della facoltà di chiedergli alcuni dati personali al fine di stabilire la sua l’identità con maggiore certezza, benché non sia tenuta a farlo. La Banca non si assumerà alcuna responsabilità per aver rifiutato di eseguire qualsiasi ordine impartito da una persona la cui l’identità non è stata stabilita con sufficiente chiarezza. Una disposizione impartita da o per conto del Cliente non potrà essere annullata, revocata né modificata senza l’esplicito consenso della Banca. A sua insindacabile discrezione, la Banca potrà rifiutare qualsiasi ordine di negoziazione impartito da o per conto del Cliente senza fornire ragione alcuna o essere responsabile di eventuali perdite da questo derivanti. Il Cliente darà prontamente (ed entro i limiti imposti dalla Banca) tutte le disposizioni che la Banca potrà richiedere al Cliente in merito a qualsiasi transazione effettuata o proposta. Qualora il Cliente non darà prontamente dette disposizioni, la Banca potrà, a sua insindacabile discrezione, prendere le misure che consideri necessarie ed adeguate per la protezione propria o del Cliente, a spese del Cliente stesso. Qualora il Cliente non comunichi alla Banca la propria intenzione di esercitare un’opzione OTC al momento stabilito dalla Banca, questa potrà considerare l’opzione come abbandonata dal Cliente e, in tal caso, ne darà comunicazione al Cliente. Qualora la Banca non riceva dal Cliente l’ordine di regolare eventuali transazioni aperte entro la fine del giorno lavorativo precedente di due giorni la data di valuta delle transazioni in oggetto, essa è autorizzata (ma non obbligata) ai sensi del presente Contratto a differire tutte le dette transazioni alla data di valuta successiva. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Nei giorni di chiusura del mercato e nei fine settimana prestabiliti dalla Banca non verrà eseguito alcun ordine. Il Cliente accetta di tenere indenne e sollevare la Banca da qualsiasi responsabilità per qualsivoglia danno o perdita che la stessa possa subire in seguito a disposizioni trasmesse tramite uno qualsiasi dei mezzi summenzionati. Le comunicazioni potranno essere recapitate al Cliente all’indirizzo, numero di telefono, numero di fax o indirizzo e-mail comunicati di volta in volta alla Banca a questo scopo. Qualsiasi comunicazione per telefono, fax o email verrà considerata come effettuata o (a seconda dei casi) recapitata al momento dell’invio. Qualsiasi comunicazione per lettera verrà considerata come effettuata quarantotto ore dopo essere stata inviata all’indirizzo del destinatario con posta prioritaria prepagata, nel caso di un indirizzo sviz- 4/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito to it at that address by mail. The Client shall ensure that at all times the Bank will be able to communicate with the Client or his appointed representative by telephone, facsimile or email. At the specific request and at cost of the Client, the Bank will reconstruct the instructions and/or the exchange of communication. Communications may be made to the Bank at the address and telephone number notified to the Client or this purpose and shall be considered to have been duly made only upon their actual receipt by the Bank. The above conditions are also applicable to any attorney(s) appointed by the Client. The Client is aware of the risks associated with these means of communication and release the Bank from any liability resulting from their use. The Client confirms that he/she shall assume all risks of abuse of these means of communication, such as non-discovered falsifications, mistakes, distortions, duplications, misunderstandings or losses that might occur, as a result of instructions given by any of the above communication means. 2.1.5 Margin Deposits, Collateral and Payments The Client shall pay to the Bank : zero, oppure, nel caso di un indirizzo fuori dal territorio elvetico, sei giorni lavorativi dopo essere stata inviata a tale indirizzo per posta. Il Cliente garantirà alla Banca di essere sempre reperibile, in prima persona o mediante un proprio rappresentante nominato, per telefono, fax o e-mail. La Banca ricostruirà le disposizioni e/o lo scambio di comunicazioni tra la Banca e il Cliente su specifica richiesta e a spese di quest’ultimo. Le comunicazioni potranno essere recapitate alla Banca all’indirizzo e al numero di telefono notificati al Cliente a tale scopo, e saranno considerate come debitamente effettuate soltanto alla loro effettiva ricezione da parte della Banca. Le suddette condizioni si applicano altresì al/ai procuratore/i nominato/i dal Cliente. Il Cliente è consapevole dei rischi associati a tali mezzi di comunicazione e solleva la Banca da qualsiasi responsabilità derivante dal loro uso. Il Cliente conferma di assumersi tutti i rischi derivanti dall’abuso di detti mezzi di comunicazione, quali falsificazioni non individuate, errori, distorsioni, duplicati, malintesi o perdite che possano verificarsi in seguito a disposizioni fornite mediante qualsiasi dei summenzionati mezzi di comunicazione. 2.1.5 DEPOSITI DEI MARGINI, GARANZIE COLLATERALI E PAGAMENTI Il Cliente pagherà alla Banca: a) such amounts of money as required by the Bank, and in a currency acceptable to the Bank, as initial or variation margin; b) such amounts of money, as may be required from time to time, due to the Bank under a transaction; and c) such amounts of money as may be required in or towards clearance of any debit balance on any account. a) come margine iniziale o di variazione, le somme in denaro richieste dalla Banca, in una valuta accettata dalla medesima; b) le somme in denaro, eventualmente richieste di volta in volta, dovute alla Banca per una transazione; c) le somme in denaro eventualmente richieste per la liquidazione di qualsiasi saldo passivo di qualsiasi conto. With the prior agreement of the Bank, the Client may provide the Bank with a Bank guarantee, in a form acceptable to the Bank, instead of cash, for the purpose of complying with its obligations under clause above. Previo consenso della Banca, allo scopo di ottemperare ai propri obblighi ai sensi della clausola precedente, il Cliente potrà fornire alla Banca una garanzia bancaria in una forma da essa accettata, anziché fondi liquidi. Without limiting the Client’s obligation to pay margin deposits, the Bank will have no obligation to ensure margin deposit requirements have been satisfied by the Client before effecting a transaction and the Client’s obligations in respect of a transaction will not be diminished by any failure by the Bank to enforce payment of outstanding margin deposits prior to entering into the transaction. Senza che questo limiti l’obbligo del Cliente di versare i depositi dei margini, la Banca non sarà tenuta a garantire che i requisiti di versamento dei margini siano stati soddisfatti dal Cliente prima di effettuare una transazione; gli obblighi del Cliente in relazione ad una transazione non verranno meno per l’eventuale mancata imposizione, da parte della Banca, del pagamento dei depositi a copertura dei margini dovuti prima di effettuare la transazione. The Client shall promptly deliver any money deliverable by it under a transaction in accordance with the terms of that transaction and with any instructions given by the Bank for the purpose of enabling the Bank to perform its obligations under any corresponding transaction entered into between the Bank and a third party. Il Cliente corrisponderà prontamente qualsiasi importo monetario che sarà tenuto a versare per una transazione secondo i termini della transazione stessa e secondo tutte le disposizioni date dalla Banca, allo scopo di consentire alla medesima di adempiere ai suoi obblighi in relazione a qualsivoglia transazione corrispondente effettuata tra la Banca ed una terza parte. The Bank may (but shall not be obliged to) convert any monies held by it for the Client into such other currency as the Bank considers necessary or desirable to cover the Client’s obligations and liabilities in that currency at such rate of exchange as the Bank shall select. La Banca potrà (ma non sarà obbligata a) convertire, ad un tasso di cambio di sua scelta, tutte le somme detenute per conto del Cliente in altra valuta, qualora ciò si renda necessario o opportuno per coprire gli obblighi e le passività del Cliente in tale valuta. If the Client fails to provide any margin deposit or other sum due under this Conditions and Regulations in respect of any transaction, the Bank may close out any open transaction without prior notice to the Client and apply any proceeds thereof to payment of any amounts due to the Bank. Qualora il Cliente ometta di versare i depositi dei margini o altre somme dovute ai sensi delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento in relazione a qualsiasi transazione, la Banca potrà chiudere senza preavviso tutte le transazioni aperte ed utilizzare i proventi così ottenuti per il saldo tutti gli importi dovuti alla Banca. 2.1.6 Transaction Monitoring 2.1.6 MONITORAGGIO DELLE TRANSAZIONI Each transaction entered into by the Bank with the Client can be seen through the Online Service provided by the Bank. Transaction entered after 23:00 PM CET will be treated as having been effected on the next following business day. Il Cliente può monitorare tutte le transazione effettuate presso la Banca attraverso il Servizio Online fornito dalla medesima. Le transazioni eseguite dopo le ore 23.00 CET verranno considerate come effettuate il giorno lavorativo successivo. History of transactions can be printed from the Online Service provided by the Bank any time. La cronologia delle transazioni potrà essere stampata in qualsiasi momento attraverso Servizio Online offerto dalla Banca. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 5/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito The Client must verify the contents of each document received from the Bank and all transactions published on its online service continuously. Such documents and transactions published shall, in the absence of manifest error, be conclusive unless the Client notifies the Bank the contrary immediately after having access to this information. Il Cliente dovrà verificare continuamente il contenuto di ogni documento ricevuto dalla Banca e tutte le transazioni pubblicate sul suo Servizio Online. In assenza di errori manifesti, le transazioni e i documenti pubblicati saranno considerati definitivi, salvo che il Cliente non comunichi alla Banca il contrario immediatamente dopo aver avuto accesso a tali informazioni. 2.1.7 Default 2.1.7 INADEMPIENZA Without prior notice to, or receiving further authority from the Client, the Bank shall have the right to close out all or any part of any transaction, and realize any assets of the Client held by the Bank, upon or at any time after the happening of any of the following events : Senza preavviso e senza ricevere ulteriore autorizzazione dal Cliente, la Banca avrà facoltà di chiudere qualsiasi transazione, in tutto o in parte, nonché di liquidare tutte le attività che il Cliente detiene presso la Banca, al verificarsi di uno degli eventi di seguito indicati o in un momento successivo: a) the Client fails to make any payment due under these Conditions and Regulations on the due date; b)the Client fails to observe or perform in whole or in part any of the provisions of these Conditions and Regulations or commits a material breach of the representations, warrants or undertakings; c) the Client dies, is declared absent or becomes of unsound mind. d)a Bankruptcy petition is presented in respect to the Client or, if a partnership, in respect to one or more of its partners or, if a company, any steps are taken or proceedings initiated or protection sought under, any applicable Bankruptcy reorganization or insolvency law by it in respect of itself or against it including, without limitation, the taking of any steps for the appointment of a receiver, trustee, administrator or similar officer to be appointed over its undertakings or assets or any part of them; e) a petition is presented for the winding up of the Client; f) an order is made or a resolution is passed for the winding up of the Client (other than for the purposes of a bona fide reconstruction or amalgamation); g) the Client convenes a meeting for the purpose of making or proposing or entering into any arrangement or composition for the benefit of its creditors (other than for the purposes of a bona fide reconstruction or amalgamation); h) a distress, execution, or other process is levied against any property of the Client and is not removed, discharged or paid within seven days; i) any security created by a mortgage or charge created by the Client becomes enforceable and the mortgagee or the charge take steps to enforce the security; j) any indebtedness of the Client or any of its subsidiaries becomes immediately due and payable, or capable of being declared so due and payable, prior to its stated maturity by reason of default of the Client (or any of its subsidiaries) or the Client (or any of its subsidiaries) fails to discharge any indebtedness on its due date; k) the Bank or the Client is requested to close out a transaction (or any part of a transaction) by any regulatory agency or authority; l) the Bank reasonably considers it necessary for its own protection. Without prejudice to any other rights the Bank may have, it shall be entitled to combine or consolidate all or any of the accounts maintained by the Client with the Bank to set off any amount at any time owing from the Client against any amount owing by the Bank to the Client. Any security, guarantee or indemnity given to the Bank by the Client for any purpose shall extend to any amount owing from the Client after exercise of such right set-off. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 a) il Cliente non effettua alla scadenza un pagamento dovuto ai sensi delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento; b) il Cliente non osserva o non adempie, in tutto o in parte, alle disposizioni delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento, o commette una violazione rilevante delle dichiarazioni, delle garanzie o degli impegni; c) il Cliente muore, risulta scomparso o diventa incapace di intendere e di volere; d) viene presentata un’istanza di fallimento per il Cliente o, in caso di una società di persone, per uno o più dei suoi soci o, in caso di una società di capitali, vengono prese misure o viene avviata un’azione giudiziaria o cercata adeguata protezione ai sensi delle leggi vigenti in materia di insolvenza o di riorganizzazione in seguito a fallimento, inclusa, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, l’assunzione di tutte le misure necessarie per la nomina di un curatore fallimentare, un amministratore fiduciario, o un funzionario simile per la tutela dei propri impegni o delle proprie attività o di qualsiasi loro parte; e) viene presentata un’istanza di messa in liquidazione del Cliente; f) viene impartito un ordine o approvata una risoluzione per la messa in liquidazione del Cliente (per finalità diverse da una ricostituzione o una fusione in buona fede); g) il Cliente convoca una riunione allo scopo di effettuare o proporre o stipulare qualsiasi accordo o composizione a beneficio dei suoi creditori (per finalità diverse da una ricostituzione o una fusione in buona fede); h) viene attuato un pignoramento, un processo esecutivo o un procedimento di altra natura contro qualsiasi proprietà del Cliente, che non viene annullato, adempiuto o pagato entro sette giorni; i) una garanzia creata mediante ipoteca o un gravame creato dal Cliente diventano esecutivi e il creditore ipotecario o il beneficiario del vincolo prendono misure adeguate a rendere esecutiva tale garanzia; j) un debito contratto dal Cliente o da una qualsiasi delle sue controllate diventa immediatamente dovuto ed esigibile, o passibile di essere dichiarato dovuto ed esigibile, prima della sua scadenza fissata, per motivi legati all’insolvenza del Cliente (o di qualsiasi sua controllata) o all’impossibilità del Cliente (o di qualsiasi sua controllata) di saldare i debiti alla loro scadenza; k) un organismo di vigilanza o altra autorità richiede alla Banca o al Cliente di liquidare una transazione (o qualsiasi parte di una transazione); l) la Banca lo consideri ragionevolmente necessario per la propria protezione. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Fatti salvi tutti gli altri diritti, la Banca avrà altresì facoltà di combinare o consolidare la totalità o una parte dei conti mantenuti dal Cliente presso la Banca al fine di compensare gli importi dovuti in qualsiasi momento dal Cliente alla Banca con gli importi dovuti dalla Banca al Cliente. Le garanzie o le indennità fornite dal Cliente alla Banca per qualsiasi scopo verranno estese agli importi dovuti dal Cliente dopo l’esercizio di tale giusta compensazione. 6/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito 2.1.8 Client Representations and Warranties 2.1.8 DICHIARAZIONI E GARANZIE FORNITE DAL CLIENTE The Client represents, warrants and undertakes at the time this agreement is made and the making of each transactions hereunder that : Il Cliente dichiara, garantisce e certifica, all’atto della sottoscrizione del presente Contratto e dell’esecuzione di ogni transazione ai sensi del medesimo: a) it is not under any legal disability with respect to, and is not subject to any law or regulation which prevents its performance of, this agreement or any transaction contemplated by this Agreement; b) it has obtained all necessary consents and has the authority to enter into this agreement (and if the Client is a company, it is properly empowered and has obtained necessary corporate or other authority pursuant to its constitutional and organizational documents); c) all sums made by way of deposit or security shall, subject to this agreement, at all times be free from any charge, lien, pledge or encumbrance; d) it is in compliance with all laws to which it is subject including, without limitation, all tax laws and regulations, exchange control requirements and registration requirements; and e) the information provided by the Client to the Bank is complete, accurate and not misleading in any material respect. 2.1.9 Tape Recording of Conversation The Client acknowledges and expressly accepts that the Bank shall record all telephone conversations between the parties as per regulatory applicable requirements. Such recordings shall remain the property of the Bank and the Client agrees to the use thereof or transcript there from as evidence by the Bank in any dispute or anticipated dispute between the parties. Any such recordings or transcripts made by the Bank may be destroyed by it in accordance with its usual practice. a) di non essere colpito da alcuna invalidità giuridica per quanto attiene il presente Contratto o qualsiasi transazione prevista dal medesimo, e di non essere soggetto ad alcuna legge o norma che gliene impedisca l’esecuzione; b) di aver ottenuto tutti i permessi necessari e di avere l’autorità di stipulare il presente Contratto (e, qualora il Cliente sia una società, di essere adeguatamente autorizzato e di aver ottenuto i necessari poteri societari o di altro tipo ai sensi dei documenti costitutivi e organizzativi rilevanti); c) che tutti gli importi versati a titolo di deposito o di garanzia saranno, ai sensi del presente Contratto, sempre esenti da qualsiasi vincolo, pegno o onere; d) di osservare tutte le leggi a cui è soggetto inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, la normativa fiscale nella sua interezza, le disposizioni in materia di controllo valutario e gli obblighi di registrazione; e e) che le informazioni fornite dal Cliente alla Banca sono complete, precise e non fuorvianti in nessun aspetto rilevante. 2.1.9 REGISTRAZIONE DELLE CONVERSAZIONI Il Cliente riconosce e accetta esplicitamente che la Banca registri tutte le conversazioni telefoniche tra le Parti ai sensi della normativa in vigore. Tali registrazioni rimarranno di proprietà della Banca e il Cliente ne accetta l’uso o la trascrizione da parte della Banca, che potrà addurle come prove in qualsiasi controversia esistente o prevedibile tra le Parti. Tutte dette registrazioni o trascrizioni effettuate dalla Banca potranno essere distrutte dalla medesima conformemente alla sua prassi abituale. 2.1.10 Banking Secrecy Information Disclosure 2.1.10 DIVULGAZIONE DI INFORMAZIONI AFFERENTI IL SEGRETO BANCARIO In its capacity as a Bank pursuant to the Federal Law on Banks and Savings Banks, the Bank is subject to Banking secrecy. The Bank is therefore obliged to observe the strictest discretion regarding all business relations with the Client, even after the Client’s relationship with the Bank is ceased. Swiss Banking secrecy does, however, only apply to data located in Switzerland. Nella sua veste di banca ai sensi della Legge federale sulle banche e sulle casse di risparmio, la Banca è tenuta a rispettare il segreto bancario. La Banca è pertanto obbligata ad osservare la più rigorosa discrezione su tutti i rapporti commerciali intrattenuti con il Cliente, anche dopo la cessazione del rapporto tra il Cliente e la Banca. Tuttavia, il segreto bancario svizzero si applica esclusivamente ai dati conservati in Svizzera. However, by entering into this agreement the Client authorizes the Bank to disclose such information relating to the Client as may be required by any law, rule or regulatory authority, including any applicable Market Rules, without prior notice to the Client. 2.1.11 Swiss Act on the Prevention of Money Laundering (“MLA”) As the Client is aware that the Bank has to comply with the Swiss Federal Money Laundering Act the Client agrees to provide the Bank, as per separate document, with full and accurate information regarding, among others, the identification of the contracting partner, the identification of the beneficial owner and the origin of the assets. The Bank is also entitled to ask the Client to supply information regarding the circumstances or background of a certain transaction. In such event, the Client must immediately disclose such information as requested. As long as the Client fails to supply the information requested by the Bank, the Bank is entitled not to carry out the instructions received from the Client, and in particular not to execute instructions requiring the transfer of assets. In case the Bank deems the information supplied unsatisfactory or incomplete, it may at its discretion immediately terminate the business relationship with the Client and ordain that assets may no longer be withdrawn. Furthermore, the Bank may, pursuant to the provisions of the MLA and the Swiss regulation on Banks, submit a report to the competent prosecuting authorities and take precautionary measures to freeze the Client relationship until the authorities have decided the case at hand. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Con la stipula del presente Contratto, il Cliente autorizza la Banca a divulgare senza preavviso eventuali informazioni che lo riguardano come richiesto da qualsivoglia normativa, regolamento o autorità di vigilanza, incluse tutte le vigenti Regole del Mercato. 2.1.11 LEGGE SVIZZERA SUL IL RICICLAGGIO DI DENARO (“LRD”) Dichiarandosi consapevole dell’obbligo della Banca di adempiere agli obblighi previsti dalla Legge federale svizzera sul riciclaggio di denaro, il Cliente accetta di fornire alla Banca, in un documento distinto, informazioni complete e precise relative, tra gli altri, all’identificazione della controparte, l’identificazione del titolare effettivo e l’origine delle sue attività patrimoniali. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Dichiarandosi consapevole dell’obbligo della Banca di adempiere agli obblighi previsti dalla Legge federale svizzera sul riciclaggio di denaro, il Cliente accetta di fornire alla Banca, in un documento distinto, informazioni complete e precise relative, tra gli altri, all’identificazione della controparte, l’identificazione del titolare effettivo e l’origine delle sue attività patrimoniali. Dichiarandosi consapevole dell’obbligo della Banca di adempiere agli obblighi previsti dalla Legge federale svizzera sul riciclaggio di denaro, il Cliente accetta di fornire alla Banca, in un documento distinto, informazioni complete e precise relative, tra gli altri, all’identificazione della controparte, l’identificazione del titolare effettivo e l’origine delle sue attività patrimoniali. 7/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito Provided the Bank has proceeded in accordance with the provisions and regulations set forth in the Swiss legislation for the prevention of money laundering (e.g. the MLA) and the rules and regulation of the Swiss Banking regulator (FINMA), respectively, the Client shall bear losses resulting from unexecuted instructions or the delayed execution of instructions. Furthermore, the Client confirms wishing to execute cross-border or foreign currency payments in the future. Learning about the rules for cross-border or foreign currency payments the Client authorizes the Bank to disclose his name and further Client details in case of payments made to Bank account abroad, or payments made in foreign currencies both within Switzerland as well as abroad. Purché la Banca abbia proceduto ai sensi delle disposizioni e delle norme stabilite dalla legislazione svizzera in materia di lotta al riciclaggio (ad es. la LRD) e le norme e i regolamenti dell’autorità svizzera di vigilanza (FINMA), rispettivamente, il Cliente sosterrà le perdite derivanti dalle istruzioni non eseguite o dalla ritardata esecuzione delle medesime. Il Cliente conferma altresì il desiderio di eseguire in futuro pagamenti internazionali o pagamenti in valuta estera. Dichiarandosi a conoscenza delle norme che regolano i pagamenti internazionali o in valuta, il Cliente autorizza la Banca a divulgare il suo nome e ulteriori dati personali in caso di pagamenti effettuati su un conto bancario estero o di pagamenti effettuati in valuta estera sia in Svizzera che all’estero. 2.1.12 ESAME E LEGITTIMAZIONE DELLE FIRME 2.1.12 Examination of signatures and legitimating The Bank undertakes to examine the signatures of Clients and their authorized attorneys with care. The Bank is not required to undertake any additional extensive check of their identity. The Bank will not be responsible for the consequences of any falsifications or faulty identification that it has not recognized provided it has observed due care. La Banca s’impegna ad esaminare diligentemente le firme dei Clienti e dei loro procuratori autorizzati. La Banca non è obbligata a svolgere ulteriori controlli più approfonditi della loro identità. La Banca non sarà responsabile delle conseguenze di falsificazioni o identificazioni erronee che non abbia potuto riconoscere pur esercitando la dovuta diligenza. 2.1.13 INCAPACITÀ CIVILE 2.1.13 Civil incapacity Losses resulting from the Client’s civil incapacity are exclusively borne by the Client, unless that incapacity has been published in an official Swiss gazette. In any case, the Client will bear the loss resulting from the civil incapacity of the people he/she has mandated or of other third parties having access to the Client’s account(s)/save custody account(s). 2.1.14 Joint Accounts If the Client is more than one person (in the case of joint account holders), the liabilities of each such person shall be joint and several, and the Bank may act upon instructions received from any one person who is, or appears to the Bank to be, such a person. 2.1.15 Complaints by the Client Any complaint by the Client concerning the execution or non-execution of any order, and any dispute concerning an account or other communication from the Bank must be issued immediately after receiving the information, but not later than one day after the date of communication, failing of which the execution or non-execution and the corresponding statements and communications will be taken to have been approved. In the case of a late complaint, the Client will bear any resulting loss. If the Client does not react according to this clause within the period of time allowed, statements are deemed to have been accepted. Express or tacit acknowledgement of the account statement implies approval of the individual headings it contains and of any reservation the Bank may have formulated. Any claim for indemnification must be addressed in writing (per post) by the Client or its representative to the address of the Bank to the attention of the Chief Executive Officer. The Client acknowledges that the Bank will not answer any claim which is not addressed in writing and/or not signed by its author. 2.1.16 Right of pledge, lien set-off and retention The Bank has a right of lien for the discharge of all indebtedness and the Client’s other obligations towards the Bank on securities and other property now or hereafter held, carried or maintained by the Bank in its possession or control, for any purpose, in or for the benefit of any of the Client’s accounts, now or hereafter opened, including any account in which the Client may have an interest. The Bank has a right of set-off regarding all debts receivable against its existing claims against the Client regardless of the dates they are due for payment or the currencies in which they are expressed. The same applies to all the credits it has granted in exchange for the issuing of special guarantees or guarantees in blank. Upon notice served on the Client, the Bank is entitled, at its sole discretion, to proceed with the compulsory realization or the over-the-counter or market sale of the securities pledged, at the Client’s cost if necessary. The Client authorizes the Bank and the Bank shall have the right to transfer securities and other D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Le perdite derivanti dall’incapacità civile del Cliente vengono sostenute esclusivamente dal Cliente stesso, salvo qualora tale incapacità sia stata resa nota mediante pubblicazione in una gazzetta ufficiale svizzera. In ogni caso, il Cliente sosterrà la perdita derivante dall’incapacità civile delle persone a cui ha affidato il mandato o di altre terze parti che abbiano accesso al/ai conto/i e/o al/ai conto/i di custodia in deposito del Cliente. 2.1.14 CONTI COINTESTATI Qualora il Cliente sia costituito da più persone (nel caso di titolari di conti cointestati), ognuna di tali persone sarà responsabile in solido, e la Banca potrà agire sulla base delle disposizioni ricevute da qualsiasi individuo che sia, o risulti essere alla Banca, una tale persona. 2.1.15 RECLAMI DA PARTE DEL CLIENTE Qualsiasi reclamo da parte del Cliente relativo all’esecuzione o alla mancata esecuzione di qualsiasi ordine, e qualsiasi controversia concernente un conto o altre comunicazioni da parte della Banca, dovranno essere inviati immediatamente dopo la ricezione delle informazioni e comunque entro e non oltre il giorno successivo alla data di comunicazione; in caso contrario, l’esecuzione o la mancata esecuzione e i corrispondenti estratti e comunicazioni verranno considerati come approvati. Il Cliente sosterrà l’intera perdita derivante da un reclamo tardivo. Qualora il Cliente non risponda ai sensi della presente clausola entro il periodo consentito, gli estratti verranno considerati come accettati. Il riconoscimento esplicito o tacito dell’estratto conto implica l’approvazione delle singole voci ivi contenute e di tutte le riserve che la Banca può avere formulato. Qualsiasi reclamo relativo ad eventuali indennizzi deve essere inviato per iscritto (per posta) dal Cliente o dal suo rappresentante all’indirizzo della Banca, all’attenzione del Direttore generale. Il Cliente riconosce che la Banca non risponderà ad alcun reclamo che non sia stato inviato per iscritto e/o non sia stato firmato dal suo estensore. 2.1.16 DIRITTO DI PEGNO E DI PRELAZIONE, DIRITTO DI COMPENSAZIONE E RITENUTA General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI La Banca ha un diritto di prelazione sui valori mobiliari e altre proprietà detenute, custodite o mantenute dalla Banca in suo possesso o controllo, attualmente o in futuro, a qualsiasi scopo, su o a beneficio di qualsiasi conto del Cliente, aperto attualmente o in futuro, inclusi tutti i conti in cui il Cliente possa avere un interesse, per il pagamento della totalità dei debiti e di altri obblighi del Cliente verso la Banca. La Banca ha un diritto di compensazione in relazione a tutti i crediti esigibili per le somme rivendicate verso il Cliente, indipendentemente dalle date entro cui è dovuto il pagamento o le valute in cui sono espresse. Lo stesso diritto vale per tutti i crediti che abbia concesso in cambio dell’emissione di garanzie speciali o garanzie in bianco. Avendone data notifica al Cliente, la Banca ha il diritto, a sua esclusiva discrezione, di procedere alla realizzazione obbligatoria o mediante vendita sul mercato o fuori borsa dei valori mobiliari dati in pegno, se necessario a spese del Cliente. Il Cliente autorizza la Banca, e la Banca avrà il diritto, a trasferire i valori mobiliari e le altre proprietà detenute per conto del Cliente o del suo rappresentante da o verso qualsiasi altro 8/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito property held on behalf of the Client or his/her representative from or to any other account of the Client at the Bank whenever, in the Bank’s judgment, it considers such transfer necessary for its protection. The Bank shall, at any time, be entitled to offset against each other the balances of all accounts the Client maintains with the Bank (regardless of designation of currency of the account) or to offset each balance individually. For all its claims arising from its business relations with the Client, irrespective of the maturity dates of such claims or of the currencies in which they are denominated, including unsecured or collateralized claims, the Bank shall have a right of lien and pledge, and a right of retention, on all assets held in the Client’s name or otherwise deposited with the Bank. 2.1.17 Fees and rates The Bank shall charge fees and rates for its services according to its prevailing Schedule of Fees & Rates with which the Client declares himself to be in agreement. These fees and rates are published on our website www.migbank.com The Client expressly acknowledges that the Bank may pay remunerations to third parties, such as business finders and/or external asset managers under cooperation agreements. Such remunertions may be based on the volume of assets and/or transaction-related fees and rates on any Client transaction. The Client will receive a special information from the Bank on any additional spread or commission he may be charged as per agreement given. The Client understands and agrees that the Bank may receive payments, or other pecuniary benefits of any kind, from third parties. Such payments may be based on the volume of assets invested and/ or may be based on the volume of clients transaction. The client agrees that such payments may be treated and retained by the Bank as compensation in addition to that paid by the Client for the services provided by the Bank, and need not to be paid on to the Client. The Bank shall not be obliged to disclose the nature or amount of any payment received. 2.1.18 Accounts managed by the client The Client shall be solely responsible for making any investments or trading decision on his assets deposited with the Bank and shall make such decisions entirely at his own risk. The Client acknowledges and agrees that the Bank shall not be liable in respect of any investment or trading decision made by the Client or any potential consequences resulting therefrom. All act performed by the Client shall be fully binding upon the client. The Client hereby releases the Bank fully and in advance from any responsibility and liability for any of the Client’s act and/or omission. In particular, the Bank is under no obligation to examine the instructions of the Client with respect to their appropriateness, suitability, frequency or extent. No liability shall accrue the Bank in respect of any investment decision made by the Client and the Client hereby expressly releases the Bank from any obligation to provide any advice, information or warning whatsoever in relation to the acts or omissions of the Client. conto del Cliente presso la Banca ogniqualvolta, a giudizio della Banca, tale trasferimento sia necessario ai fini della sua protezione. In qualsiasi momento la Banca avrà diritto di compensare tra loro i saldi di tutti i conti che il Cliente mantiene presso la Banca (indipendentemente dalla valuta di denominazione del conto) o di compensare ogni saldo singolarmente. Per tutte le richieste di rimborso conseguenti ai suoi rapporti commerciali con il Cliente, indipendentemente dalle scadenze di tali richieste o dalle valute in cui sono denominate, incluse le richieste di rimborso con o senza garanzia, la Banca avrà il diritto di pegno e di prelazione, e un diritto di ritenuta a garanzia, su tutte le attività detenute a nome del Cliente o altrimenti depositate presso la Banca. 2.1.17 COMMISSIONI E SPESE La Banca addebiterà commissioni e spese per i servizi forniti, in base al “Prospetto commissioni e spese” vigente, che il Cliente dichiara di accettare. Tali commissioni e spese sono pubblicate sul sito web www.migbank. com. Il Cliente riconosce espressamente che la Banca, in virtù di contratti di collaborazione, può pagare remunerazioni a terzi, come procacciatori di opportunità commerciali e/o gestori patrimoniali esterni. Tali remunerazioni potranno essere calcolate sul volume delle attività e/o costituite di commissioni e spese collegate alle transazioni e applicate a qualsiasi operazione svolta dal Cliente. Il Cliente riceverà una comunicazione speciale dalla Banca su qualsiasi ulteriore spread o commissione che potrebbe vedersi addebitato/a ai sensi del pertinente contratto. Il Cliente intende e accetta che la Banca possa ricevere da terzi pagamenti o altri benefici pecuniari di qualsiasi tipo. Tali pagamenti potranno essere basati sul volume delle attività investite e/o sul volume delle transazioni del Cliente. Il Cliente accetta che tali pagamenti vengano trattati e trattenuti dalla Banca come ulteriore compenso in aggiunta a quello pagato dal Cliente per i servizi forniti dalla Banca, e che non vengano necessariamente accreditati al Cliente. La Banca non sarà obbligata a divulgare la natura né l’importo dei pagamenti ricevuti. 2.1.18 CONTI GESTITI DAL CLIENTE Il Cliente sarà l’unico responsabile di tutte le decisioni di investimento o di trading prese in relazione alle sue attività depositate presso la Banca, e assumerà tali decisioni interamente a proprio rischio. Il Cliente riconosce e accetta che la Banca non sarà responsabile di alcuna decisione d’investimento o transazione effettuata dal Cliente, né di alcuna potenziale conseguenza da queste derivante. Tutte le azioni eseguite dal Cliente saranno pienamente vincolanti per il medesimo. Con il presente Contratto il Cliente solleva la Banca pienamente e anticipatamente da qualsiasi responsabilità legale o di altra natura per qualsiasi azione e/o omissione del Cliente. In particolare, la Banca è in alcun modo tenuta a esaminare le disposizioni del Cliente per quanto attiene alla loro idoneità, adeguatezza, frequenza o portata. Nessuna responsabilità deriverà alla Banca in relazione a qualsivoglia decisione d’investimento presa dal Cliente. Con il presente Contratto, il Cliente esonera espressamente la Banca dall’onere di fornire consigli, informazioni o avvertimenti di qualsivoglia natura in relazione alle azioni o alle omissioni del Cliente. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 2.1.19 CONTI GESTITI DA TERZI 2.1.19 Accounts managed by a third party The Client shall be solely responsible for any investments or trading decision done by any Attorney designated by the Client on assets of the Client deposited with the Bank and such decisions are made entirely at the own risk of the Client. The Client acknowledges and agrees that the Bank shall not be liable in respect of any investment or trading decision made by the Attorney or any potential consequences resulting therefrom. All act performed by an Attorney shall be fully binding upon the Client. The Client hereby releases the Bank fully and in advance from any responsibility and liability for any of the Attorney’s act and/or omission. In particular, the Bank is under no obligation to examine the instructions of the Attorney with respect to their appropriateness, suitability, frequency or extent. No liability shall accrue the Bank in D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Il Cliente sarà l’unico responsabile di tutte le decisioni di investimento o di trading, prese da qualsiasi Procuratore che il Cliente avrà nominato, in relazione alle attività del Cliente depositate presso la Banca; tali decisioni verranno prese interamente a rischio del Cliente. Il Cliente riconosce e accetta che la Banca non sarà responsabile di alcuna decisione d’investimento o transazione effettuata dal Procuratore, né di alcuna potenziale conseguenza da queste derivante. Tutte le azioni eseguite dal Procuratore saranno pienamente vincolanti per il Cliente. Con il presente Contratto il Cliente solleva la Banca pienamente e anticipatamente da qualsiasi responsabilità legale o di altra natura per qualsiasi azione e/o omissione del Procuratore. In particolare, la Banca è in alcun modo tenuta a esaminare le disposizioni del Procuratore per quanto attiene alla loro idoneità, adeguatezza, frequenza o portata. Nessuna responsabilità deriverà alla Banca in relazione a qualsivoglia decisione 9/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito respect of any investment decisions made by the Attorney and the Client hereby expressly releases the Bank from any obligation to provide any advice, information or warning whatsoever in relation to the acts or omissions of the Attorney. d’investimento presa dal Procuratore. Con il presente Contratto il Cliente esonera espressamente la Banca dall’onere di fornire consigli, informazioni o avvertimenti di qualsivoglia natura in relazione alle azioni o alle omissioni del Procuratore. Furthermore, the Client acknowledges that the Bank does not monitor the volume or the appropriateness of the remuneration paid to the Attorney. The Client undertakes to monitor at all times the remuneration paid to the Attorney. Inoltre, il Cliente riconosce che la Banca non controlla né l’importo né l’adeguatezza della remunerazione versata al Procuratore. Il Cliente si impegna a monitorare continuativamente la remunerazione versata al Procuratore. 2.2 Technical installation and password 2.2 INSTALLAZIONE TECNICA E PASSWORD 2.2.1 Login / Identification 2.2.1 LOGIN / IDENTIFICAZIONE The Bank sends the User ID and password per e-mail. Together with the User ID, the password allows access to Banking services provided by the Bank. The Client is at any time requested to keep the password and the User ID secret and to protect them from misuse. La Banca invia per e-mail l’ID Utente e la password. Insieme con l’ID Utente, la password consente l’accesso ai servizi forniti dalla Banca. Il Cliente deve sempre mantenere segreti la password e l’ID Utente e proteggerli da eventuali usi impropri. Anyone who identifies himself/herself each time he/she uses the system by entering the User ID and the personal password or identifies himself/herself when remitting orders by telephone to the Bank’s telephone consumer representative using the User ID and the personal password, has access to the Bank’s electronic transaction devices and other services as provided on the Bank’s online-trading site. At the occasion of contact over the telephone the Bank’s telephone consumer representatives will require the complete User ID and three positions of the 8-digit personal password, chosen at random. Chiunque si identifichi con l’ID Utente e la password personale ogni qualvolta che utilizza il sistema o impartisce ordini per telefono all’addetto dell’assistenza telefonica della Banca avrà accesso ai dispositivi di transazione elettronica della Banca e ad altri servizi forniti sul sito di trading online della Banca. Durante il contatto telefonico, gli addetti dell’assistenza telefonica della Banca chiederanno l’ID Utente completo e tre delle otto cifre che compongono la password personale, scelte a caso. The Client is requested to modify the password regularly and to keep it in safe custody denying access to third person. The Client bears all risks resulting from the loss and the misuse, respectively, of the User ID and/or the password. The Bank is not liable for any damages that might result from the loss or misuse of the User ID and/or the password. The Client undertakes to inform the Bank immediately in the event the account has to be blocked and/or the User ID and/or the password have to be cancelled and/or replaced. After checking the legitimacy of the Client’s identity (User ID and password) and the availability of his/her assets, the Bank undertakes to carry out all the orders and instructions received from him/her immediately. However, the Bank may decide to accept specific orders from the Client only through dedicated sites or by other means communicated to the Client. The Bank is entitled at its discretion but not bound to accept instructions in writing. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Bank has at any time and at its sole discretion the right to ignore any orders and instructions and to require written verification of identity. The Bank may, at its own discretion, introduce and require additional levels of identification for all or part of its services, including but not limited to scratch-lists and/or secure-ID. 2.2.2 Irrevocable legitimating Whoever legitimates himself/herself according to article 2.2.1 above is considered to be entitled to use the Bank’s services. The Bank may consider such orders and communications as being undoubtedly authorized and issued by the Client and/or his/her legitimate representative. 2.2.3 Blocking access The Client may at any time require the Bank to block access to the Client’s account immediately. Such blockage can only be revoked by the Client in writing. The Bank reserves its right to block the Client’s access via the Internet or by telephone at any time, without giving further explanation and without further notice, to the extent it deems such a blockage appropriate. 2.2.4 Security / Internet risks The Bank’s liability for any damage occurring on the Client’s or his/ her representative side, respectively, as a result of transmission errors, failures of transmission, technical errors, overload, breakdowns (including but not limited to maintenance services due to system maintenance), malfunction, interference, illegal invasion (e.g. hacking) and willful blockage of telecommunication devices and networks (e.g. “mail bombing”, denial of services attacks etc.) or due to other D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Il Cliente è tenuto a modificare periodicamente la password ed a custodirla in luogo sicuro, dove non sia accessibile a terzi. Il Cliente si assume tutti i rischi derivanti dalla perdita e dal cattivo utilizzo dell’ID Utente e/o della password. La Banca non è responsabile di alcun danno eventualmente derivante dalla perdita o dal cattivo utilizzo dell’ID Utente e/o della password. Il Cliente si impegna a informare immediatamente la Banca nell’eventualità che si renda necessario bloccare il conto e/o annullare e/o sostituire l’ID Utente e/o la password. Dopo aver verificato la corretta identità del Cliente (ID Utente e password) e le sue disponibilità finanziarie, la Banca si impegna ad eseguire immediatamente tutti gli ordini e le istruzioni ricevuti dalla persona così identificata. Tuttavia, la Banca può decidere di accettare specifici ordini dal Cliente solo tramite siti all’uopo dedicati o altri mezzi comunicati al Cliente. La Banca ha facoltà di accettare istruzioni per iscritto, a propria discrezione e senza obbligo alcuno. Fatto salvo quanto precede, in qualsiasi momento e a sua esclusiva discrezione, la Banca potrà ignorare qualsiasi ordine e disposizione e richiedere la verifica scritta dell’identità. La Banca potrà, a propria discrezione, introdurre e richiedere ulteriori livelli di identificazione per la totalità o una parte dei suoi servizi, inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, liste di stralcio e/o ID sicuri. 2.2.2 LEGITTIMAZIONE IRREVOCABILE Chiunque si identifichi legittimamente ai sensi del precedente articolo 2.2.1 viene considerato come avente diritto all’utilizzo dei servizi della Banca. La Banca potrà considerare tali ordini e comunicazioni come indubbiamente autorizzati e impartiti dal Cliente o dal/dalla suo/a legittimo/a rappresentante. 2.2.3 BLOCCO DELL’ACCESSO Il Cliente potrà in qualsiasi momento richiedere alla Banca di bloccare immediatamente l’accesso al proprio conto. Tale blocco potrà essere esclusivamente revocato dal Cliente per iscritto. La Banca si riserva il diritto di bloccare in qualsiasi momento l’accesso del Cliente via Internet o telefono, senza fornire ulteriori spiegazioni e senza darne ulteriore comunicazione, nella misura in cui consideri tale blocco appropriato. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 2.2.4 SICUREZZA / RISCHI CORRELATI A INTERNET È esclusa espressamente ogni responsabilità della Banca per qualsiasi danno subito rispettivamente dal Cliente o dal/dalla suo/a rappresentante, in conseguenza di errori di trasmissione, difetti nella trasmissione, errori tecnici, sovraccarico, interruzioni (incluse, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, quelle necessarie per la manutenzione del sistema), disfunzioni, interferenze, accessi illegali (pirateria informatica) e il deliberato blocco dei dispositivi e delle reti di telecomunicazione (es. bombardamento della casella di posta elettronica, attacchi “denial of services” ecc.), o in conseguenza di altre mancanze dei provider dei servizi di telecomunicazione o di rete. Il Cliente è consapevole del fatto che i dati vengono trasmessi attra- 10/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito inadequateness of telecommunication- or network-service providers is expressly excluded. The Client is aware of the fact that data are transmitted over open, generally public networks (e.g. the Internet). Therefore, data are transmitted regularly and uncontrolled and also outside the borders of the country of Switzerland even in the case that sender as well as addressee reside in Switzerland. Even in case of encryption of the data sender and addressee may not be encrypted which may result in conclusion of sender and addressee by third parties. The Bank is not liable nor does it guarantee and/or represent that data transmitted over the Internet are correct, accurate or complete. Namely data with regard to accounts (transaction confirmations, statements of account, balances etc.) as well as information accessible by public, e.g. stock exchange quotations or exchange rates, are not binding. verso reti aperte, generalmente pubbliche (ad es. Internet); pertanto, i dati verranno trasmessi periodicamente, in modo incontrollato e possibilmente fuori dai confini svizzeri anche nel caso in cui il mittente e il destinatario risiedano entrambi in Svizzera. Anche in caso di crittografia dei dati, gli indirizzi del mittente e del destinatario potrebbero essere intelligibili, e ciò potrebbe rendere nota la loro identità a terzi. La Banca non è responsabile né garantisce e/o dichiara che i dati trasmessi via Internet siano corretti, accurati o completi. Nella fattispecie i dati relativi ai conti (conferme di transazioni, estratti conto, saldi ecc.) nonché le informazioni accessibili da parte del pubblico, ad es. le quotazioni di borsa o i tassi di cambio, non sono vincolanti. The Client is particularly aware of the following Internet relied risks for which the Bank shall not be liable : + La conoscenza inadeguata del sistema e misure di sicurezza deficitarie possono favorire un accesso non autorizzato. Il Cliente ha l’obbligo di informarsi con precisione delle necessarie misure di sicurezza, sotto la propria completa responsabilità. + Inadequate knowledge of the system and defective security measures can facilitate unauthorized access. Entirely on his/her own responsibility, the Client is under the obligation to inform himself/ herself exactly of the necessary security measures. + Internet providers may prepare user statistics and thus deduce from them that the Client has contacted the Bank. + Particularly via the Internet and through the exchange of diskettes, it is also possible for computer viruses to reach the Client’s computer without being noticed. + The use of computers that are not permanently used by the Client in person adds additional risks. The use and storage or any information including, without limitation, the password, the user ID, portfolio information, transaction activity, account balances and any other information or orders available on the Client’s personal computer is at the Client’s own risk and in his/her sole responsibility. + Software and hardware should only be acquired from a trustworthy source. + The Client expressly consents to correspondence being sent to him/her in electronic form. The Client is aware and accepts any consequences, losses and risks that could result from the transmission of information in electronic form. 2.2.5 Hard – and software The Client assumes responsibility for technical access to the Bank’s services. The Client is responsible for acquiring, installing and configuring hardware and software appropriate to set up connection/ communication to/with the Bank’s online services (computer, modem, browser, etc.). Consequently, the Bank does not assume any responsibility for the access provider or for any foreign software and hardware that it has not provided itself. 2.2.6 Outsourcing The Client is aware and agrees that the Bank may outsource and/ or assign part(s) of its business areas within its own organization or, under its responsibility, with third parties, to provide services on an on-going basis, in particular but not limited to the areas of IT, administration or accounting. In the event of an outsourcing or assignment the Client will be informed accordingly. In this context, the Client is informed that the Bank has outsourced some of its IT activities to external professional providers. 2.2.7 License grant and right of use The Bank is supplying the Client with software for use of the Online Service. The Client may use the software solely for his/her own internal business purposes. Neither the software nor the Online Service may be used to provide third party training or as a service bureau for any third parties. The Client agrees to use the Online Service and the software strictly in accordance with the terms and conditions, as D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 In particolare, il Cliente è consapevole dei rischi collegati a Internet di seguito elencati, per i quali la Banca non si assume alcuna responsabilità: + I fornitori di accesso a Internet potrebbero predisporre statistiche d’uso, e quindi dedurre da queste che il Cliente ha contattato la Banca. + È possibile inoltre che virus informatici infettino il computer del Cliente senza essere rilevati, particolarmente via Internet e attraverso lo scambio di dischetti e altri supporti informatici. + L’utilizzo di computer che non sono impiegati esclusivamente dal Cliente in persona comportano ulteriori rischi. L’uso e l’archiviazione di qualsiasi informazione, inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, la password, l’ID Utente, le informazioni sui portafogli, le transazioni, i saldi dei conti e qualsiasi altra informazione o ordine disponibile sul personal computer del Cliente, vengono effettuati a rischio del Cliente e sotto la sua esclusiva responsabilità. + Il software e l’hardware dovrebbero essere acquistati esclusivamente da fornitori affidabili. + Il Cliente acconsente espressamente a ricevere la corrispondenza in forma elettronica. Il Cliente è consapevole delle perdite e dei rischi che potrebbero derivare dalla trasmissione di informazioni in forma elettronica, e ne accetta tutte le conseguenze. 2.2.5 HARDWARE E SOFTWARE Il Cliente si assume la responsabilità dell’accesso tecnico ai servizi della Banca. Il Cliente è responsabile dell’acquisto, dell’installazione e della configurazione di hardware e software adeguati per l’impostazione della connessione/comunicazione ai/con i servizi online della Banca (computer, modem, browser ecc.). Di conseguenza, la Banca non si assume alcuna responsabilità in relazione al fornitore di accesso o a qualsiasi software e hardware sconosciuti che non siano stati forniti dalla medesima. 2.2.6 ESTERNALIZZAZIONE Il Cliente riconosce e accetta che la Banca potrà esternalizzare e/o assegnare parte/i delle sue aree d’affari all’interno della propria organizzazione o, sotto la propria responsabilità, a terzi che forniscano servizi su base continuativa, in particolare ma non limitatamente nelle aree di informatica, amministrazione o contabilità. Nell’eventualità di esternalizzazione o assegnazione, il Cliente verrà informato di conseguenza. Nel presente contesto, si informa il Cliente che la Banca ha esternalizzato alcune sue attività informatiche a fornitori esterni di servizi professionali. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 2.2.7 CONCESSIONE DI LICENZE E DIRITTO D’USO La Banca fornisce al Cliente il software da utilizzare per il Servizio Online. Il Cliente potrà usare il software esclusivamente per le proprie finalità commerciali interne. Né il software né il Servizio Online potranno essere utilizzati per impartire formazione a terzi o per svolgere funzioni di agenzia di servizio per terzi. Il Cliente accetta di usare il Servizio Online e il software esclusivamente in conformità con i termini e le condizioni, e le successive modificazioni di volta in volta apportate dalla Banca. Il Cliente accetta altresì di rispettare tutte le norme, le procedure e le condizioni stabilite dalla 11/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito amended from time to time by the Bank. The Client also agrees to be bound by any rules, procedures and conditions established by the Bank concerning the use of the Online Service provided by the Bank. 2.2.8 Accesses and security The Online Service may be used to transmit, receive and confirm execution of orders, subject to prevailing market conditions and applicable rules and regulations. The Bank consents to Client’s access and use in reliance upon his/her having adopted procedures to prevent unauthorized access to and use of the Online Service, and in any event, the Client agrees to any financial liability for trades executed through the Online Service. The Client acknowledges, represents and warrants that : a) He/She has received a number, code or other sequence, which provides access to the Online Service (“the Password”). b) He/She is the sole and exclusive owner of the Password c) He/She is the sole and exclusive owner of any identification or login number (the “Login”) and number d)He/She accepts full responsibility for use and protection of the Password and the Login as well as for any transaction occurring in an account opened, held or accessed through the Login and/or Password. The Client accepts responsibility for the monitoring of his/her account(s). The Client will immediately notify the Bank in writing if he/she becomes aware of any of the following : a) Any loss, theft or unauthorized use of his/her Password(s), Login and/ or account number(s); or b) Any failure by him/her to receive a message indicating that an order was received and/or executed; or c) Any failure by him/her to receive an accurate confirmation of an execution; or d) Any receipt of confirmation of an order and/or execution, which he/ she did not place; or e) Any inaccurate information in his/her account balances, positions, or transaction history. Banca relativamente all’uso del Servizio Online fornito 2.2.8 ACCESSI E SICUREZZA Il Servizio Online potrà essere usato per trasmettere, ricevere e confermare l’esecuzione di ordini, subordinatamente alle condizioni di mercato prevalenti e alle norme e disposizioni vigenti. La Banca acconsente all’accesso e all’uso da parte del Cliente, confidando nel fatto che il Cliente adotti le misure necessarie per impedire l’accesso e l’uso non autorizzati del Servizio Online. In ogni caso, il Cliente accetta tutte le passività finanziarie derivanti dalle transazioni eseguite attraverso il Servizio Online. Il Cliente riconosce, dichiara e garantisce: a) di aver ricevuto un numero, un codice o altra sequenza, che gli consente di accedere al Servizio Online (la “Password”); b) di essere l’unico ed esclusivo proprietario della Password; c) di essere l’unico ed esclusivo proprietario di qualsiasi numero d’identificazione o numero di accesso (l’“Identificativo”); d) di assumersi la piena responsabilità dell’uso e della protezione della Password e dell’Identificativo e di qualsiasi transazione eseguita in un conto aperto, detenuto o a cui si abbia avuto accesso utilizzando l’Identificativo e/o la Password. Il Cliente si assume la responsabilità di monitorare il/i propri(o) conto/i. Il Cliente informerà immediatamente la Banca per iscritto qualora venga a conoscenza di uno o più dei fatti di seguito elencati: a) la perdita, il furto o l’uso non autorizzato della/e propria/e Password, del/i proprio/i Identificativo/i e/o del/i proprio/i numero/i di conto; oppure b) la mancata ricezione da parte sua di un messaggio di conferma della ricezione e/o dell’esecuzione di un ordine; oppure c) la mancata ricezione da parte sua dell’accurata conferma di un’esecuzione; oppure d) la ricezione della conferma di un ordine e/o esecuzione che non ha impartito; oppure e) qualsiasi informazione imprecisa sui saldi dei conti, sulle posizioni o sulla cronologia delle sue transazioni. 2.2.9 RISCHI INSITI NEL TRADING ONLINE 2.2.9 Risk of online trading The Client’s access to the Online Service, or any portion thereof, may be restricted or unavailable during periods of peak demands, extreme market volatility, systems upgrades or other reasons. The Bank makes no express or implied representations or warranties to the Client regarding the usability, condition or operation thereof. The Bank does not warrant that access to or use of the Online Service will be uninterrupted or error free or that the Online Service will meet any particular criteria of performance or quality. Under no circumstances including negligence, shall the Bank or anyone else involved in creating, producing, delivering or managing the Online Service be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special or consequential damages that result from the use of or inability to use the Online Service, or out of any breach of any warranty, including, without limitation, those for business interruption or loss of profits. The Client assumes full responsibility and risk of loss resulting from use of, or materials obtained through the Online Service. Neither the Bank, nor any of the Bank’s directors, officers, employees, agents, contractors, affiliates, third party vendors, facilities, information providers, licensors, exchanges, clearing organizations or other suppliers providing data, information, or services, warrant that the Online Service will be uninterrupted or error free; nor does the Bank make any warranty as to the results that may be obtained from the use of the Online Service or as to the timeliness, sequence, accuracy, completeness, reliability or content of any information, service, or transaction provided through the Online service. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 L’accesso del Cliente al Servizio Online, o a qualsiasi sua parte, potrà essere limitato o indisponibile nei periodi di picco delle richieste, di estrema volatilità del mercato, di aggiornamenti dei sistemi o per altri motivi. La Banca non fornisce al Cliente alcuna dichiarazione né garanzia esplicita o implicita relativa all’utilizzabilità, alla condizione o al funzionamento del Servizio Online. La Banca non garantisce che l’accesso o l’uso del Servizio Online sarà continuativo o privo di errori o che il Servizio Online soddisfi particolari criteri di prestazione o di qualità. In nessuna circostanza, inclusa la negligenza, la Banca o qualsiasi altro soggetto coinvolto nella creazione, nella produzione, nella fornitura o nella gestione del Servizio Online sarà responsabile di qualsiasi danno diretto, indiretto, accidentale, speciale o conseguente derivante dall’uso del Servizio Online, o dall’impossibilità di utilizzarlo, o dalla violazione di qualsivoglia garanzia, incluse, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, quelle inerenti l’interruzione dell’attività o la perdita di profitti. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI Il Cliente si assume la piena responsabilità e il rischio di perdite derivanti dall’uso del Servizio Online o di materiali ottenuti tramite il medesimo. Né la Banca, né qualsiasi suo direttore, funzionario, dipendente, agente, collaboratore, società affiliata, produttore terzo, struttura, fornitore d’informazioni, licenziante, borsa valori, organismo di compensazione o altro fornitore di dati, informazioni o servizi, garantiscono che il Servizio Online sarà continuativo o privo di errori. La Banca non offre alcuna garanzia sui risultati che si possono ottenere dall’uso del Servizio Online o dalla tempestività, dalla sequenza, dall’accuratezza, dalla completezza, dall’affidabilità o dal contenuto di qualsiasi informazione, servizio o transazione forniti tramite il Servizio Online. 12/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito In the event that the Client’s access to the Online Service or any portion thereof is restricted or unavailable for any reason, the Client agrees to use other means to place his/her orders or access information, such as calling the Bank. Qualora l’accesso del Cliente al Servizio Online o a qualsiasi sua parte sia limitato o indisponibile, il Cliente accetta di usare altri mezzi per impartire gli ordini o accedere alle informazioni, ad esempio telefonando alla Banca. By placing an order through the Online Service, the Client acknowledges that his/her order may not be reviewed by a registered representative prior to execution. The Client agrees that the Bank is not liable to him/her for any losses, lost opportunities or increased commissions, which may result from his/her inability to use the Online Service to place orders or access information. Nel trasmettere un ordine mediante il Servizio Online, il Cliente riconosce che il suo ordine potrebbe non essere esaminato da un operatore autorizzato prima dell’esecuzione. Il Cliente riconosce che la Banca non è responsabile nei suoi confronti per alcuna perdita, mancata opportunità o accresciuta commissione che potrebbero derivare dall’impossibilità di usare il Servizio Online per trasmettere ordini o accedere alle informazioni. 2.2.10 Market data and information 2.2.10 DATI E INFORMAZIONI DI MERCATO Neither the Bank nor any provider shall be liable in any way to the Client or to any other person for : Né la Banca né qualsiasi altro fornitore saranno responsabili in alcun modo verso il Cliente o qualsiasi altra persona per: a) Any inaccuracy, error or delay in, or omission of any such data, information or message or the transmission or delivery of any such data, information or message; or a) Eventuali imprecisioni, errori, ritardi o omissioni in tali dati, informazioni o messaggi o nella trasmissione o nella fornitura dei medesimi; oppure b) Any loss or damage arising from or occasioned by any such inaccuracy, error, delay, omission, non performance, interruption in any such data, information or message, due either to any negligent act or omission or to any event of “Force Majeure” or any other cause, whether or not within the Bank or any provider’s control. The Bank shall not be deemed to have received any order or communication transmitted electronically by the Client, until the Bank has actual knowledge of such order or communication. Additionally, if a client executed a trade at a price which at the time the trade was executed was wrong and/or delayed from the actual market price, then the Bank may cancel that trade from the Client’s account and the Bank shall remain harmless of any damages or costs arising thereof. b) Eventuali perdite o danni derivanti o causati da qualsiasi imprecisione, errore, ritardo, omissione, mancata esecuzione, interruzione di tali dati, informazioni o messaggi, in conseguenza di negligenze o omissioni o eventi di “Forza maggiore” o qualsiasi altra causa, che si trovino o meno sotto il controllo della Banca o di qualsiasi altro fornitore. Non si possono considerare ricevuti un ordine o una comunicazione trasmessi elettronicamente dal Cliente, finché la Banca non abbia effettiva conoscenza di tale ordine o comunicazione. Inoltre, se un cliente ha eseguito una transazione ad un prezzo che all’atto dell’esecuzione della transazione era errato e/o ritardato rispetto all’effettivo prezzo di mercato, la Banca potrà annullare tale transazione dal conto del Cliente restando sollevata da tutti i danni o i costi da questo derivanti. 2.2.11 DICHIARAZIONI 2.2.11 Representations The Client acknowledges that from time to time, and for any reason, the Online Service may not be operational or otherwise unavailable for his/her use due to servicing, hardware malfunction, software defect, service or transmission interruption or other cause, and he/she agrees to hold the Bank and any provider harmless from liability of any damage which results from the unavailability of the Online Service. The Client acknowledges that he/she has alternative arrangements, which will remain in place for the transmission and execution of his/ her orders, in the event, for any reason, circumstances prevent the transmission and execution of all, or any portion of his/her orders through the Online Service. The Client represents and warrants that he/she is fully authorized to enter into this type of online transactions and under no legal disability which prevents him/her from trading, and that he/she shall remain in compliance with all laws, rules and regulations applicable to his/her business. The Client agrees that he/she is familiar with and will abide by any rules or procedures adopted by the Bank and any provider in connection with use of the Online Service and he/she has provided necessary training in its use. The Client shall not (and shall not permit any third party) to copy, use, analyze, modify, decompile, disassemble, reverse engineer, translate or convert any software provided to him/her in connection with use of the Online Service or distribute the software or the Online Service to any other third party. 3. Account balances / Schedule of fees The Client has access to accounts balances and statements through the Online Service offered by the Bank. At its own discretion, the Bank may send account balances. Interest and commissions are net. Taxes, dues and other expenses are debited from Client’s account. The Bank shall be remunerated according to the schedule of fees as valid and altered by the Bank from time to time, particularly if the conditions prevailing on the money market are modified. It will so inform the Client by posting the respective information on its website, by circular or by any other appropriate means. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Il Cliente riconosce che, di tanto in tanto e per qualsiasi motivo, il Servizio Online potrebbe essere non operativo o altrimenti inutilizzabile a causa di manutenzione, malfunzionamento dell’hardware, difetti del software, assistenza o interruzione della trasmissione o altra causa, e accetta di sollevare la Banca e i fornitori da qualsiasi responsabilità per eventuali danni derivanti dall’indisponibilità del Servizio Online. Il Cliente dichiara di aver predisposto misure alternative che rimarranno in vigore per la trasmissione e l’esecuzione dei suoi ordini, qualora, per qualsiasi motivo, le circostanze impediscano la trasmissione e l’esecuzione della totalità o di parte dei suoi ordini tramite il Servizio Online. Il Cliente dichiara e garantisce di essere pienamente abilitato ad effettuare questo tipo di transazioni online, di non essere colpito da alcuna incapacità giuridica che gli impedisca di effettuare operazioni di trading, e di operare sempre in conformità con tutte le leggi, le norme e le disposizioni vigenti per la sua attività. Il Cliente dichiara di conoscere e di rispettare tutte le norme e le procedure adottate dalla Banca e da qualsiasi fornitore concernenti l’uso del Servizio Online, nonché di aver ricevuto la necessaria formazione per il relativo uso. Il Cliente non potrà (e non permetterà a terzi di) copiare, usare, analizzare, modificare, decompilare, disassemblare, reingegnerizzare, tradurre o convertire qualsiasi applicazione software fornitagli nell’ambito dell’uso del Servizio Online, né distribuire il software o il Servizio Online a terzi. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito I. GENERAL BUSINESS CONDITIONS / CONDIZIONI COMMERCIALI 3. SALDI DEI CONTI / PROSPETTO DELLE COMMISSIONI Il Cliente ha accesso ai saldi dei conti e agli estratti conto tramite il Servizio Online offerto dalla Banca. La Banca potrà inviare i saldi dei conti a propria discrezione. Gli interessi e le commissioni si intendono al netto. Le imposte, i diritti e altre spese verranno addebitati sul conto del Cliente. Le commissioni dovute alla Banca verranno calcolate in conformità con il prospetto delle commissioni in vigore e di volta in volta modificato dalla medesima, in particolare qualora si modifichino le condizioni prevalenti sul mercato monetario. La Banca ne darà comunicazione al Cliente mediante la pubblicazione delle rispettive informazioni sul proprio sito web, tramite circolare o qualsiasi altro mezzo adeguato. 13/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito 4. General rules 4. REGOLE GENERALI 4.1 Validity 4.1 VALIDITÀ The present Regulations shall apply to the assets and other objects (hereinafter referred to as “assets”) entrusted to and accepted by the Bank for safe custody. In the case of special agreements or special custody accounts governed by special regulations, these shall apply in addition to the present Regulations. In the event of differences, the Regulations shall prevail. Il presente Regolamento si applicherà alle attività e ad altri valori (in seguito definiti “Attività”) affidati alla Banca, e da questa accettati, per la custodia in deposito. Nel caso di accordi speciali o conti di custodia speciali disciplinati da disposizioni particolari, queste avranno validità in aggiunta al presente Regolamento. In caso di conflitto, prevarrà il Regolamento. 4.2 ATTIVITÀ ACCETTATE 4.2 Accepting assets In genere la Banca accetterà: In general, the Bank will accept : a) Monies on all kinds; a) Somme di denaro di qualsiasi tipo; b) Securities on all kinds, which are tradable on the Banks system, for safekeeping in an open custody account; b) Valori mobiliari di qualsiasi tipo che siano negoziabili nel sistema bancario, per la conservazione in un conto di custodia aperto; c) Money and capital market investments not evidenced in the form of securities, for book-entry and administration in an open custody account. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Bank may in its sole discretion refuse to accept assets without further explanation. c) Investimenti nel mercato monetario e nei mercati dei capitali in forme diverse da quella dei valori mobiliari, per la scrittura contabile e l’amministrazione in un conto di custodia aperto. Fatto salvo quanto precede, la Banca potrà a propria insindacabile discrezione rifiutare di accettare alcune attività senza dare ulteriori spiegazioni. 4.3 Duty of care The Bank undertakes to safeguard the assets it holds in safe custody with the same degree of care as it does with regard to its own assets. 4.4 Delivery Provided both the specific period of notice and mandatory legal provisions are respected, the Client may request at any time that assets be delivered or made available to him/her. The customary periods of time required for such delivery shall apply. 4.5 Form of safekeeping The Bank is expressly authorized to deposit the assets with an external custodian for the account of and at the risk of the Client. Unless instructed otherwise, the Bank is entitled to hold the assets with other assets of their kind, transfer them to a third party for safekeeping or hold them in collective depository. If the assets are held in collective depository in Switzerland, the Client shall have a right of co-ownership based on the relation between the value of the assets deposited by him/her and the total value of the collective depository. This does not apply to assets that must be held separate due to specific reasons. Assets held abroad shall be subject to the laws and established practices of the place where they are held. Assets in registered form are only registered in the name of the Client on his/her specific request. In such case, he or she accepts that his/her name may be made known to any third party custodian. In cases where registering the assets in the Client’s name is not customary or possible, the Bank may register such assets in its own name or the name of a third party for the account of and at the risk of the Client. Assets redeemable by drawings may also be held in collective custody. Assets so redeemed shall be distributed among the clients by the Bank in a second drawing, using a method which guarantees all clients the same chance of being considered as in the first drawing. 4.6 Deferred printing of certificates If the physical issuance of certificates is deferred, for the period during which the assets are held in the Bank’s custody, the Bank is expressly authorized to : a) have the certificates in question cancelled upon their delivery into the custody account, b)carry out, during the period the assets are held in custody and for the account of the Client, the usual administration services and issue the requisite instructions to the issuer and/or obtain the necessary information, and c) request the printing of the certificates for the Client in case they are withdrawn from the account. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 4.3 DOVERE DI DILIGENZA La Banca si impegna a custodire le attività che conserva in custodia con la stessa diligenza con cui custodisce le proprie attività. 4.4 CONSEGNA A condizione che vengano rispettate sia lo specifico periodo di notifica che le disposizioni legali obbligatorie, il Cliente potrà richiedere in qualsiasi momento la consegna o la messa a disposizione delle sue attività. In tal caso si applicheranno gli abituali periodi di tempo necessari per tale consegna. 4.5 FORMA DI CUSTODIA La Banca è espressamente autorizzata a depositare le attività presso un depositario esterno per conto ed a rischio del Cliente. Salvo diversamente disposto, la Banca ha facoltà di detenere dette attività con altre dello stesso tipo, di trasferirle a terzi per la custodia o di detenerle presso depositari collettivi. Qualora le attività vengano detenute presso un depositario collettivo in Svizzera, il Cliente vanterà un diritto di comproprietà in proporzione al rapporto tra il valore delle attività depositate dal Cliente e il valore totale del depositario collettivo. Ciò non si applica alle attività che devono essere tenute separate per motivi specifici. Le attività detenute all’estero saranno soggette alle normative e alle prassi vigenti nel luogo dove sono detenute. Le attività in forma nominativa sono registrate solo a nome del Cliente su sua specifica richiesta. In tal caso, il Cliente accetta che il suo nome venga reso noto ad eventuali depositari terzi. Qualora la registrazione delle attività a nome del Cliente non sia prevista dalla prassi o non sia consentita, la Banca potrà registrare tali attività a nome proprio o di una terza parte per conto e a rischio del Cliente. Le attività rimborsabili mediante estrazioni potranno anche essere detenute in un deposito collettivo. Le attività così rimborsate verranno distribuite tra i clienti dalla Banca in una seconda estrazione, effettuata con un metodo che garantisca a tutti i clienti la stessa probabilità di essere considerati come nella prima estrazione. 4.6 STAMPA DIFFERITA DEI CERTIFICATI General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito II. SAFE CUSTODY REGULATION / REGOLAMENTO PER LA CUSTODIA DEI VALORI IN DEPOSITO Qualora venga differita l’emissione fisica dei certificati, per il periodo durante il quale le attività sono detenute in custodia presso la Banca questa sarà espressamente autorizzata a: a) far annullare i certificati in questione alla loro consegna nel conto di custodia; b) nel periodo in cui le attività vengono detenute in custodia e per conto del Cliente, svolgere gli abituali servizi di amministrazione e inviare le istruzioni necessarie all’emittente e/o ottenere le necessarie informazioni; e c) richiedere la stampa dei certificati per il Cliente qualora essi vengano prelevati dal conto. 14/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito 4.7 Administration 4.7 AMMINISTRAZIONE In the absence of any specific instructions from the Client, the Bank shall perform the customary administration services, such as collecting coupons and redeemable amounts, obtaining new coupon sheets, monitor drawings, calls, conversions and subscription rights, etc., and shall generally prompt the Client to make those arrangements which fall to him/her as specified hereafter. To proceed in such manner, the Bank will use the usual sources of information available to it as a basis. It will not, however, assume any responsibility for these activities. In cases the Bank is unable to administer individual assets in the customary manner it shall notify the Client thereof, using any appropriate means. In assenza di specifiche istruzioni da parte del Cliente, la Banca fornirà gli abituali servizi di amministrazione, come la raccolta delle cedole e degli importi rimborsabili, l’ottenimento di nuovi fogli cedole, il monitoraggio delle estrazioni, i richiami, le conversioni e i diritti di sottoscrizione ecc., e inviterà generalmente il Cliente a prendere tutti i provvedimenti di sua competenza, come specificato di seguito. A tale scopo, la Banca farà ricorso alle abituali fonti d’informazione disponibili, senza tuttavia assumersi alcuna responsabilità per tali attività.Qualora la Banca non sia in grado di amministrare singole attività nel modo abituale, ne darà comunicazione al Cliente, usando qualsiasi mezzo adeguato. In the case of registered shares not bearing coupons, administrative services shall only be performed if the address to which dividends and subscription rights are to be delivered is that of the Bank. In the absence of any instructions otherwise, the Client is responsible for making all arrangements in respect of the safeguarding of the rights accruing to the assets. In particular, these rights cover such aspects as the issuing of instructions for conversions, the exercising or purchase/sale of subscription rights as well as the exercising of conversion rights. If instructions are not received in due course, the Bank is authorized, but not obliged, to act as it deems appropriate. Nel caso di azioni nominative senza cedole, i servizi amministrativi verranno forniti esclusivamente se l’indirizzo al quale dovranno essere inviati i dividendi e i diritti di sottoscrizione coinciderà con quello della Banca. Salvo diverse istruzioni, il Cliente ha la responsabilità di prendere tutte le misure necessarie per la salvaguarda dei diritti maturati il relazione alle attività. In particolare, tali diritti riguardano aspetti quali l’invio di istruzioni per la conversione, l’esercizio o la compravendita dei diritti di sottoscrizione nonché l’esercizio dei diritti di conversione. Qualora le istruzioni non vengano ricevute a tempo debito, la Banca avrà la facoltà ma non l’obbligo di agire come riterrà più opportuno. 4.8 ACQUISIZIONE DI ATTIVITÀ SU BASE FIDUCIARIA 4.8 Acquisition of assets on a fiduciary basis Where it is not customary or possible to transfer ownership of assets to the Client, the Bank may acquire them or cause them to be acquired in either (i) its own name or (ii) the name of a third party and may exercise the rights arising from the assets acquired, or cause them to be exercised. Such transaction will, however, be executed for the account and at the risk of the Client. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 Qualora non sia previsto dalla prassi o non sia consentito cedere la proprietà delle attività al Cliente, la Banca potrà acquisirle o indurre altri ad acquisirle a (i) proprio nome o (ii) a nome di una terza parte, e potrà esercitare i diritti derivanti dalle attività acquisite o indurre altri ad esercitarli. Tuttavia, tale transazione verrà eseguita per conto e a rischio del Cliente. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito II. SAFE CUSTODY REGULATION / REGOLAMENTO PER LA CUSTODIA DEI VALORI IN DEPOSITO 15/16 | Page General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito 5. Termination The Bank and the Client are entitled to terminate their relationship in writing at any time without further explanation. The termination also extinguishes the Client’s right to use the installations and software the Bank has made available. 5. ESTINZIONE DEL CONTRATTO La Banca e il Cliente hanno diritto ad estinguere il loro rapporto per iscritto, in qualsiasi momento, senza fornire ulteriori spiegazioni. Con l’estinzione cessa inoltre il diritto del Cliente di usare le installazioni e il software resi disponibili dalla Banca. Upon or any time after termination, the Bank shall have the right (but shall not be obliged) to close out all or any part of any open transaction in effect at the date of termination and the terms of this agreement shall continue to bind both parties in relation to such transactions. All’atto dell’estinzione o in qualsiasi momento successivo, la Banca avrà la facoltà (ma non l’obbligo) di liquidare, in tutto o in parte, le transazioni ancora aperte alla data dell’estinzione; i termini del presente Contratto resteranno vincolanti per le parti in relazione a tali transazioni. In case of death, liquidation, Bankruptcy of the Client or any other similar cause, the Bank may terminate the relation with immediate effect and without notice. The Bank shall then close the Client’s positions and keep the investments under custody until instructions are provided to the Bank by the competent authority. In caso di decesso, liquidazione, fallimento del Cliente o di qualsiasi altro evento simile, la Banca potrà estinguere la relazione con effetto immediato e senza preavviso. La Banca chiuderà quindi le posizioni del Cliente e manterrà la custodia degli investimenti finché non riceverà apposite istruzioni dall’autorità competente. 6. Indemnity and limitation of liability 6. RISARCIMENTO E LIMITAZIONE DELLA RESPONSABILITÀ The Client hereby agrees to indemnify the Bank and keep the Bank indemnified against all losses, expenses, costs (including legal costs), and liabilities whatsoever which arise, directly or indirectly, as a result of the Bank proper performance of its obligations, or the enforcement of its rights pursuant to these Conditions and Regulations, or by reason of any breach by the Client of any applicable conditions. Con il presente Contratto il Cliente accetta di tenere la Banca indenne da qualsiasi perdita, spesa, costo (inclusi quelli legali) e passività di qualsiasi tipo derivanti, direttamente o indirettamente, dal corretto adempimento degli obblighi da parte della Banca o dall’esercizio dei diritti di quest’ultima, ai sensi delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento, o da qualsiasi violazione da parte del Cliente di qualsiasi condizione vigente. These indemnities shall be in addition to any other right, indemnity or claim which the Bank may have under the general law and shall not be affected by any variation or limitation of these Conditions and Regulations. Tali indennizzi andranno ad aggiungersi a tutti gli altri diritti, indennizzi e risarcimenti che possano essere riconosciuti alla Banca ai sensi della normativa generale, e non saranno condizionati da alcuna variazione o limitazione delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento. These indemnities shall survive termination of these Conditions and Regulations. Tali indennizzi saranno dovuti anche dopo l’estinzione delle presenti Condizioni e del presente Regolamento. 7. Modification 7. MODIFICA At any time, the Bank is entitled to alter the present Conditions and Regulations and the services offered. Such modification shall be reported to the Client by appropriate means and will be deemed accepted unless the Client submits a written objection within one month from the date of communication. In qualsiasi momento, la Banca avrà diritto a modificare le presenti Condizioni e il presente Regolamento e i servizi offerti. Eventuali modifiche verranno comunicate al Cliente tramite mezzi adeguati e saranno considerate accettate salvo qualora il Cliente invii un reclamo scritto entro un mese dalla data di comunicazione. 8. Reservation of legal regulations 8. RISERVA DI DISPOSIZIONI LEGALI Any existing or future legal and regulatory provisions in the field of Banking services, data protection, money laundering, the operation and use of the Internet or any other regulation applicable in the frame of the services offered by the Bank remain reserved and shall apply to the provision of the Bank’s services as from the date when they come into effect and to the extent the present Conditions and Regulations do not provide otherwise. Sono fatte salve le disposizioni legislative e regolamentari, presenti e future, nel campo dei servizi bancari, della protezione dei dati personali, del riciclaggio di denaro, del funzionamento e dell’uso di Internet o qualsiasi altra disposizione vigente nell’ambito dei servizi offerti dalla Banca, e si applicheranno alla fornitura dei servizi della Banca dalla data della loro entrata in vigore e nella misura in cui le presenti Condizioni e il presente Regolamento non prevedano diversamente. All transactions in the Client’s account shall be sub ject to the bylaws, constitution, rules, regulations, oversight, customs and usages of the exchange or market, and its clearing house, if any, on which such transactions are executed and/or cleared by the Bank or its agents, including but not limited to the Bank’s subsidiaries and affiliates. Tutte le transazioni effettuate tramite il conto del Cliente saranno soggette alle ordinanze, alla costituzione, ai regolamenti, alle disposizioni, alla supervisione, agli usi e alle prassi delle borse valori o dei mercati, e dell’eventuale stanza di compensazione, in cui tali transazioni vengono eseguite e/o compensate dalla Banca o dai suoi agenti, incluse, a titolo esemplificativo e non esaustivo, le società controllate e affiliate della Banca. 9. Applicable law and jurisdiction These General Business Conditions and Safe Custody Regulations shall be governed by Swiss law. The place of performance and the place of jurisdiction for any proceedings whatsoever, including for the Client domiciled abroad, is NEUCHÂTEL, Switzerland. However, the Bank retains the right to file an action in the country of domicile of the Client or before any other competent court, in which case Swiss law will still apply. General Business Conditions And Safe Custody Regulations / Condizioni commerciali e Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito III. SPECIAL CLAUSES / CLAUSOLE SPECIALI INTRODUCTION 9. NORMATIVA VIGENTE E GIURISDIZIONE Le presenti Condizioni commerciali e il presente Regolamento per la custodia dei valori in deposito saranno disciplinati dalla normativa svizzera. Il luogo di esecuzione e il foro competente per qualsivoglia procedimento, ivi compreso per il Cliente domiciliato all’estero, è NEUCHÂTEL, Svizzera. Tuttavia, la Banca si riserva la facoltà di intentare un’azione giudiziaria nel paese di domicilio del Cliente o davanti a qualsiasi altro tribunale competente, nel qual caso resterà applicabile la legislazione svizzera. Translation of documents is provided for the added convenience of the Client. In the event of conflict between the original English text and any translation or any other agreement between the Bank and the Client, the English version shall take precedence. La traduzione dei documenti è per comodità di lettura. In caso di conflitto tra la versione originale inglese in corso e qualsiasi altra versione tradotta, la versione inglese sarà quella valida e prevarrà sulle altre. D-CLIENT-01-07-EN_IT_v1.0 16/16 | Page Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari What this DOCUMENT is about I CONTENUTI DEL PRESENTE DOCUMENTO 1_ Since 1 February 1997, commercial trading in securities is governed by the Stock Exchange Act (Swiss Federal Act on Stock Exchanges and Securities Trading of 24 March 1995). The Act requires securities dealers to inform their clients about types of transaction and investments that may involve special risks. This brochure contains information about these risks. The term “securities dealer” is used in this brochure to mean your bank. 1_ Dal 1° febbraio 1997 la negoziazione di valori mobiliari è regolata dalla Legge federale del 24 marzo 1995 sulle borse e il commercio di valori mobiliari (Legge sulle borse, LBVM). Questa normativa impone agli intermediari finanziari di informare i loro clienti sui tipi di transazioni e gli investimenti che potrebbero comportare rischi particolari. Il presente opuscolo fornisce informazioni su tali rischi. In questo documento per “intermediario finanziario” si intende la Sua banca. Securities and the risks involved I VALORI MOBILIARI E I RISCHI AD ESSI ASSOCIATI 2_ Securities are standardised certificates which are suitable for mass trading, as well as rights not represented by a certificate but with similar features (book-entry securities). They include equities, bonds, units of mutual funds and derivatives. They are offered to the public in a standardised form and denomination, or are sold to more than 20 clients. 2_ Per valori mobiliari, o titoli, si intendono certificati standardizzati e idonei alla negoziazione su grande scala, nonché diritti non rappresentati da certificati ma aventi caratteristiche simili (titoli scritturali). Tra questi si annoverano le azioni, le obbligazioni, le quote di fondi comuni d’investimento e i derivati. I valori mobiliari sono offerti al pubblico in una forma e con una denominazione standardizzata, o sono venduti a più di 20 clienti. 3_ Derivatives are financial instruments for which the price is derived either from assets (underlyings) such as equities, bonds, precious metals and other commodities; or from benchmark rates such as currencies, interest rates and indices; or from credit or catastrophe events. 3_ I derivati sono strumenti finanziari il cui prezzo viene derivato da attività (sottostanti) quali azioni, obbligazioni, metalli preziosi e altre materie prime; da tassi di riferimento quali valute, tassi di interesse e indici; o da eventi creditizi o catastrofici. 4_ An equity option, for example, derives its value from the “underlying” equity. In the following chapters, we will go on to look at different types of derivatives, including forwards, futures and structured products as well as options. 4_ Ad esempio, un’opzione su azioni trae il suo valore dal titolo azionario “sottostante”. Nelle prossime sezioni esamineremo diversi tipi di derivati, compresi i contratti a termine, i future e i prodotti strutturati, nonché le opzioni. 5_ Securities, and especially derivatives, entail financial risks. Derivatives are financial instruments based on a separate underlying and are often composed of different elements, which sometimes makes them difficult to understand. This is particularly true for “exotic” options. This brochure explains these financial instruments and their associated risks. However, it is no substitute for the product descriptions provided by issuers and securities dealers. If you have any further questions, consult your securities dealer. 5_ I valori mobiliari, e specialmente i derivati, comportano rischi finanziari. I derivati sono strumenti finanziari basati su altre attività sottostanti e sono spesso composti di diversi elementi, il che talvolta rende difficoltosa la loro comprensione. Ciò è particolarmente vero per le opzioni “esotiche”. Il presente opuscolo spiega tali strumenti finanziari e i rischi ad essi associati, senza tuttavia sostituire le descrizioni dei prodotti fornite dagli emittenti e dagli intermediari finanziari. Per ulteriori ragguagli si raccomanda all’investitore di consultare il suo intermediario di fiducia. 6_ There are basically two types of financial instruments : those with limited risk and those with unlimited risk. The purchase of equities or options involves limited risk. At worst, you will lose the entire amount of your invested capital and not make a profit. 6_ Esistono essenzialmente due tipi di strumenti finanziari: quelli a rischio limitato e quelli a rischio illimitato. L’acquisto di azioni o opzioni comporta un rischio limitato. Al peggio, l’investitore perde l’intero ammontare del capitale investito e non realizza alcun profitto. 7_ On the other hand, there are certain types of derivatives that can require an additional outlay of capital over and above the original investment. The obligation to make such margin payments can amount to many times the purchase price of the investment. Unlimited risk is particularly associated with : 7_ D’altro canto, vi sono certi tipi di derivati che possono richiedere un esborso addizionale di capitale in aggiunta all’investimento originario. Questo obbligo di versamento aggiuntivo può ammontare a un multiplo molto elevato del prezzo di acquisto dell’investimento. Il rischio illimitato è in particolare associato a: + selling (writing) an uncovered call option, + selling (writing) a put option or + forwards and futures transactions. + la vendita (sottoscrizione) di un’opzione call senza copertura + la vendita (sottoscrizione) di un’opzione put + le transazioni su contratti a termine e future. Your right to information 8_ The Stock Exchange Act obliges securities dealers to inform their clients about the risks associated with a given type of transaction. 9_ The obligation to inform is dependent of the client’s level of experience and specialist knowledge in the area concerned. Clients must be informed about transactions that entail higher levels of risk or have a complex risk profile, but not about the specific risks relating to individual transactions. IL DIRITTO ALL’INFORMAZIONE 8_La Legge sulle borse impone agli intermediari finanziari di informare i loro clienti sui rischi associati a un dato tipo di transazione. 9_ L’obbligo di fornire informazioni dipende dal livello di esperienza e di conoscenze specialistiche del cliente in materia. I clienti devono essere informati sulle transazioni che comportano livelli di rischio più elevati o che presentano un profilo di rischio complesso, ma non sui rischi specifici di singole transazioni. Limits of the duty to provide information LIMITI ALL’OBBLIGO DI FORNIRE INFORMAZIONI 10_ If you are already familiar with the risks pertaining to a particular type of transaction, you may choose not to receive this information from your securities dealer. 10_ Chi già conosce i rischi relativi a un particolare tipo di transazione può scegliere di non ricevere tali informazioni dal proprio intermediario finanziario. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 Introduction / Introduzione Introduction / introduzione 1/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 11_ Securities dealers are not obliged to inform you about normal risks. These are not covered in this brochure. Normal risks chiefly include : – The risks attached to conventional, widely used financial instruments, such as equities, bonds and collective investments (e.g. units in mutual funds) 12_ For example, the debtor (issuer) can get into financial difficultiesmaking him/her incapable of payment (credit and default risks). Country risks 13_ A country risk can arise if a country restricts securities trading, for instance by imposing economic sanctions or currency restrictions. Settlement risks 14_ A settlement risk occurs when you have to pay the purchase price of a security in advance but do not actually receive the security until later. In this event, the risk is that you will pay the purchase price and receive the securities late or even not at all. Conversely, when you are obliged to deliver securities that you have sold, you may not simultaneously receive the purchase price from the buyer. Settlement risks mainly occur in emerging markets (see 209). Risks associated with custody of financial instruments 15_ Financial instruments can be held either in your country or abroad. Generally, they are held where they are most often traded, and are governed by the regulations that apply there. If your securities dealer becomes insolvent, Swiss law stipulates that the financial instruments deposited with that dealer will not form part of their bankruptcy assets, but will be kept separate for your benefit. However, insolvency proceedings can delay the transfer of the financial instruments to you or another securities dealer. If a third-party custodian becomes insolvent, the law in many countries provides that the financial instruments deposited with that custodian by your securities dealer are also normally protected. In less advanced markets (see 196 ff.), however, financial instruments deposited with a third-party custodian in the country concerned may be included in the custodian’s bankruptcy assets. Liquidity risk 16_ Liquidity risk is the risk that you will not always be able to obtain an appropriate price for your investment when you sell it. When certain securities and derivatives are impossible to sell, or can only be sold with difficulty and at a sharply reduced price,the market is said to be illiquid. Illiquidity risk occurs especially with shares in unlisted or poorly capitalised companies, investments with sales restrictions, and certain structured products. 17_ The Stock Exchange Act does not require securities dealers to inform you about risks associated with investments in alternative (nontraditional) investments and emerging or developing markets. Given the significance of these types of investment, we nonetheless explain the risks typically encountered in these markets in Section Two of this brochure (see 196 ff. below). 18_ This brochure does not deal with the issues of taxation or any other legal consequences pertaining to securities transactions (e.g. duties of disclosure). We advise you to look into these matters yourself or obtain professional advice. 19_ Please read through this document carefully and consult your securities dealer if you have any questions. 11_ L’intermediario finanziario non è tenuto a informare l’investitore sui rischi normali, i quali pertanto non sono trattati nel presente opuscolo. Sono rischi normali: – I rischi associati a strumenti finanziari convenzionali, ampiamente utilizzati, come azioni, obbligazioni e gli investimenti collettivi di capitale (ad es., le quote di fondi comuni d’investimento) 12_ Per esempio, un debitore (emittente) può trovarsi in difficoltà finanziarie, che lo rendono insolvente (rischio di credito e di insolvenza). Rischio paese 13_ Un rischio paese può sorgere allorché una nazione limita la compravendita di valori mobiliari, ad esempio introducendo sanzioni economiche o restrizioni valutarie. Rischio di adempimento 14_ Un rischio di adempimento può sorgere qualora l’investitore debba pagare in anticipo il prezzo di acquisto di un titolo che tuttavia gli viene consegnato in un momento successivo. In questo caso, l’investitore corre il rischio di pagare il prezzo di acquisto e di ricevere i valori mobiliari in ritardo o di non riceverli affatto. Il rischio di adempimento si verifica anche nel caso contrario, allorché a fronte dell’obbligo di consegnare i valori mobiliari che ha venduto, l’investitore potrebbe non ricevere simultaneamente il prezzo d’acquisto dal compratore. I rischi di adempimento sono tipici dei mercati emergenti (si veda §209). Introduction / Introduzione Introduction / introduzione Rischi associati alla custodia degli strumenti finanziari 15_Gli strumenti finanziari possono essere custoditi in patria o all’estero. Di solito sono custoditi nel luogo dove vengono negoziati con maggiore frequenza e vi si applicano le normative vigenti in quel paese. Se un intermediario finanziario diventa insolvente, la legislazione svizzera stabilisce che gli strumenti finanziari affidatigli in custodia non diventino parte della massa fallimentare, ma siano tenuti distinti a beneficio dell’investitore. Tuttavia, le procedure fallimentari possono ritardare il trasferimento degli strumenti finanziari all’investitore o a un altro intermediario finanziario. Se un depositario terzo diventa insolvente, la legislazione di molti paesi prevede ugualmente la tutela degli strumenti finanziari depositati in custodia presso quest’ultimo dall’intermediario finanziario. Tuttavia, nei mercati meno avanzati (si veda §196 e ss.), gli strumenti finanziari affidati in custodia a un depositario terzo nel paese in questione potrebbero essere inclusi nella massa fallimentare del depositario. Rischio di liquidità 16_ Per rischio di liquidità si intende il rischio che un investitore non possa sempre ottenere un prezzo adeguato all’atto della liquidazione del suo investimento. Quando determinati valori mobiliari e derivati non possono essere venduti, o sono vendibili unicamente con grande difficoltà e a prezzi fortemente ridotti, si dice che il mercato è illiquido. Il rischio di illiquidità si verifica specialmente con i titoli azionari di società non quotate o a bassa capitalizzazione, nel caso di investimenti con restrizioni alla vendita e con certi prodotti strutturati. 17_ La legge sulle borse non impone agli intermediari finanziari di informare i clienti sui rischi associati agli investimenti in strumenti alternativi (non tradizionali) e nei mercati emergenti o in via di sviluppo. Tuttavia, data l’importanza di questi tipi di investimenti, spiegheremo i rischi tipicamente associati a tali mercati nella seconda parte di questo opuscolo (si veda §196 e ss.). 18_ Il presente opuscolo non affronta i temi della tassazione o degli altri obblighi legali connessi alle operazioni su valori mobiliari (ad es., gli obblighi di informativa). Si raccomanda di approfondire tali argomenti o di ottenere consulenza professionale al riguardo. 19_ Si invita l’investitore a leggere attentamente il presente opuscolo e a consultare il proprio intermediario di fiducia per ulteriori delucidazioni. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 2/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Options OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 20_ As the buyer of an option, you have the right to buy a specified amount of an underlying asset (often simply referred to as the “underlying”) from the seller (call option) or sell it to the seller (put option) at a predefined price (strike price) up until a set time (expiration date). The price you pay for this right is called the premium. 20_ L’acquirente di un’opzione ottiene il diritto di acquistare dal venditore (opzione call) o di vendere a quest’ultimo (opzione put) una determinata quantità di un’attività sottostante (spesso denominata semplicemente il “sottostante”), a un prezzo predefinito (detto prezzo d’esercizio o strike price) fino a una data prestabilita (data di scadenza). Il prezzo pagato per acquisire tale diritto è detto premio. 21_ As the seller (writer) of an option, you must sell the underlying to the buyer at the strike price (call option) or buy the underlying from him/her at the strike price (put option) up until the expiration date, irrespective of the market value of the underlying asset at the time, if he/she chooses to exercise the option. 22_ The price of an option is closely linked to that of the underlying asset. Any change in the market value of the underlying asset will result in a greater change in the price of the option. This is termed the leverage effect. It means you participate disproportionately in any rise or fall in the market value of the underlying asset. 23_ The commonest underlying assets for options are : – – – – assets such as equities, bonds, precious metals and other commodities, benchmark rates such as currencies, interest rates and indices, derivatives and any combination of the above. 24_ “American-style” options can normally be exercised on any trading day up to the expiration date. 25_ “European-style” options can only be exercised on the expiration date, in other words the date set out in the contract. This does not, however, normally affect their tradability on the secondary market (e.g. on a stock exchange). 26_ Where a call option provides for physical settlement, you can require the seller of the option (writer) to deliver the underlying asset when you exercise the option. With a put option, the writer is obliged to buy the underlying asset from you. 27_ If an option provides for cash settlement, you are only entitled to a sum of money corresponding to the difference between the strike price and the current market value of the underlying asset. 28_ A call option is in the money if the current market value of the underlying asset is above the strike price. A put option is in the money if the current market value of the underlying asset is below the strike price. An option that is in the money is said to have an intrinsic value. 29_ A call option is out of the money if the current market value of the underlying asset is below the strike price. A put option is out of the money if the current market value of the underlying asset is above the strike price. In this case, the option has no intrinsic value. 30_ If the current market value of the underlying asset is the same as the strike price, the option is at the money. In this case, it has no intrinsic value. 21_ Il venditore (sottoscrittore) di un’opzione è obbligato a vendere all’acquirente (opzione call) o a comprare da quest’ultimo (opzione put) il sottostante al prezzo d’esercizio entro la data di scadenza, indipendentemente dal valore di mercato del sottostante all’atto della transazione, qualora l’acquirente decida di esercitare il diritto di opzione. 22_ Il prezzo di un’opzione è strettamente correlato a quello dell’attività sottostante. Qualsiasi variazione del valore di mercato del sottostante si traduce in una variazione ancora più pronunciata del prezzo dell’opzione. Questo è detto effetto leva, e fa sì che l’investitore partecipi in misura più che proporzionale all’aumento o alla diminuzione del valore di mercato del sottostante. 23_ Le più comuni attività sottostanti a un’opzione sono: 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI - valori patrimoniali come azioni, obbligazioni, metalli preziosi e altre materie prime, - valori patrimoniali come azioni, obbligazioni, metalli preziosi e altre materie prime, - tassi di riferimento, come valute, tassi di interesse e indici - derivati - qualsiasi combinazione dei suddetti. 24_ Le opzioni “americane” possono essere normalmente esercitate in qualsiasi giorno di contrattazione fino alla scadenza. 25_ Le opzioni “europee” possono essere esercitate soltanto alla data di scadenza, cioè alla data stabilita nel contratto. Ciò tuttavia non condiziona normalmente la loro negoziabilità nel mercato secondario (ad es., in borsa). 26_ Laddove un’opzione prevede la consegna fisica del sottostante, l’investitore può esigere che il venditore dell’opzione (sottoscrittore) fornisca il sottostante all’atto di esercizio dell’opzione. Nel caso di un’opzione put, il sottoscrittore è obbligato ad acquistare il sottostante dall’investitore. 27_ Laddove un’opzione prevede la liquidazione in contanti, l’investitore ha il diritto a ricevere una somma in denaro corrispondente alla differenza tra il prezzo d’esercizio e il valore di mercato corrente dell’attività sottostante. 28_ Un’opzione call è detta “in the money” se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è superiore al prezzo d’esercizio. Un’opzione put è “in the money” se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è inferiore al prezzo d’esercizio. Se un’opzione è “in the money”, si dice che ha valore intrinseco. 29_ Un’opzione call è detta “out of the money” se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è inferiore al prezzo d’esercizio. Un’opzione put è “out of the money” se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è superiore al prezzo d’esercizio. In tal caso, l’opzione non ha valore intrinseco. 30_ Se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è pari al prezzo d’esercizio, l’opzione è “at the money”. In tal caso, l’opzione non ha valore intrinseco. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 3/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 31_ The price of an option depends on its intrinsic value and on what is referred to as the time value. The latter depends on a variety of factors, including the remaining life of the option and the volatility of the underlying. The time value reflects the chance that the option will be in the money. It is higher for options with a long duration and a very volatile underlying and for options that are at the money. 31_ Il prezzo di un’opzione dipende dal suo valore intrinseco e dal cosiddetto valore temporale. Quest’ultimo dipende da una molteplicità di fattori, tra cui la vita residua dell’opzione e la volatilità del sottostante. Il valore temporale riflette la probabilità che un’opzione sia “in the money”, ed è più elevato per le opzioni con una lunga vita residua e un sottostante molto volatile, nonché per le opzioni che sono “at the money”. 32_ Warrants are options in securitised form that are traded on an exchange or over the counter (OTC). 32_ I certificati d’opzione (warrant) sono opzioni in forma di titoli che vengono negoziate in borsa o fuori borsa. 33_ Exchange Traded Options are non-securitised, but are traded on an exchange. 33_ Le opzioni negoziate in mercati regolamentati (“exchange traded options”) non sono incorporate in titoli ma vengono negoziate in borsa. 34_ OTC (Over-the-Counter) options are neither securitised nor traded on-exchange. They are agreed directly off-exchange between the seller and the buyer. If you wish to cancel (close out) an option of this type before the expiration date, you must make a corresponding offsetting trade with your counterparty. OTC options with precious metals and currencies as their underlying are offered publicly as standardised products. Tailor-made OTC options, by contrast, are specially created for individual investors. 34_ Le opzioni OTC (“over-the-counter”) non sono né incorporate in titoli né negoziate in borsa. Vengono negoziate direttamente tra venditore e acquirente, senza passare per un mercato regolamentato. Se l’investitore desidera liquidare (“close out”) un’opzione di questo tipo prima della scadenza, deve effettuare un’operazione di compensazione corrispondente con la controparte. Le opzioni OTC aventi come sottostante metalli preziosi e valute sono offerte al pubblico come prodotti standardizzati. Le opzioni OTC su misura, invece, sono create appositamente per i singoli investitori. 35_ If you sell an option, you have to deposit either an amount of the underlying asset or another form of collateral for the entire duration of the contract. The level of this collateral or margin is determined by the securities dealer. The exchange stipulates a minimum margin for traded options. 36_ If the margin cover proves insufficient, the securities dealer can require you to provide additional collateral (via a margin call). 37_ Generally speaking, if the market value of the underlying asset falls, so does the value of your call option. The value of your put option tends to fall if the underlying asset rises in value. Normally, the less your option is in the money, the larger the fall in the option’s value. In such cases, value reduction normally accelerates close to the expiration date. 38_ The value of your call option can drop even when the value of the underlying remains un changed or rises. This can happen as the time value of your option falls or if supply and demand factors are unfavourable. Put options behave in precisely the opposite manner. 39_ You must therefore be prepared for a potential loss in the value of your option, or for it to expire entirely without value. In such a scenario, you risk losing the whole of the premium you paid. 40_ If, as writer of a call option, you already have a corresponding quantity of the underlying at your disposal, the call option is described as covered. If the current market value of the underlying exceeds the strike price, your opportunity to make a profit is lost since you must deliver the underlying to the buyer at the strike price, rather than selling the underlying at the (higher) market value. You must have the underlying assets freely available as long as it is possible to exercise the option, i.e. they may not, for example, be blocked by being pledged for other purposes. Otherwise, you are essentially subject to the same risks as when writing an uncovered call option (see 41 below). 41_ If, as writer of a call option, you do not have a corresponding quantity of the underlying at your disposal, the call option is described as uncovered. In the case of options with physical settlement, your potential loss amounts to the price difference between the strike price paid by the buyer and the price you must pay to acquire the underlying assets concerned. Options with cash settlement can incur a loss amounting to the difference between the strike price and the market value of the underlying. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 35_ Chi vende un’opzione è obbligato a depositare, per tutta la durata del contratto, l’ammontare corrispondente del sottostante o un’altra forma di garanzia collaterale. Il livello di questa garanzia o margine viene fissato dall’intermediario finanziario. Per le opzioni negoziate in mercati regolamentati, la borsa stabilisce un margine minimo. 36_ Se margine di copertura si rivela insufficiente, l’intermediario finanziario può esigere dall’investitore garanzie addizionali (tramite un richiamo di margine, o “margin call”). 37_ In termini generali, se il valore di mercato del sottostante diminuisce, anche il valore dell’opzione call subisce un ribasso. Il valore di un’opzione put tende invece a diminuire a fronte di un aumento del valore di mercato del sottostante. Normalmente, quanto meno un’opzione è “in the money”, tanto maggiore è la flessione del suo valore. In questi casi, la riduzione di valore accelera di norma all’approssimarsi della data di scadenza. 38_ Il valore di un’opzione put può diminuire anche laddove il valore del sottostante rimane invariato oppure aumenta; ciò può verificarsi se il valore temporale dell’opzione diminuisce o se le condizioni di domanda e offerta sono sfavorevoli. Le opzioni put presentano un andamento esattamente opposto. 39_ L’investitore deve perciò essere preparato a una perdita di valore dell’opzione o alla possibilità che giunga a scadenza priva di qualsivoglia valore. In tal caso, l’investitore rischia di perdere la totalità del premio originariamente corrisposto. 40_ Se il sottoscrittore di un’opzione call dispone della quantità corrispondente del sottostante, l’opzione è detta coperta. Se il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante è superiore al prezzo d’esercizio, il venditore dell’opzione perde l’opportunità di realizzare un guadagno poiché deve cedere il sottostante all’acquirente al prezzo di esercizio, anziché venderlo al valore di mercato corrente (più elevato). Fintanto che l’esercizio dell’opzione è possibile, il venditore deve mantenere a propria disposizione il sottostante, evitando, ad esempio, che venga bloccato mediante la costituzione in pegno per altri scopi; in caso contrario, si espone agli stessi rischi in cui incorrerebbe con la vendita di un’opzione call scoperta (si veda §41 sotto). 41_ Se il sottoscrittore di un’opzione call non dispone della quantità corrispondente del sottostante, l’opzione è detta scoperta. Nel caso di opzioni con consegna fisica del sottostante, la perdita potenziale è pari alla differenza tra il prezzo d’esercizio pagato dall’acquirente e il prezzo che il venditore deve pagare per acquistare il sottostante in questione. Nel caso di opzioni con liquidazione in contanti, la perdita potenziale è pari alla differenza tra il prezzo d’esercizio e il valore di mercato del sottostante. 4/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 42_ Since the market value of the underlying can move well above the strike price, your potential loss cannot be determined and is theoretically unlimited. 42_ Poiché il valore di mercato del sottostante può superare notevolmente il prezzo d’esercizio, la perdita potenziale del venditore non può essere determinata a priori ed è teoricamente illimitata. 43_ As far as American-style options in particular are concerned, you must also be prepared for the fact that the option may be exercised at a highly unfavourable time when the markets are against you. If you are then obliged to make physical settlement, it may be very expensive or even impossible to acquire the corresponding underlying assets. 43_ Per quanto concerne in particolare le opzioni americane, l’investitore dev’essere preparato all’eventualità che l’opzione venga esercitata in un momento molto sfavorevole, quando le condizioni di mercato sono per lui negative. Nel caso di opzioni con consegna fisica del sottostante, potrebbe essere molto costoso o persino impossibile acquistare il sottostante corrispondente. 44_ You must be aware that your potential losses can be far greater than the value of the underlying assets you lodged as collateral (margin cover) either when entering into the contract or thereafter. 44_ L’investitore deve essere consapevole che le perdite potenziali potrebbero eccedere di gran lunga il valore del sottostante depositato come garanzia (margine di copertura) alla stipula del contratto o successivamente. 45_ As the writer of a put option, you must be prepared for potentially substantial losses if the market value of the underlying falls below the strike price you have to pay the seller. Your potential loss corresponds to the difference between these two values. 46_ As the writer of an American-style put option with physical settlement, you are obliged to accept the underlying assets at the strike price if the buyer exercises the option, even though it may be difficult or impossible to sell the assets and may well entail substantial losses. 47_ Your potential losses can be far greater than the value of any underlying assets you may have lodged as collateral (margin cover). You could in a worst case lose your entire capital invested. 48_ With a covered option, you purchase an underlying asset (equity, bond or currency) and simultaneously write a call option on that same asset. In return, you are paid a premium, which limits your loss in the event of a fall in the market value of the underlying asset. By the same token, however, your potential return from any increase in the asset’s market value is limited to gains up to the option’s strike price. Traditional covered options require that the underlying asset be lodged as collateral, which makes you the covered writer. 49_ Synthetic covered options are based on the idea of replicating traditional covered options. However, this is achieved by means of only one transaction. Both the purchase of the underlying asset and the writing of the call option are carried out synthetically using derivatives. The purchase price of such a product is identical to that of the underlying, less the premium received for the sale of the call option. Hence, the synthetic product is sold more cheaply than its underlying. 50_ Covered options do not contain a hedge against falls in the market value of the underlying. However, by writing a call option (traditional covered option) or by calculating the return from the sale of a call option into the product price (synthetic covered option), any loss in market value of the underlying has less impact than it would in the case of a direct investment. In effect, the option premium thereby limits any loss in the market value of the underlying. 51_ Either cash settlement or physical delivery of the underlying takes place on the expiration date. If the market value of the underlying on expiration is higher than the strike price, the holder of an option with cash settlement is paid a specified cash amount as settlement. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 45_ Il sottoscrittore di un’opzione put deve essere preparato a subire perdite potenziali notevoli se il valore di mercato del sottostante scende al di sotto del prezzo d’esercizio che deve corrispondere. La perdita potenziale è pari alla differenza tra questi due valori. 46_ Il sottoscrittore di un’opzione put americana con consegna fisica del sottostante è obbligato ad accettare le attività sottostanti al prezzo di esercizio qualora l’acquirente eserciti l’opzione, anche se risultasse difficile o impossibile rivendere le attività e se ciò comportasse perdite considerevoli. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 47_ Le perdite potenziali potrebbero eccedere di gran lunga il valore del sottostante depositato come garanzia (margine di copertura). Nel peggiore dei casi l’investitore potrebbe perdere l’intero capitale investito. 48_ Con un’opzione coperta, l’investitore acquista un’attività sottostante (azioni, obbligazioni o valuta) e contemporaneamente vende un’opzione call su quella stessa attività. In cambio l’investitore riceve un premio, che limita la sua perdita nell’eventualità di un ribasso del valore di mercato del sottostante. Per lo stesso motivo, tuttavia, il rendimento potenziale dal rialzo del valore di mercato del sottostante è limitato al prezzo d’esercizio dell’opzione. Le opzioni coperte tradizionali esigono che il sottostante venga depositato come garanzia, in modo che il sottoscrittore divenga un venditore coperto. 49_ Le opzioni coperte sintetiche mirano a riprodurre le opzioni coperte tradizionali. Tuttavia, questo viene realizzato tramite un’unica transazione. Sia l’acquisto del sottostante sia la vendita dell’opzione call sono effettuati sinteticamente con l’utilizzo di derivati. Il prezzo di acquisto di un tale prodotto è identico al prezzo del sottostante al netto del premio ricevuto per la vendita dell’opzione call. Perciò il prodotto sintetico è venduto a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello del sottostante. 50_ Le opzioni coperte non assicurano alcuna copertura contro la diminuzione del valore di mercato del sottostante. Tuttavia, mediante la sottoscrizione di un’opzione call (opzione coperta tradizionale) o mediante l’imputazione dei proventi dalla vendita di un’opzione call nel prezzo del prodotto (opzione coperta sintetica), un eventuale ribasso del valore di mercato del sottostante ha un impatto di minore di quello che avrebbe nel caso di un investimento diretto. In effetti, il premio dell’opzione limita l’eventuale ribasso del valore di mercato del sottostante. 51_ Alla data di scadenza l’adempimento può avvenire mediante la liquidazione in contanti oppure mediante la consegna fisica del sottostante. Se il valore di mercato del sottostante alla data di scadenza è superiore al prezzo d’esercizio, il detentore di un’opzione con liquidazione in contanti riceve in pagamento una somma di denaro specificata. 5/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 52_ If, however, the market value of the underlying is lower than the strike price, the holder of an option with physical settlement receives physical delivery of the underlying asset. In this case, the option holder bears the full risk associated with the underlying. 53_ If you acquire two or more options, based on the same underlying, which differ in either the option type (call or put), the quantity, the strike price, the expiration date or the type of position (long or short), this is referred to as an option strategy. 54_ Given the large number of possible combinations, we cannot go into detail here about the risks involved in any particular case. Before entering into any such transaction, be sure to consult your securities dealer about the particular risks involved. 55_ Unlike the “plain vanilla” put and call options described above, exotic options are linked to additional conditions and agreements. Exotic options come in the form of tailor-made OTC options or as warrants. 56_ Given the special composition of exotic options, their price movements can vary markedly from those of their “plain vanilla” cousins. 57_ You must be aware that larger transactions can trigger price movements even shortly before expiration and that these can render an option worthless. Before buying or selling any exotic options, be sure to seek comprehensive advice about the particular risks involved. 58_ There is no limit to the possible structures for exotic options. We cannot describe in full here the risks involved in any particular case.The examples of exotic options listed below can be broadly divided into two categories : path-dependent options and options on more than one underlying. 59_ Unlike “plain vanilla” options, for path-dependent options, it is not just when the option expires or is exercised that the market value of the underlying is important. You also need to take into account fluctuations in the market value of the underlying during the life of the option when contemplating such an investment. The following are examples of path-dependent options : Barrier options 60_ Your exercise rights for knock-in barrier options only arise if the market value of the underlying reaches a fixed threshold (barrier) within a specified period. Exercise rights for knock-out barrier options expire if the market value of the underlying reaches the specified barrier during the given time period. 61_ If this barrier is between the market value of the underlying at the time the option was entered into and its strike price, it is referred to as a kick-in/kick-out barrier option. 62_ Double-Barrier options have both an upper and a lower barrier and may take the form of knock-in and knock-out barrier options. 63_ When buying a barrier option, you must be aware that your exercise rights only arise when the market value of the underlying reaches the barrier (knock-in/kick-in option) or that they expire irrevocably when that barrier is reached (knock-out/kickout option). 52_ Se invece il valore di mercato del sottostante alla data di scadenza è inferiore al prezzo d’esercizio, il detentore di un’opzione con consegna fisica del sottostante riceve in consegna il sottostante in oggetto. In tal caso, il titolare dell’opzione sostiene l’intero rischio associato al sottostante. 53_ Se l’investitore acquista due o più opzioni basate sullo stesso sottostante, ma che differiscono per tipo (call o put), quantità, prezzo d’esercizio, scadenza o posizione acquisita (lunga o corta), si parla di strategie su opzioni. 54_ Dato l’elevato numero di potenziali combinazioni, è impossibile illustrare in dettaglio in questo contesto tutti i rischi associati alle singole varianti. Prima di effettuare operazioni di questo tipo, si invita l’investitore a rivolgersi al suo intermediario finanziario di fiducia per una consulenza sui rischi specifici che esse comportano. 55_ Contrariamente alle opzioni call e put classiche (“plain vanilla”) più sopra descritte, le opzioni esotiche sono soggette a ulteriori accordi e condizioni. Esse possono presentarsi sotto forma di opzioni OTC “su misura” (tailor-made) o di certificati d’opzione (warrant). 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 56_ Data la particolare composizione delle opzioni esotiche, l’andamento dei prezzi di queste ultime può divergere nettamente da quello delle opzioni “plain vanilla”. 57_ Si deve rammentare che il valore di queste opzioni può essere azzerato, fino all’immediata vigilia della scadenza, da movimenti dei prezzi provocati da grosse operazioni. Prima di comprare o vendere opzioni esotiche, si raccomanda all’investitore di chiedere una consulenza dettagliata sui rischi ad esse associati. 58_ Le possibili strutture delle opzioni esotiche sono potenzialmente infinite. Non è dunque possibile fornire, in questo contesto, una descrizione esaustiva dei rischi associati a ciascun caso particolare. Gli esempi di opzioni esotiche riportati a seguire possono essere suddivisi in due categorie: le opzioni “path-dependent” (cioè “dipendenti dal percorso compiuto”) e le opzioni su molteplici attività sottostanti. 59_ A differenza delle opzioni “plain vanilla”, per le opzioni “path-dependent” il valore di mercato del sottostante è rilevante non soltanto al momento della scadenza o dell’esercizio dell’opzione. Nel valutare un investimento in questo tipo di strumento finanziario, si devono dunque considerare anche le fluttuazioni del valore di mercato del sottostante durante tutta la durata dell’opzione. Illustriamo a seguire alcuni esempi di opzioni “path-dependent”. Opzioni barriera (“barrier option”) 60_ Nel caso di opzioni barriera “knock-in”, i diritti d’opzione sorgono unicamente se il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge una soglia prestabilita (barriera) entro un determinato periodo. Nel caso di opzioni barriera “knock-out”, i diritti d’opzione invece si estinguono se il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge la soglia prestabilita entro tale periodo. 61_ Si definiscono opzioni barriera “kick-in/kick-out” quelle in cui tale barriera, o limite, si situa tra il valore di mercato del sottostante al momento della stipula dell’opzione e il prezzo d’esercizio. 62_ Le opzioni a barriera doppia (“double-barrier option”) prevedono un limite superiore e uno inferiore e sono diffuse sia nella variante “knock-in” sia in quella “knock-out”. 63_ Nell’acquistare un’opzione barriera, si deve rammentare che i diritti d’opzione maturano soltanto quando il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge la barriera (opzioni “knock-in”/”kick-in”), oppure che si estinguono irrevocabilmente al raggiungimento di tale barriera (opzioni “knock-out”/”kick-out”).Opzioni payout (payout option) D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 6/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Payout options 64_ The Payout options accord you the right to payment of a fixed amount agreed in advance. Opzioni payout (payout option) 64_ Le opzioni payout conferiscono il diritto a percepire un importo fissato anticipatamente. 65_ In the case of a digital (otherwise known as “binary”) option, you receive payment if the market value of the underlying reaches a fixed value once during a specified time period (one-touch digital option) or precisely on the day of expiration (all-ornothing option). For the one-touch digital option, payment occurs either immediately the barrier is reached or on the date of expiration (lock-in option). 65_ Nel caso di un’opzione digitale (altresì detta “binaria”), si percepisce un pagamento se il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge un livello prefissato almeno una volta in un intervallo di tempo prestabilito (opzione digitale “one-touch”) oppure esattamente alla data di scadenza (opzione “all-or-nothing”, cioè “tutto o niente”). Per l’opzione digitale “one-touch”, il pagamento ha luogo immediatamente al raggiungimento della barriera oppure alla data di scadenza (opzione “lockin”). 66_ With lock-out options, you only receive the fixed payment if the market value of the underlying does not reach the agreed barrier during a specified time period. 67_ If you sell a payout option you owe the fixed amount if the barrier is reached, regardless of whether or not the option is in the money when exercised or on the expiration date, or to what extent. This means that the amount you owe can be considerably larger than the option’s intrinsic value. Asian options 68_ For Asian options, an average value is derived from the market value of the underlying over a specified time period. This average is used to determine the underlying’s value for an average-rate option and to calculate the strike price for an averagestrike option. 69_ The calculation of an average value for the underlying in the case of the average-rate option can result in the value of the option on the expiration date being considerably lower for the buyer and considerably higher for the writer than the difference between the strike price and the current market value on expiry. 70_ For an average-strike option, the average strike price of a call option can be considerably higher than the price originally set. For an equivalent put option, the strike price can similarly be lower than the price originally set. 66_ Nel caso delle opzioni “lock-out”, si percepisce il pagamento pattuito soltanto se il valore di mercato del sottosante non raggiunge la barriera prestabilita durante un intervallo di tempo specificato. 67_ Con la vendita di un’opzione payout, ci si impegna a versare l’importo pattuito in caso di raggiungimento della barriera, indipendentemente dal fatto e dalla misura in cui l’opzione, al momento dell’esercizio o alla data di scadenza, sia “in the money”. Ciò significa che l’importo dovuto può essere notevolmente superiore al valore intrinseco dell’opzione. Opzioni asiatiche 68_ Nel caso delle opzioni asiatiche, si calcola una media del valore di mercato del sottostante in un intervallo di tempo specificato. Tale media è usata per determinare il valore del sottostante stesso nel caso di un’opzione “average rate” oppure il prezzo d’esercizio per un’opzione “average strike”. 69_ Nel caso di un’opzione “average rate”, il calcolo del valore di mercato medio del sottostante può far sì che alla data di scadenza il valore dell’opzione risulti notevolmente inferiore per l’acquirente e notevolmente più elevato per il venditore rispetto alla differenza tra il prezzo d’esercizio e il valore di mercato corrente del sottostante alla scadenza. Lookback options 71_ With a lookback option, the market value of the underlying is recorded periodically over a specified time period. 70_ Nel caso di un’opzione “average strike”, il prezzo di esercizio medio di un’opzione call può risultare notevolmente più elevato di quanto originariamente pattuito. Per un’opzione put equivalente, il prezzo di esercizio medio può risultare invece nettamente inferiore a quanto originariamente pattuito. 72_ For a strike-lookback option the lowest value (call option) or the highest value (put option) of the underlying becomes the strike price. Opzioni lookback 71_ Nel caso di un’opzione lookback, il valore di mercato del sottostante viene rilevato periodicamente in un intervallo di tempo specificato. 73_ The strike price remains unchanged for a price-lookback option, with the highest value (call option)/lowest value (put option) being used in calculating the option value of the underlying. 72_ Per un’opzione strike-lookback, il prezzo d’esercizio è determinato dal valore minimo (opzione call) o massimo (valore put) del sottostante. 74_ For lookback options, both the calculated strike price and the calculated value of the underlying can vary considerably from the market prices prevailing on the expiration date. If you sell an option of this type, you must be aware that it will always be exercised at the most unfavourable value for you. Contingent options 75_ When you buy a contingent option you must pay the premium only if the market value of the underlying reaches or exceeds the strike price during the life of the option (American-style option) or on the expiration date (European-style option). 76_ You will have to pay the entire premium even if the option is only just at the money or just in the money. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 73_ Nel caso di un’opzione price-lookback il prezzo d’esercizio rimane invariato, mentre il valore massimo (opzion call) o il valore minimo (opzione put) vengono impiegati per il calcolo del valore d’opzione del sottostante. 74_ Nel caso delle opzioni lookback, sia il prezzo d’esercizio sia valore del sottostante così calcolati possono divergere notevolmente dai prezzi di mercato prevalenti alla data di scadenza. Nel vendere un’opzione di questo tipo, si deve rammentare che verrà sempre esercitata al valore più sfavorevole per il venditore. Opzione contingent 75_ L’acquirente di un’opzione contingent è tenuto a pagare il premio soltanto se il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge o supera il prezzo d’esercizio nell’arco della durata dell’opzione (opzione “americana”) o alla data di scadenza (opzione “europea”). 76_ L’acquirente è tenuto a pagare l’intero premio anche se l’opzione è “at the money” o solo leggermente “in the money”. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 7/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Cliquet and Ladder option 77_ For cliquet options (also known as ratchet options), the strike price is modified for the following period, normally at regular intervals, in line with the market value of the underlying. Any intrinsic value of the option is locked in. All lock-ins arising over the entire life of the option are accumulated. Opzioni cliquet e ladder 77_ Nel caso dell’opzione cliquet (altresì detta opzione ratchet), il prezzo d’esercizio per il periodo successivo viene aggiornato, di norma ad intervalli regolari, in linea con il valore di mercato del sottostante. Il valore intrinseco dell’opzione viene bloccato (lock-in), e tutti i valori così bloccati vengono capitalizzati per tutta la durata dell’opzione. 78_ For ladder options, these modifications take place when the underlying reaches specified market prices, rather than at regular intervals. Normally, only the highest intrinsic value is locked in. In rare cases, all the intrinsic values recorded are added together. 78_ Nel caso dell’opzione ladder, tali modifiche hanno luogo quando il sottostante raggiunge determinati valori di mercato, anziché ad intervalli regolari. Di norma soltanto il valore intrinseco massimo viene bloccato (lock-in); in casi rari, tutti i valori intrinseci rilevati vengono sommati tra loro. 79_ If you sell a cliquet option, you are required on the expiration date to pay the buyer all the accumulated lock-ins in addition to any intrinsic value of the option. If you sell a ladder option you must pay the buyer the highest lock-in amount, which can be considerably higher than the option’s intrinsic value on the expiration date. Examples of options on more than one underlying are : Spread and outperformance options 80_ Both spread and outperformance options are based on two underlyings. With a spread option, the absolute difference in movement between the two underlyings forms the basis for calculating the option’s value. By contrast, the value of an outperformance option is based on the relative difference, i.e. the percentage outperformance of one underlying compared to the other. 81_ Even if the underlying performs positively, the difference between the underlyings may be equal or lower in absolute as well as relative terms, thus having a negative impact on the value of the option. Compound options 82_ The Compound options have an option as their underlying, i.e. they are options on options. 83_ Compound options can have an especially large leverage effect. If you sell an option of this type, you can be faced with very substantial obligations. Credit default options 84_ With a credit default option, a credit risk of the original risktaker (risk seller) is transferred to a third party (risk buyer), who receives a premium in return. If the defined credit event occurs, the risk buyer is obliged to effect a cash settlement or take on the nonperforming loan (or another delivery obligation) by way of physical settlement at a previously determined price. Credit default options are a form of credit derivatives. 85_ The risk of chain reactions on the credit market is high and can easily be underestimated. There is also the risk that lack of liquidity will lead to price distortions when volumes are low. This may mean that the investment can only be sold at a low price, longer term or even not at all. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 79_ Il venditore di un’opzione cliquet è tenuto, alla data di scadenza, a versare all’acquirente tutti i lock-in accumulati in aggiunta all’eventuale valore intrinseco dell’opzione. Il venditore di una un’opzione ladder è tenuto a versare al compratore un importo pari al massimo lock-in rilevato, che può essere notevolmente superiore al valore intrinseco dell’opzione alla data di scadenza. Esempi di opzioni su molteplici attività sottostanti. Opzioni spread e outperformance 80_ Le opzioni sia di tipo spread sia di tipo outperformance sono basate su due sottostanti. Nel caso dell’opzione spread, il valore dell’opzione è calcolato in base alla differenza assoluta dell’andamento dei valori di mercato dei due sottostanti. Il valore di un’opzione outperformance, invece, è basato sulla differenza relativa, cioè sullo scarto percentuale di performance positivo di un sottostante rispetto all’altro. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 81_ Anche se i valori dei sottostanti hanno un andamento favorevole, la loro differenza in termini assoluti o relativi può rimanere costante o persino diminuire, con ripercussioni negative sul valore dell’opzione. Opzioni composte 82_ Le opzioni composte hanno quale sottostante un’opzione, cioè sono opzioni di opzioni. 83_ Le opzioni composte possono produrre un effetto leva particolarmente elevato. Il venditore di un’opzione di questo tipo potrebbe esporsi a impegni di notevole entità. Credit 84_ Una credit default option permette di trasferire un rischio di credito dal soggetto si è assunto originariamente il rischio (venditore del rischio) a un terzo (acquirente del rischio), che riceve in contropartita un premio. Qualora si verifichi l’evento creditizio prestabilito, l’acquirente del rischio è tenuto ad effettuare una liquidazione in contanti o ad assumersi il prestito in sofferenza (o altro impegno di pagamento) tramite consegna fisica del sottostante ad un prezzo previamente concordato. Le credit default option sono un tipo di derivato di credito. 85_ Nel mercato del credito vi è un rischio elevato di reazioni a catena che può essere facilmente sottovalutato. Vi è anche il rischio che la mancanza di liquidità determini distorsioni dei prezzi in caso di bassi volumi. Pertanto, l’investimento potrebbe essere vendibile soltanto ad un prezzo sfavorevole, a lungo termine, oppure non essere vendibile affatto. 8/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Forwards and Futures CONTRATTI A TERMINE E FUTURE 86_ With forwards and futures you undertake to deliver or take delivery of a defined quantity of an underlying on a specified expiration date at a price agreed on the contract date. Unlike with options, which (for the buyer at least) only give rise to rights, forwards and futures involve both parties entering into obligations. You do not have to pay a premium when the contract is concluded. 86_ Con i contratti a termine e future, ci si impegna a ricevere o a consegnare, alla data di scadenza, una determinata quantità di un sottostante al prezzo pattuito alla stipula del contratto. A differenza delle opzioni, che prevedono unicamente un diritto (quanto meno per l’acquirente), nel caso dei contratti a termine e future entrambe le controparti si assumono un obbligo. Alla stipula del contratto non è previsto il pagamento di un premio. 87_ Forwards and futures can involve special risks. You should therefore only make investments of this type if you are familiar with this type of instrument, have sufficient liquid assets and are able to absorb any losses that may arise. 87_ I contratti a termine e future possono comportare rischi particolari. Pertanto, si raccomanda di effettuare tali investimenti soltanto se si conosce questo tipo di strumenti, se si dispone di mezzi liquidi sufficienti e si è in grado di sostenere possibili perdite. 88_ Futures are traded on an exchange. They take the form of contracts in which the quantity of the underlying and the expiration date are standardised. 88_ I future sono negoziati in mercati regolamentati, essendo contratti standardizzati in termini di quantità del sottostante e data di scadenza. 89_ Forwards are not traded on an exchange; hence they are referred to as OTC (over-thecounter) forwards. Their specifications may also be standardised; otherwise they may be individually agreed between the buyer and seller. 89_ I contratti a termine non sono trattati in borsa; per questo motivo, sono detti contratti a termine OTC (over-the-counter, o fuori borsa). Le loro caratteristiche possono essere standardizzate oppure pattuite individualmente tra acquirente e venditore. 90_ The most common underlyings for forwards and futures are : – assets (equities, bonds, precious metals and other commodities), – benchmark rates such as currencies, interest rates and indices. 90_ I sottostanti più comuni per i contratti a termine e i future sono: 91_ When you buy or sell (short) an underlying asset on the futures market, you must supply a specified initial margin when entering into the contract. This is usually a percentage of the total value of the contracted instruments. In addition, a variation margin is calculated periodically during the life of the contract. This corresponds to the book profit or loss arising from any change in value in the contract or underlying instrument. The way in which the variation margin is calculated will depend on the rules of the exchange concerned and/or the conditions of the contract. 92_ As the investor, you are obliged to deposit the required initial and variation margin cover with the securities dealer for the entire life of the contract. 93_ In the event of a book loss, the variation margin can be several times as large as the initial margin. 94_ As the investor, you are entitled to close out the contract at any time prior to the expiration date. How this is done depends on the type of contract or stock exchange practice. You either “sell” the contract or agree an offsetting trade with identical terms. Concluding such an offsetting trade means that the obligations to deliver and receive cancel one another out. 95_ If you do not close out the contract prior to the expiration date, you and the counterparty must settle it. 96_ If the underlying in your contract is a physical asset, settlement is achieved by physical delivery or a cash payment. Generally, the asset is physically delivered. Only in exceptional cases do the contract provisions or stock exchange practice call for cash settlement. All other fulfilment specifications, especially the definition of the place of fulfilment, can be found in the relevant contract provisions. 97_ The difference between physical delivery and cash settlement is that with physical delivery, underlyings amounting to the entire contractual value must be delivered, whereas with cash settlement, only the difference between the agreed price and the market value on settlement needs to be paid. This means that you need more funds available for physical delivery than for cash settlement. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI - valori patrimoniali (azioni, obbligazioni, metalli preziosi e altre materie prime) - tassi di riferimento, come valute, tassi di interesse e indici 91_ Se si acquista o si vende (allo scoperto) un’attività sottostante nel mercato dei future, alla stipula del contratto si deve fornire un determinato margine iniziale, il quale corrisponde di norma ad una percentuale del valore totale del contratto. Inoltre, durante il periodo di validità del contratto viene calcolato periodicamente un margine di variazione, Che corrisponde all’utile o alla perdita contabile derivanti dalla variazione del valore del contratto o del sottostante. Le modalità di calcolo del margine di variazione dipendono dalle norme di borsa vigenti e/o dalle condizioni del contratto. 92_ L’investitore è tenuto a depositare presso l’intermediario finanziario i necessari margini iniziali e di variazione per tutta la durata del contratto. 93_ Nell’eventualità di una perdita contabile, il margine di variazione può essere notevolmente superiore al margine iniziale. 94_ L’investitore ha facoltà di liquidare il contratto in qualsiasi momento prima della data di scadenza, secondo le modalità previste dal tipo di contratto o dalle prassi di borsa. L’investitore può “vendere” il contratto oppure effettuare un’operazione di compensazione con caratteristiche identiche; in quest’ultimo caso gli obblighi di consegna e di accettazione si annullano a vicenda. 95_ Se il contratto non viene liquidato prima della scadenza, deve essere adempiuto da ambo le controparti. 96_ Se il sottostante del contratto è un’attività materiale, l’adempimento può avvenire sia mediante la consegna fisica del sottostante sia mediante liquidazione in contanti. Di norma ha luogo la consegna fisica del sottostante; soltanto in casi eccezionali le condizioni del contratto o le prassi di borsa impongono la liquidazione in contanti. Tutte le altre disposizioni relative all’adempimento, ed in particolare la definizione del luogo di adempimento, sono specificate nelle clausole rilevanti del contratto. 97_ La differenza tra la consegna fisica del sottostante e la liquidazione in contanti consiste nel fatto che, nel primo caso, si deve consegnare il sottostante corrispondente all’intero valore contrattuale; nel secondo caso, invece, si è tenuti a corrispondere unicamente la differenza tra il prezzo pattuito e il valore di mercato del sottostante al momento dell’adempimento. Di conseguenza, la consegna fisica del sottostante richiede maggiori disponibilità finanziarie che la liquidazione in contanti. 9/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 98_ If the underlying in your contract is a reference rate or benchmark, fulfilment by physical delivery is not permitted (except for currencies). Instead, settlement is always in cash. 99_ For forward sales, you must deliver the underlying at the price originally agreed even if its market value has since risen above the agreed price. In such a case, you risk losing the difference between these two amounts. 100_ Theoretically, there is no limit to how far the market value of the underlying can rise. Hence, your potential losses are similarly unlimited and can substantially exceed the margin requirements. 101_ For forward purchases, you must take delivery of the underlying at the price originally agreed even if its market value has since fallen below the agreed price. Your potential loss corresponds to the difference between these two values. Your maximum loss therefore corresponds to the originally agreed price. Potential losses can substantially exceed the margin requirements. 102_ In order to limit price fluctuations, an exchange may set price limits for certain contracts. Find out what price limits are in place before effecting forward or futures transactions. This is important since closing out a contract can be much more difficult or even impossible if a price limit of this type is reached. 103_ If you sell forward an underlying which you do not hold at the outset of the contract, this is referred to as a short sale. In this case, you risk having to acquire the underlying at an unfavourable market value in order to fulfil your obligation to effect delivery on the contract’s expiration date. 104_ The market for standardised OTC forwards is transparent and liquid. Hence, contracts can normally be closed out without difficulty. There is no actual market for OTC forwards agreed individually, and hence the positions they entail may only be closed out with the agreement of the counterparty. 105_ Since combinations comprise a number of elements, closing out individual elements can considerably alter the risks inherent in the overall position. Before entering into any such transaction, be sure to consult your securities dealer about the particular risks involved. 106_ Given the many possible combinations, we cannot go into detail in this brochure about the risks involved in any particular case. Before making a purchase, be sure to seek comprehensive advice about these risks. Structured Products 107_ Structured products are issued either publicly or privately. Their redemption value depends on the performance of one or more underlyings. They may have a fixed or unlimited term and consist of one or more components. 108_ Here is a list of the common product categories, based on the categorisation model used by the Swiss Structured Products Association (SSPA) : – capital protection products (see 116 ff. below) – yield enhancement products (see 126 ff. below) – participation products (see 130 ff. below) – leverage products (see 135 ff. below) 109_ Structured products may be listed for trading on an exchange, but do not have to be. 98_ Se il sottostante del contratto è un tasso di riferimento (o benchmark), l’adempimento mediante la consegna fisica del sottostante non è ammesso (eccezion fatta per le valute); pertanto l’adempimento è sempre in contanti. 99_ Nel caso di vendita a termine, il venditore è tenuto a consegnare il sottostante al prezzo originariamente pattuito, anche se nel frattempo il suo valore di mercato fosse divenuto superiore a tale prezzo; in tal caso, si rischia di perdere la differenza tra questi due importi. 100_ In teoria, non c’è limite all’aumento del valore di mercato del sottostante; di conseguenza, le perdite potenziali sono anch’esse illimitate e possono eccedere considerevolmente i margini di copertura richiesti. 101_ Nel caso di acquisto a termine, il compratore è tenuto a ricevere il sottostante al prezzo originariamente pattuito, anche se nel frattempo il suo valore di mercato fosse divenuto inferiore a tale prezzo. La perdita potenziale corrisponde alla differenza tra questi due valori, e la perdita massima è pari quindi al prezzo originariamente pattuito. Le perdite potenziali possono eccedere considerevolmente i margini di copertura richiesti. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 102_ Per impedire un’oscillazione eccessiva dei prezzi, una borsa può stabilire limiti di prezzo per determinati contratti. Si raccomanda di informarsi su tali limiti prima di effettuare operazioni su contratti a termine o future; questo è importante poiché la liquidazione di un contratto può risultare molto difficoltosa o addirittura impossibile al raggiungimento del limite di prezzo. 103_ Se si vende a termine un sottostante che non si possiede al momento della stipula del contratto, si effettua una vendita allo scoperto. In tal caso si rischia di dover acquistare il sottostante a un prezzo sfavorevole per adempiere all’obbligo di consegna alla scadenza. 104_ Il mercato per i contratti a termine OTC standardizzati è liquido e trasparente; di conseguenza, i contratti possono essere di norma liquidati senza particolari difficoltà. Per i contratti a termine OTC pattuiti individualmente non esiste un vero mercato, perciò le relative posizioni possono essere liquidate soltanto con il consenso della controparte. 105_ Poiché le operazioni combinate consistono di diversi elementi, si possono modificare notevolmente i rischi insiti nella posizione complessiva liquidando soltanto singoli elementi. Prima di effettuare operazioni di questo tipo, si invita l’investitore a rivolgersi al suo intermediario finanziario di fiducia per una consulenza sui rischi specifici che esse comportano. 106_ Dato l’elevato numero di potenziali combinazioni, è impossibile illustrare in dettaglio in questo opuscolo tutti i rischi associati a ciascun caso particolare. Prima di effettuare un acquisto, si raccomanda all’investitore di chiedere una consulenza dettagliata su tali rischi. PRODOTTI STRUTTURATI 107_ I prodotti strutturati sono emessi pubblicamente o privatamente. Il loro valore di rimborso dipende dall’andamento di una o più attività sottostanti; possono avere durata limitata o illimitata e consistere di una o più componenti. 108_ Si riporta a seguire un elenco delle categorie di prodotti più diffuse, sulla base del modello di classificazione adottato dall’Associazione svizzera per i prodotti strutturati: - prodotti con protezione del capitale (§116 e ss.) - prodotti con ottimizzazione del rendimento (§126 e ss.) - prodotti a partecipazione (§130 e ss.) - prodotti con leva finanziaria (§135 e ss.) 109_ I prodotti strutturati possono, ancorché non necessariamente, essere quotati in borsa. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 10/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 110_ The tradability of a structured product depends on whether the issuer or a market maker is prepared to make a price. Even if they are, liquidity risks can still arise. If the market is not liquid, you run the risk of having to either hold the financial instrument until the end of its term or sell it during the term at an unfavourable price. It can also be difficult or impossible to determine a fair price or even compare prices at all, as there is often only one market maker. 111_ You bear the risk that the debtor of a structured product may become insolvent (issuer risk). The instrument’s value is therefore dependent not only on the performance of the underlying asset but also on the creditworthiness of the issuer, which may change over the term of the structured product. 112_ Every structured product has its own risk profile, and the risks of its individual components may be reduced, eliminated or increased. In particular, it may profit to different degrees from rising, constant or falling market values of the underlying, depending on the product involved. 113_ It is extremely important to find out exactly what the risks are before acquiring a product of this kind. This information can be found in, for example, the issue documents or the product description concerned. 114_ Structured products are not categorised as collective investments under the Collective Investment Schemes Act (Federal Act on Collective Investment Schemes of 23 June 2006). Unlike with collective investments, the issuer is liable with his or her own assets (as is any guarantor, to the extent of a guarantee they have provided), and there is no backing from specially protected assets. You therefore need to bear in mind that in addition to a potential loss resulting from a decline in the market value of the underlyings (market risk), you may in the worst case lose your entire investment because the issuer or guarantor becomes insolvent (issuer or guarantor risk). 115_ You do not normally have any entitlement to voting rights or dividends if you buy a structured product. Capital Protection Products 116_ Some structured products offer capital protection. The level of this protection is fixed by the issuer when the product is issued and indicates the percentage of the nominal value that will be repaid to the investor on expiration. However, capital protection generally only applies at the end of the term and may, depending on the product conditions, be (far) lower than 100% of the invested capital. 117_ Some structured products offer only conditional capital protection, which can be lost if the value touches, falls below or rises above a predefined threshold (barrier, knockout level). Repayment is then dependent on the performance of one or more underlyings. 118_ Structured products with capital protection consist of two elements, such as a fixedincome investment (especially a bond or a money market investment) and an option. This combination enables the holder to participate in the performance of one or more underlyings (via the option or participation component) while at the same time limiting potential losses (via the fixed-income investment or capital protection component). The capital protection component may only cover a portion of the capital invested. 119_ The capital protection component determines the minimum repayment you receive on expiration, regardless of how the participation component performs. 110_ La negoziabilità di un prodotto strutturato dipende dalla disponibilità dell’emittente o di un market maker a fissare un prezzo; anche in questo caso, tuttavia, può insorgere un rischio di liquidità. Se il mercato non è liquido, si rischia di dover detenere lo strumento finanziario fino alla scadenza oppure di doverlo vendere prima della scadenza ad un prezzo sfavorevole. Inoltre, potrebbe essere difficile o impossibile calcolare un prezzo equo o persino effettuare una comparazione dei prezzi, poiché spesso esiste un solo market maker. 111_ Con i prodotti strutturati ci si espone al rischio che il debitore possa diventare insolvente (rischio emittente). Pertanto il valore dell’investimento dipende non soltanto dall’andamento del sottostante ma anche dalla solvibilità dell’emittente, la quale può variare nel periodo di durata del prodotto strutturato. 112_ Ogni prodotto strutturato ha il proprio profilo di rischio; i rischi delle singole componenti possono essere ridotti, eliminati o incrementati. In particolare, a seconda del prodotto, si può trarre profitto in diversa misura dal rialzo, dalla stabilità o dal ribasso del valore di mercato del sottostante. 113_ Prima di acquistare un prodotto di questo tipo è estremamente importante scoprire esattamente quali sono i rischi ad esso associati. Questa informazione si trova, ad esempio, nei documenti di emissione o nella descrizione del prodotto in oggetto. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 114_ I prodotti strutturati non sono considerati investimenti collettivi ai sensi della Legge sugli investimenti collettivi (Legge federale sugli investimenti collettivi di capitale del 23 giugno 2006). A differenza degli investimenti collettivi, l’emittente risponde degli obblighi con il suo patrimonio (al pari di un eventuale garante, che risponde nella misura della garanzia fornita) e non con valori patrimoniali protetti allo scopo. Si deve quindi rammentare che in aggiunta alle perdite potenziali derivanti da una flessione del valore di mercato del sottostante (rischio di mercato), si può nel peggiore dei casi perdere l’intero ammontare dell’investimento qualora l’emittente o il garante diventino insolventi (rischio emittente o garante). 115_ A chi acquista un prodotto strutturato di norma non spettano diritti di voto o dividendi. PRODOTTI CON PROTEZIONE DEL CAPITALE 116_ Alcuni prodotti strutturati offrono una protezione del capitale. Il livello di tale protezione è stabilito dall’emittente al momento dell’emissione ed indica la percentuale del valore nominale che verrà rimborsata all’investitore alla scadenza. Tuttavia, la protezione del capitale si applica di norma soltanto alla scadenza e, a seconda delle condizioni del prodotto, può essere (notevolmente) inferiore al 100% del capitale investito. 117_ Alcuni prodotti strutturati offrono unicamente una protezione del capitale condizionata, che può venir meno se il valore raggiunge, scende al di sotto o supera una soglia convenuta (barriera, livello di knock-out). Il rimborso è quindi dipendente dall’andamento di una o più attività sottostanti. 118_ I prodotti strutturati con protezione del capitale consistono di due elementi, come ad esempio un investimento in attività a reddito fisso (specialmente obbligazioni ed investimenti sul mercato monetario) ed un’opzione. Tale combinazione permette al detentore di partecipare all’andamento di uno o più sottostanti (grazie all’opzione, che rappresenta la componente di partecipazione) limitando contemporaneamente le perdite potenziali (grazie all’investimento a reddito fisso, cioè la componente di protezione del capitale). La componente di protezione del capitale potrebbe coprire soltanto una parte del capitale investito. 119_ La componente di protezione del capitale determina il rimborso minimo che si ottiene alla scadenza, indipendentemente dall’andamento della componente di partecipazione. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 11/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 120_ The capital protection is linked to the nominal value rather than the issue price or purchase price. Hence, if the issue/purchase price you pay exceeds the nominal value, only the nominal value is capital-protected. The protection of your capital outlay drops accordingly. If, however, the issue/purchase price is less than the nominal value, the protection of your capital outlay rises accordingly. 121_ The capital protection component can be well under 100% of the capital invested, depending on the product. Capital protection does not therefore mean 100% repayment of nominal value or the purchase price for all products. Structured products with capital protection generally offer lower returns than direct investments in the underlying, as the capital protection costs money. 122_ If you wish to sell a structured product with capital protection before it expires, you may receive less than the capital protection component as the capital protection only applies if you keep the product until the redemption date. 123_ The participation component determines how you benefit from price movements in the underlying(s) when you buy a structured product. In other words, it fixes the level of your potential return over and above the capital protection component. Some structured products with capital protection offer only a limited potential participation (those with a cap); some (those without a cap) offer unlimited potential participation. Others require the market value of the underlying to touch, rise above or fall below a specific barrier before you can make a profit. 124_ The risk on the participation component is the same as that on the corresponding option or combination of options. Depending on the movements in the market value of the underlyings, the participation component may therefore be zero. 125_ Your maximum loss on a structured product with capital protection is limited to the difference between the purchase price and the capital protection, provided you continue to hold the product until expiration. You may also miss out on a profit due to the fact that full or partial repayment of the capital is guaranteed but no income (interest) is paid. Please be aware that there is also issuer risk (see 111). Yield Enhancement Products 126_ Structured products with yield enhancement consist of two elements, such as a fixed-income investment and an option (mainly on equities or currencies), and possibly a currency swap. This combination enables you to participate in the performance of one or more underlyings (via the option component). However, these financial instruments offer no or only conditional capital protection. The interest that is paid means you receive a higher return than with a direct investment if the price of the underlying remains essentially unchanged. On the other hand, you will not benefit from the full potential return of the underlying. 127_ If the market value of the underlying rises, you will receive the stipulated interest and the nominal value on expiration (equally, the product may provide for a discount on the issue price). If the market value of the underlying rises sharply, you could possibly have earned a higher return on a direct investment. However, if the market value of the underlying falls sharply, you will receive both the interest payment and the underlying on expiration (unless the product offered a discount on the issue price). D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 120_ La protezione del capitale è collegata al valore nominale anziché al prezzo di emissione o di acquisto. perciò, se il prezzo di emissione/acquisto pagato è superiore al valore nominale, soltanto il valore nominale gode della protezione del capitale, e pertanto la protezione del capitale investito si riduce di conseguenza. Se invece il prezzo di emissione/acquisto è inferiore al valore nominale, la protezione del capitale investito aumenta di conseguenza. 121_ A seconda del tipo di prodotto, la componente di protezione del capitale può risultare di gran lunga inferiore al 100% del capitale investito. Pertanto, la protezione del capitale non equivale ad un rimborso del 100% del valore nominale o del prezzo di acquisto per tutti i prodotti. I prodotti strutturati con protezione del capitale offrono di norma rendimenti inferiori rispetto ad un investimento diretto nel sottostante, poiché la protezione del capitale ha un costo. 122_ Vendendo un prodotto strutturato con protezione del capitale prima della scadenza si corre il rischio di ricevere un importo inferiore alla componente di protezione, la quale si applica unicamente se il prodotto viene detenuto fino alla data di rimborso. 123_ Quando si acquista un prodotto strutturato, la componente di partecipazione determina la misura in cui si trae beneficio dall’andamento del/i sottostante/i. In altre parole, tale componente determina il livello di potenziale rendimento al di sopra della protezione del capitale. Alcuni prodotti strutturati con protezione del capitale offrono unicamente un potenziale di partecipazione limitato (i prodotti con un “cap”, o tetto massimo); altri (senza “cap”) assicurano una partecipazione illimitata. Altri ancora permettono di realizzare un guadagno soltanto a condizione che il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunga, superi o scenda al di sotto di una determinata soglia. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 124_ Il rischio collegato alla componente di partecipazione coincide con quello della rispettiva opzione o combinazione di opzioni. Quindi, a seconda dell’andamento del valore di mercato del sottostante, la componente di partecipazione può essere nulla. 125_ La perdita massima su un prodotto strutturato con protezione del capitale è limitata alla differenza tra il prezzo di acquisto e la protezione del capitale, purché il prodotto venga detenuto fino alla scadenza. Inoltre, si possono registrare perdite di guadagno anche laddove è previsto il rimborso totale o parziale del capitale ma non il pagamento di interessi. Si rammenti inoltre che è presente un rischio emittente (si veda §111). PRODOTTI CON OTTIMIZAZIONE DEL RENDIMENTO 126_ I prodotti strutturati con ottimizzazione del rendimento consistono di due elementi, come ad esempio un investimento in un’attività a reddito fisso e un’opzione (soprattutto su azioni o valute), e possibilmente uno swap su valute. Tale combinazione permette al detentore di partecipare all’andamento di uno o più sottostanti (grazie alla componente di opzione). Tuttavia, questi strumenti non prevedono una componente di protezione del capitale, oppure la prevedono solo in forma condizionata. In virtù degli interessi pagati, l’investitore ottiene un rendimento più elevato rispetto all’investimento diretto qualora il prezzo del sottostante rimanga essenzialmente invariato. Per contro, l’investitore non trarrà beneficio dal massimo rendimento potenziale del sottostante. 127_ Se il valore di mercato del sottostante aumenta, alla scadenza l’investitore riceve gli interessi pattuiti ed il valore nominale del capitale investito (analogamente, può anche essere previsto uno sconto sul prezzo di emissione). Nell’eventualità di un brusco aumento del valore di mercato del sottostante, un investimento diretto darebbe probabilmente un rendimento più elevato. Se invece il valore di mercato del sottostante diminuisce, alla scadenza l’investitore riceve gli interessi pattuiti ed il sottostante (a meno che il prodotto non prevedesse uno sconto sul prezzo di emissione). 12/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 128_ Many products with yield enhancement refer to several underlyings. You as investor receive the security with the worst performance on expiration (either physically or in the form of cash) if the underlying touches, rises above or falls below a predefined barrier during the term of the financial instrument. If the performance of the underlying is negative, the financial instrument can trade some way below the issue price during its term even if the barrier is not touched, exceeded or undershot. The level of interest rate is directly related to the level of the barrier. The nearer the barrier is to the market price of the underlying on the day of issue, the higher the interest you receive will generally be, but the higher the risk that the barrier will be reached, and vice versa. 128_ Molti prodotti con ottimizzazione del rendimento fanno riferimento a numerosi sottostanti; alla scadenza l’investitore riceve (fisicamente o in contanti) il titolo che ha avuto l’andamento peggiore, qualora il sottostante raggiunga, superi o scenda al di sotto di una determinata soglia nel periodo di durata dello strumento finanziario. Se l’andamento del sottostante è negativo, lo strumento finanziario può registrare una quotazione nettamente inferiore al prezzo di emissione, anche in caso di mancato raggiungimento o superamento della soglia. Il livello del tasso di interesse è direttamente correlato a quello della soglia. Quanto più la soglia è vicina al valore di mercato del sottostante il giorno dell’emissione, tanto più elevati sono gli interessi percepiti, ma tanto maggiore è il rischio che la soglia venga raggiunta, e viceversa. 129_ When you invest in a structured product with yield enhancement, you could in the worst case scenario lose the entire capital that you have invested. 129_ Quando si investe in un prodotto strutturato con ottimizzazione del rendimento, nel caso peggiore si rischia di perdere l’intero ammontare del capitale investito. Participation Products PRODOTTI CON PARTECIPAZIONE 130_ Structured products with participation enable you to participate in the performance of one or more underlyings. However, they offer no or only conditional capital protection. If the participation product offers conditional capital protection, the risk is smaller than with a direct investment provided the market value of the underlying does not reach a specific barrier (termed the “knock-out”). 130_ I prodotti strutturati con partecipazione permettono di partecipare all’andamento di uno o più sottostanti; tuttavia, tali strumenti non prevedono una componente di protezione del capitale, oppure la prevedono solo in forma condizionata. Se il prodotto strutturato con partecipazione offre una protezione del capitale condizionata, il rischio insito nell’investimento è minore che nel caso di un investimento diretto, purché il sottostante non raggiunga una specifica soglia (detta “knockout”). 131_ If the market value of the underlying touches, rises above or falls below the barrier, you will lose the capital protection. 132_ The risk of a structured product with participation is generally the same as that of the underlying. Unlike with a direct investment, however, you do not receive voting rights and you are not entitled to a dividend. You do, though, bear the credit risk of the product’s issuer 133_ Many products with participation refer to several underlyings. You as investor receive the security with the worst (or sometimes best) performance on expiration (either physically or in the form of cash) if the market value of the underlying touches, rises above or falls below a predefined barrier during the term of the financial instrument. The financial instrument can trade some way below the issue price during its term even if the barrier is not touched, exceeded or undershot. Moreover, the level of participation is directly related to the level of the barrier. If you have a higher risk tolerance when selecting the barrier, you will enjoy a higher participation. 134_ When you invest in a structured product with participation, you could in the worst case scenario lose the entire capital that you have invested. Leverage Products 135_ Structured products with leverage enable you to achieve a leverage effect by investing less capital than you would have to if you invested directly in the underlying. This means you can benefit from short-term trends. 136_ Structured products with leverage are suitable for short-term speculation but also for strategically hedging a portfolio. 137_ Because of the leverage effect, you need to carefully and regularly monitor the underlying, since structured products with leverage can experience a larger rise in profits but also a bigger loss than the underlying. 138_ When you invest in a structured product with leverage, you could in the worst case lose the entire capital that you have invested. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 131_ Se il valore di mercato del sottostante raggiunge, supera o scende al di sotto di una determinata soglia, si perde la protezione del capitale. 132_ La rischiosità di un prodotto strutturato con partecipazione coincide in generale con quella del sottostante; a differenza di un investimento diretto, tuttavia, non si hanno né un diritto di voto né il diritto a percepire un dividendo, ma ci si espone comunque al rischio di credito associato all’emittente del prodotto. 133_ Molti prodotti strutturati con partecipazione fanno riferimento a molteplici sottostanti; alla scadenza l’investitore riceve (fisicamente o in contanti) il titolo che ha avuto l’andamento peggiore (o talvolta migliore), qualora il sottostante raggiunga, superi o scenda al di sotto di una determinata soglia nel periodo di validità dello strumento finanziario. Lo strumento finanziario può registrare una quotazione nettamente inferiore al prezzo di emissione, anche in caso di mancato raggiungimento o superamento della soglia. Inoltre, il livello di partecipazione è direttamente correlato a quello della soglia. L’investitore con un’elevata propensione al rischio può scegliere la soglia in modo da godere di una maggiore partecipazione. 134_ Quando si investe in un prodotto strutturato con partecipazione, nel caso peggiore si rischia di perdere l’intero ammontare del capitale investito. PRODOTTI CON LEVA FINANZIARIA 135_ I prodotti strutturati con leva finanziaria permettono di conseguire un effetto leva investendo meno capitale di quanto sarebbe necessario per un investimento diretto nel sottostante. Questo permette di beneficiare dalle tendenze a breve termine. 136_ I prodotti strutturati con leva finanziaria sono adatti per la speculazione a breve termine ma anche per la copertura mirata di un portafoglio. 137_ Per via dell’effetto leva è necessario seguire attentamente e con regolarità l’andamento del sottostante; infatti, i prodotti strutturati con leva possono dar luogo ad un forte aumento dei guadagni ma anche a perdite molto più sostenute rispetto a quest’ultimo. 138_ Quando si investe in un prodotto strutturato con leva finaniaria, nel caso peggiore si rischia di perdere l’intero ammontare del capitale investito. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 13/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Products Used for Financing or Risk Transfer 139_ The financial instruments discussed in this section have the same or similar profit and loss structures as certain conventional financial instruments (equities or bonds). 140_ Such financial instruments may be listed for trading on an exchange, but do not have to be. 141_ The risks associated with these products are not necessarily the same as those of the financial instruments they contain. It is therefore extremely important to find out exactly what the risks are before acquiring a product of this kind. This information can be found in, for example, the product description concerned. 142_ There are some products that are mainly used to transfer risks. These include credit and catastrophe derivatives. They are financial instruments where the “underlying” is an event such as a credit event (default of a loan or bond) or a natural disaster. Derivatives of this type can be used by the bearer of a risk to transfer it to others. Credit derivatives come in the form of swaps, options or hybrid financial instruments. 143_ Credit and catastrophe derivatives involve a liquidity risk. Often such instruments cannot be sold before the end of their term, because there is no market for them. 144_ Credit bonds securitise the risks and transfer them to third parties as credit-linked notes, collateralised debt obligations and asset-backed securities. As a result, the buyer takes on the risk associated with a loan portfolio. Credit-linked notes (CLN) 145_ CLN are bonds whose redemption and interest payments depend on the performance of a specific underlying or benchmark portfolio (e.g. loan, bond). 146_ Look closely at the creditworthiness of the debtor to which the CLN is linked, as the CLN can end up being valueless if a credit event occurs. There is an issuer risk, i.e. a credit risk of the issuing bank, just as with structured products. The secondary market for CLN is highly illiquid, and you should therefore assume that you will not be able to sell one before the end of its term. Collateralised debt obligations (CDO) 147_ CDO are bonds backed by a diversified debt portfolio (mostly loans, bonds or credit default swaps). They give you access to investments that are unattractive or even unattainable for individual investors. Since CDO are often divided up into a number of tranches with differing credit risks, you can decide what credit risk you wish to take on. If a debtor in the debt portfolio experiences a credit event, the equity-like tranches are affected first: they may be only partially redeemed, or not redeemed at all. If a number of debtors default, this affects the remaining tranches in order of creditworthiness, until finally the tranche with the highest credit rating (comparable to that of first-class bonds) may only be partially redeemed, or not redeemed at all. The value of a CDO is based primarily on the probability of a credit event affecting the individual companies in the portfolio. This probability of default is determined using statistical methods and on the basis of historical data, and can cease to be meaningful in extreme market conditions. 148_ Before you invest in a CDO, you should also look at the track record of the manager in charge of it: he or she will receive a performance-related bonus and will often have a holding in the CDO him/herself. If the portfolio is not run by a manager (which is termed a “static” portfolio), its composition remains unchanged throughout its term. In this case you should pay special attention to the composition of the portfolio. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 PRODOTTI FINALIZZATI AL FINANZIAMENTO O AL TRASFERIMENTO DEI RISCHI 139_ Gli strumenti finanziari illustrati in questa sezione presentano profili di guadagno e di perdita uguali o simili a quelli di alcuni strumenti finanziari tradizionali (azioni o obbligazioni). 140_ Tali strumenti finanziari possono, ancorché non necessariamente, essere quotati in borsa. 141_ I rischi associati a questi prodotti non coincidono necessariamente con quelli degli strumenti finanziari in essi contenuti; perciò, prima di acquistare un prodotto di questo tipo, è estremamente importante scoprire esattamente quali sono i rischi ad esso connessi. Questa informazione si trova, ad esempio, nella descrizione del prodotto in oggetto. 142_ Alcuni prodotti finanziari sono destinati principalmente al trasferimento di rischi; tra questi si annoverano i derivati su crediti e sinistri. In questi strumenti finanziari il “sottostante” è, ad esempio, un evento creditizio (come l’inadempienza su un prestito o un’obbligazione) o una calamità naturale. Questo tipo di derivati può essere utilizzato per trasferire il rischio ad altri. I derivati su crediti possono assumere la forma di swap, opzioni o strumenti finanziari ibridi. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI 143_ I derivati su crediti e sinistri comportano un rischio di liquidità: spesso non possono essere venduti prima della scedenza perché non esiste un mercato attivo. 144_ Nel caso dei titoli garantiti da crediti, i rischi vengono cartolarizzati e trasferiti a terzi sotto forma di credit-linked note, collateralised debt obligation e asset-backed security. Di conseguenza, l’acquirente si assume il rischio associato ad un portafoglio di prestiti. CREDIT-LINKED NOTE (CLN) 145_ Le CLN sono titoli obbligazionari il cui rimborso e pagamento degli interessi dipende dall’andamento di uno specifico sottostante o di un portafoglio di riferimento (ad es., prestiti, obbligazioni). 146_ È importante verificare attentamente il merito di credito del debitore al quale è collegata la CLN, poiché al verificarsi di un evento creditizio si rischia che la questa subisca una perdita totale di valore. Come nel caso dei prodotti strutturati, esiste un rischio emittente, cioè un rischio di credito associato alla banca che emette i titoli. Il mercato secondario delle CLN è molto poco liquido, e pertanto bisogna tener conto che non sarà possibile rivenderle prima della scadenza. COLLATERALISED DEBT OBLIGATION (CDO) 147_ Le CDO sono titoli obbligazionari garantiti da un portafoglio diversificato (composto principalmente da prestiti, obbligazioni o credit-default swap), che danno accesso ad investimenti poco interessanti o non persino non disponibili per i singoli investitori. Le CDO sono spesso suddivise in diverse tranche caratterizzate da rischi di credito differenti; pertanto si può decidere quale grado di rischio assumersi. Le prime tranche ad essere colpite se un debitore nel portafoglio di debiti subisce un evento creditizio sono quelle azionarie, che potrebbero essere rimborsate soltanto in parte o non esserlo affatto. Nell’eventualità che più debitori risultino insolventi, le perdite si ripercuotono alle altre tranche in ordine di merito di credito, da quelle con livello di solvibilità inferiore fino all’ultima, quella con il rating più elevato (paragonabile ad obbligazioni di prim’ordine), che potrebbe essere rimborsata soltanto in parte o non esserlo affatto. Il valore di una CDO si basa principalmente sulla probabilità che un evento creditizio colpisca le singole società nel portafoglio. Tale probabilità di insolvenza è determinata mediate metodi statistici e sulla base di dati storici, e può perdere di rilevanza in condizioni di mercato estreme. 148_ Prima di investire in una CDO, è opportuno informarsi sui risultati conseguiti dal gestore che ne è responsabile, il quale riceve un premio legato alla performance e spesso detiene in prima persona una partecipazione nella CDO. Un portafoglio non amministrato da un gestore (cioè un portafoglio “statico”) mantiene invariata la sua composizione per l’intera sua durata. In questo caso occorre prestare particolare attenzione alla composizione del portafoglio. 14/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 149_ CDO typically have a term of several years. As there is generally no secondary market, you should assume that you will not be able to sell the CDO before the end of its term. 149_ Le CDO hanno di norma una durata pluriennale; poiché di solito non esiste un mercato secondario, bisogna tener conto che non sarà possibile rivendere le CDO prima della scadenza. Asset-backed securities (ABS) 150_ In ABSs, risks (such as a range of receivables) are grouped together and transferred to a special purpose vehicle (SPV). The SPV finances this transaction by issuing securities backed by a pool of assets or a portfolio. If the collateral is a mortgage, this kind of instrument is called a mortgage-backed security (MBS). The individual components of the portfolio would be unattractive or even unobtainable in this form for individual investors. However, the composition of the portfolio makes it possible to combine together and sell a range of assets and risks. By grouping together different types of credit risk, different risk profiles can be created. ASSET-BACKED SECURITY (ABS) 151_ Even if a pool or portfolio is created, lack of diversification can lead to a concentration of risk. 151_ Anche se si crea un pool o un portafoglio, la mancanza di diversificazione può determinare una concentrazione dei rischi. 152_ Credit bonds are often issued by particular types of offshore companies (SPV). In this event you should pay special attention to the issuer risk and the quality of government supervision of such SPVs. 152_ I titoli garantiti da crediti sono spesso emessi da particolari società veicolo off-shore (SPV); in questo caso bisogna prestare particolare attenzione al rischio emittente e alla qualità della vigilanza pubblica esercitata su tali organismi. 150_ Nel caso degli ABS, i rischi (ad es., un insieme di crediti) vengono raggruppati e trasferiti ad una società veicolo (“special purpose vehicle”, o SPV). L’SPV finanzia tale transazione emettendo titoli garantiti da un pool di attività o da un portafoglio. Se la garanzia è costituita di mutui ipotecari, questo tipo di strumento è chiamato mortgage-backed security (MBS). Le singole componenti del portafoglio non sarebbero interessanti e neppure accessibili in questa forma per i singoli investitori. Tuttavia, la composizione del portafoglio permette di combinare tra loro e di vendere una vasta gamma di attività e di rischi. Raggruppando diversi tipi di rischio di credito, si possono creare profili di rischio differenti. 1. Section One / Parte Prima TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING SPECIAL RISKS / OPERAZIONI CHE COMPORTANO RISCHI PARTICOLARI Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI Alternative (Non-Traditional) Investments INVESTIMENTI ALTERNATIVI (NON TRADIZIONALI) 153_ Alternative or non-traditional investments are investments that do not fall within the traditional asset classes, such as equities, bonds or money market products. They include a wide range of instruments and strategies. This section focuses on the classes that are most important in terms of risk information : 153_ Gli investimenti alternativi o non tradizionali sono investimenti che non ricadono nelle tradizionali classi di titoli, quali azioni, obbligazioni o prodotti del mercato monetario. Questi investimenti includono una vasta gamma di strumenti e strategie. Questa sezione si concentra sulle classi più importanti ai fini dell’informativa sui rischi: – hedge funds (see 159 ff. below) – private equity (see 174 ff. below) – real estate (see 182 ff. below) – precious metals and other commodities (see 189 ff. below) 154_ This list is not exhaustive and this brochure cannot point out all the risks and issues that need to be taken into account in connection with alternative or non-traditional investments. Be sure to obtain comprehensive advice before investing in alternative or non-traditional investments, and examine the offering carefully. 155_ Instruments allowing for direct investment can make sense in terms of diversifying a portfolio (risk distribution) because their returns are less dependent on factors such as the performance of the markets and levels of interest rates than those of conventional investments. However, the minimum outlay required for direct investments is generally very high, and they are often not accessible to all investors. 156_ To overcome these obstacles and avoid the risks of the large direct investments required, the financial sector has developed instruments for indirect investment. They include certificates, notes, investment funds, funds of funds, commodity futures and forward contracts. All these structures are based on one or more of the asset classes mentioned below. If you are interested in indirect investments, you need to bear in mind not just the risks of alternative investments as an asset class, but also the risks of the instrument concerned – the risks associated with structured products, for example. Please note that this section does not deal with the risks of structured products, forward contracts and futures, as these were discussed in the preceding sections (see “Forwards and Futures” and “Structured Products”). D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 - hedge fund (si veda §159 e ss.) - private equity (si veda §174 e ss.) - immobili (si veda §182 e ss.) - metalli preziosi e altre materie prime (si veda §189 e ss.) 154_ Questo elenco non è esaustivo e il presente opuscolo non può individuare tutti i rischi e le problematiche che vanno tenute in debito conto in relazione agli investimenti alternativi o non tradizionali. Prima di effettuare un investimento alternativo o non tradizionale, si raccomanda di richiedere una consulenza completa e di esaminare attentamente l’offerta. 155_ Gli strumenti che consentono un investimento diretto possono essere indicati ai fini della diversificazione di un portafoglio (distribuzione del rischio), giacché i loro rendimenti sono meno dipendenti da fattori quali l’andamento dei mercati e il livello dei tassi di interesse rispetto agli investimenti tradizionali. Tuttavia, l’esborso minimo necessario per gli investimenti diretti è di norma molto elevato, e ciò li rende spesso inaccessibili ad alcuni investitori. 156_ Per superare tali ostacoli ed evitare i rischi associati agli investimenti diretti di notevole entità, il settore finanziario ha sviluppato strumenti per l’investimento indiretto, tra cui certificati, note, fondi comuni d’investimento, fondi di fondi, contratti future su materie prime e contratti a termine. Tutte queste strutture si basano su una o più delle classi di attività di seguito menzionate. Chi è interessato agli investimenti indiretti deve tener conto non soltanto dei rischi degli investimenti alternativi come classe di attività, ma anche di quelli del particolare strumento, ad esempio dei rischi associati ai prodotti strutturati. Si noti che questa sezione non tratta i rischi dei prodotti strutturati e dei contratti a termine e future, i quali sono stati discussi nelle sezioni precedenti (si veda “Contratti a termine e future” e “Prodotti strutturati”). 15/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 157_ Offshore investments are often structured as funds or partnerships (such as limited partnerships) and domiciled in countries where legislation and supervision can be weak – hence the name “offshore funds”. The Swiss financial supervisory authority does not permit the public distribution of such funds in Switzerland. 158_ The legislation and supervision applying to offshore funds are much less strict than for traditional investments, which means that investors may enjoy less protection. They may find it difficult to enforce their rights, and problems and delays may occur when settling buy and sell orders for units of such funds. Hedge Funds 159_ Hedge funds are the best-known form of alternative or nontraditional investments. Despite what their name suggests, hedge funds do not necessarily have anything to do with hedging. Indeed, they take on sometimes very high levels of risk in order to obtain an above-average return. Hedge funds include all forms of investment funds, investment companies and partnerships that use derivatives not just for hedging but also for investment, that are able to engage in short selling or take on significant leverage by borrowing. Other features typical of hedge funds include their freedom to choose their asset classes, markets (including emerging markets) and trading methods. Hedge funds normally require high minimum investments. They frequently offer only limited opportunities for subscription and redemption, with long notice periods. The portfolio managers of hedge funds receive performance-related bonuses and often hold a personal stake in the funds. Pay special attention to the following : 160_– A hedge fund may be less transparent than a traditional investment fund, for example, as investors are not always informed about planned strategies and changes to them, or changes of portfolio manager. Hedge funds are also not subject to any disclosure requirements. 161_– Unlike traditional collective investments, hedge funds have limited liquidity (units may generally only be redeemed once a month, quarterly or annually). Normally, investors can only invest in a hedge fund at specific times. There are generally long notice periods for redemptions and long lock-up periods (periods during which investors are obliged to leave their capital in the fund). 162_– Delays may occur, and unfavourable prices may result, when settling buy and sell orders for hedge fund units. There is no guarantee that investors will be able to enforce their rights. 163_ Investors invest in funds of hedge funds or multi-manager hedge funds in order to reduce risk. These funds invest their capital in a number of hedge funds and spread it across a range of hedge fund managers that cover different investment styles, markets and instruments. There are also structured products that you can use to invest in hedge funds or hedge fund indices. 164_ The main hedge fund strategies seen on the market are as follows : Equity hedge (“long”, “short”) 165_Equity hedge funds identify undervalued (buy or long position) and overvalued (short selling or short position) equities in specific regions or market segments and attempt to make profits in the belief that sooner or later these positions can be closed out at a profit. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 157_ Gli investimenti off-shore sono spesso strutturati in forma di fondi o società di persone (ad es. società di persone a responsabilità limitata o “limited partnership”) domiciliati in paesi caratterizzati da una legislazione e una vigilanza relativamente deboli, da cui la denominazione di “fondi off-shore”. L’autorità di vigilanza finanziaria elvetica non permette la distribuzione pubblica di questi fondi in Svizzera. 158_ Le normative e la vigilanza applicabili ai fondi offshore sono molto meno rigorose che per gli investimenti tradizionali, e pertanto gli investitori potrebbero godere di minori tutele e incontrare difficoltà nel far valere i propri diritti; inoltre, nel regolamento degli ordini di acquisto e di vendita relativi a quote di tali fondi potrebbero insorgere problemi e ritardi. HEDGE FUND 159_ Gli hedge fund sono la forma più nota di investimenti alternativi o non tradizionali. A dispetto della loro denominazione, gli hedge fund spesso non hanno nulla a che vedere con la copertura (hedging); anzi, talvolta si espongono a rischi molto elevati per conseguire un rendimento superiore alla media. Tra gli hedge fund si annoverano tutte le forme di fondi d’investimento, di società d’investimento e partnership che impiegano derivati a fini non soltanto di copertura ma anche di investimento, che possono effettuare vendite allo scoperto oppure sfruttare in misura significativa l’effetto leva mediante l’indebitamento. Tra le altre caratteristiche tipiche degli hedge fund si include la libertà di scegliere le classi di attività, i mercati (compresi quelli emergenti) e i metodi di trading. Gli hedge fund richiedono normalmente un investimento minimo elevato, 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI e spesso offrono soltanto opportunità limitate di sottoscrizione e rimborso, con lunghi periodi di preavviso. I gestori degli hedge fund percepiscono premi legati ai risultati e spesso detengono una partecipazione personale nel fondo. Si presti particolare attenzione a quanto segue: 160_- Un hedge fund può essere meno trasparente, ad esempio, di un fondo d’investimento tradizionale, poiché gli investitori non sempre vengono informati sulle strategie pianificate e sulle loro eventuali modifiche, oppure sulla sostituzione del gestore. Inoltre, gli hedge fund non sono soggetti ad alcun obbligo di informativa. 161_- A differenza degli investimenti collettivi tradizionali, gli hedge fund presentano una liquidità limitata (i rimborsi sono ammessi generalmente soltanto una volta al mese, al trimestre o all’anno), e l’investimento è consentito di norma soltanto in momenti specifici. I tempi di preavviso per i rimborsi e i periodi vincolati (durante i quali gli investitori sono obbligati a lasciare il proprio capitale nel fondo) tendono a essere piuttosto lunghi. 162_- Nel regolamento degli ordini di acquisto e di vendita relativi a quote di hedge fund potrebbero verificarsi ritardi e il prezzo può risultare sfavorevole. Non c’è garanzia che gli investitori possano far valere i propri diritti. 163_ L’investimento in fondi di fondi o in fondi multigestore (multimanager) è finalizzato a ridurre il rischio. Questi fondi investono il proprio patrimonio in una molteplicità di hedge fund e lo suddividono su numerosi gestori che coprono diversi stili di investimento, mercati e strumenti. Esistono anche prodotti strutturati che permettono di investire in hedge fund o in indici di tali fondi. 164_ Nel mercato si riscontrano principalmente le strategie di hedge fund di seguito descritte. Equity hedge (“long”, “short”) 165_ Gli hedge fund che adottano le strategie “equity hedge” identificano titoli azionari sottovalutati (posizioni “long” o di acquisto) e sopravvalutati (posizioni “short” o di vendita) in specifiche regioni o segmenti di mercato e cercano di trarre beneficio dalla possibilità di liquidare presto o tardi tali posizioni realizzando un guadagno. 16/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Arbitrage strategies 166_ Arbitrage strategies identify price differences between identical or similar investments in different markets and try to exploit them. Such strategies include equity-market neutral, fixed-income arbitrage, convertible-bond arbitrage and mortgage-backedsecurities arbitrage. Strategie di arbitraggio 166_ Le strategie di arbitraggio cercano di sfruttare le differenze di prezzo tra investimenti identici o simili in diversi mercati. Tali strategie comprendono la “equity-market neutral”, la “fixed-income arbitrage”, la “convertible-bond arbitrage” e la “mortgage-backed-securities arbitrage”. Event-driven 167_ Managers that pursue this kind of strategy try to make a profit from events such as upcoming changes in a company (mergers, takeovers, restructurings, turnarounds, etc.). Examples of such strategies are merger arbitrage, distressed securities and special situations. Strategie “event-driven” 167_ I gestori che perseguono questo tipo di strategia cercano di realizzare un guadagno da eventi quali cambiamenti imminenti all’interno di un’azienda (fusioni, acquisizioni, ristrutturazioni, risanamenti, ecc.). Esempi di tali strategie sono la “merger arbitrage”, la “distressed securities” e la “special situations”. Global macro 168_ Hedge funds that pursue global macro strategies attempt to identify macro-economic developments such as changes in interest or exchange rates at an early stage and exploit them for profit. This category includes growth funds and emerging market funds. Strategie “global macro” 168_ Gli hedge fund che perseguono strategie “global macro” cercano di identificare anticipatamente sviluppi macroeconomici quali variazioni dei tassi di interesse e dei tassi di cambio, e di sfruttarli a scopo di profitto. Questa categoria include i fondi “growth” e i fondi dei mercati emergenti. Managed futures 169_ This type of hedge fund deals in futures (standardised, exchange-listed contracts) on financial instruments, currencies and commodities. 170_ Generally speaking, hedge fund managers do not need to be licensed by an authority and are largely unregulated. In particular, hedge funds are not subject to the numerous investor protection regulations that apply to authorised collective investments. These include rules on liquidity, redemption of fund units at any time, avoiding conflicts of interest, fair prices for fund units, disclosure and limitations on borrowing. 171_ Since these rules do not apply to hedge funds, they can use much more leverage than traditional authorised funds, and engage in complex investment transactions that are not permitted for traditional collective investments. A hedge fund is allowed to adopt aggressive strategies including the widespread use of short selling, leverage, swaps, arbitrage, derivatives and programme trading. Their investment strategies are often highly complex and very intransparent. You will often receive little or no information about changes of strategy that may lead to a significant increase in risk, or receive such information only at a late stage. 172_ As part of their investment strategy, hedge funds can also use derivatives such as futures, options and swaps that may be listed for trading on an exchange but do not have to be. These instruments may be subject to significant price volatility, resulting in a high risk of loss for the fund. The low margins typically required to build up a position in such instruments mean that high levels of borrowing can be used. Depending on the instrument, a relatively small change in the price of the contract can therefore lead to a large profit or loss in comparison with the capital lodged as collateral and hence to further, unforeseeable losses that can exceed any margin cover. 173_ Investment vehicles that are not listed on an exchange also involve further risks as there is neither an exchange nor a secondary market where units can be sold or open positions closed out. It may be impossible to unwind an existing position or determine the value or risk of a position. If a hedge fund sells uncovered options on securities, it may be exposing itself to an unlimited risk of loss. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 Managed future 169_ Questo tipo di hedge fund tratta i future (contratti standardizzati e quotati in borsa) su strumenti finanziari, valute e materie prime. 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI 170_ Di norma i gestori di hedge fund possono operare senza l’autorizzazione di un organismo di vigilanza e sono perlopiù non regolamentati. In particolare, non sono soggetti alle numerose disposizioni per la tutela degli investitori che si applicano agli organismi di investimento collettivo in valori mobiliari. Tali disposizioni regolano, tra l’altro, la liquidità, il rimborso su richiesta delle quote di fondi, la necessità di evitare i conflitti di interesse, la determinazione di prezzi equi per le quote di fondi, l’informativa e i limiti all’indebitamento. 171_ Poiché non devono sottostare a tali regole, gli hedge fund possono impiegare un grado di leva finanziaria più elevato rispetto ai fondi tradizionali autorizzati, ed effettuare operazioni d’investimento non consentite ai tradizionali organismi d’investimento collettivo. Un hedge fund può adottare strategie aggressive, tra cui l’utilizzo diffuso di vendite allo scoperto, leva finanziaria, swap, arbitraggio, derivati e contrattazione automatica. Tali strategie d’investimento sono spesso altamente complesse e molto poco trasparenti. Sovente l’investitore non riceve informazioni sufficienti sui mutamenti di strategia che potrebbero comportare un aumento significativo del rischio, o le riceve soltanto con molto ritardo. 172_ Nell’ambito della propria strategia di investimento, gli hedge fund possono trattare derivati quali future, opzioni e swap, che potrebbero essere quotati in borsa, ancorché non necessariamente. Tali strumenti possono essere soggetti ad una notevole volatilità dei prezzi, da cui deriva un elevato rischio di perdita per il fondo. I bassi margini di garanzia richiesti di norma per acquisire una posizione in tali strumenti consentono di far ricorso ad elevati livelli di indebitamento. A seconda dello strumento, una variazione relativamente contenuta del prezzo del contratto può comportare dunque perdite o profitti elevati in proporzione all’importo del capitale depositato come garanzia e, di conseguenza, ulteriori perdite imprevedibili che potrebbero ccedere ogni margine di copertura. 173_ I veicoli di investimento non quotati in borsa comportano altresì rischi addizionali, poiché non vi sono né una borsa né un mercato secondario nei quali sia possibile vendere le quote o liquidare le posizioni aperte. Potrebbe essere impossibile chiudere una posizione aperta o determinare il valore o il rischio di una posizione. Vendendo posizioni scoperte su titoli, un hedge fund si espone a un rischio illimitato di perdita. 17/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Private Equity PRIVATE EQUITY 174_ Private equity is a form of risk capital financing for companies that either are not exchange-listed or – occasionally – wish to delist. Investments are usually made at an early stage in a company’s development, when its chances of success are uncertain and the risks are therefore high. 174_ Il private equity è una forma di finanziamento con capitale di rischio per le società non quotate oppure, occasionalmente, per quelle che intendono ritirarsi dalla borsa. Gli investimenti avvengono di norma in una fase iniziale dello sviluppo dell’impresa, quando le opportunità di successo sono incerte ed i rischi di conseguenza elevati. 175_ Where private equity flows into young companies (start-ups) or small companies with growth potential that are at an early stage in their development, the term venture capital is also used. Private equity now also extends to risk capital made available to a company immediately before it goes public (late-stage financing, mezzanine financing). Normally the financing is constructed in such a way that the proceeds of the initial public offering are used to wholly or partially redeem the holdings of the shareholder entrepreneurs. If a change of ownership is financed, for example a delisting, the term “buyout” is customarily used. 175_ Se l’investimento è diretto ad imprese giovani (start-up) o a piccole imprese con potenziale di crescita che si trovano in una fase iniziale del proprio sviluppo, si parla anche di “venture capital”. Per “private equity” si intende anche il capitale di rischio messo a disposizione di una società prima che venga quotata in borsa (finanziamento delle fasi di consolidamento, finanziamento mezzanino). Normalmente il finanziamento è erogato in modo tale che i proventi dall’offerta pubblica iniziale vengono impiegati in tutto o in parte per rimborsare le partecipazioni degli imprenditori azionisti. Se il finanziamento è a sostegno di un cambio di proprietà, per esempio in caso di ritiro dalla quotazione in borsa, si usa di norma il termine “buyout”. 176_ The success of a private equity investment depends on the correct timing of the “exit” or sale and – especially with indirect investments via a fund, for example – on the quality of the private equity manager. The exit can be effected by going public (initial public offering or IPO), a sale to another company (trade sale) or to another private equity fund (secondary sale), or a management buyout. The choice of solution will depend largely on the market conditions prevailing at the time. How easy or difficult the exit phase is, and whether the proceeds meet expectations, will depend on factors such as the performance of the equity markets. 177_ Private equity investments are not regulated compared to equities listed for trading on an exchange. This means that investors may be exposed to more risks, for example due to lack of transparency (e.g. limited access to financial statements, lack of publication). 178_ Private equity investments involve considerable risks and can lead to substantial losses. They are based on a long-term approach and are much less liquid than exchangelisted equities. Normally, private equity investments cannot be sold until some years after the original investment. You should be aware that your capital will be tied up, either completely or with access subject to restrictions, for a long time. No distributions are made prior to exit from investments. You do not normally have any entitlement to exit early. Companies that are potential candidates for private equity investments may have high levels of borrowing and therefore be more sensitive than established companies to negative market developments such as rising interest rates. There is also a greater danger of the company becoming insolvent and going bankrupt than with listed companies. 179_ It is not unusual for further calls for capital to be made at short notice after the initial investment. If you fail to comply with such a demand, you may lose all the capital you have invested up to that time. 180_ A change of management in a young company where the personality of the individuals occupying key functions is a particularly important factor can have a highly detrimental effect on a private equity investment. 181_ With indirect investments, there is no guarantee that the manager of a private equity fund will be able to make investments and generate profits that fulfil the expectations for this form of investment. The abilities of the private equity manager are therefore crucial to the success of an indirect investment. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 176_ Il successo di un investimento di private equity dipende dalla corretta tempistica dell’“uscita” o della vendita e – specialmente nel caso degli investimenti indiretti, ad esempio mediante un fondo – dalla qualità del gestore. L’uscita può aver luogo mediate la quotazione in borsa (offerta pubblica iniziale o IPO), la vendita ad un’altra società (vendita commerciale) o ad un altro fondo di private equity (vendita secondaria), oppure mediante un management buyout. La scelta della soluzione dipende in larga misura dalle condizioni di mercato prevalenti al tempo. La facilità o la difficoltà della fase di uscita (o disinvestimento) e l’entità dei proventi in relazione alle aspettative dipenderanno da fattori quali l’andamento dei mercati azionari. 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI 177_ Gli investimenti di private equity non sono regolamentati con altrettanto rigore quanto le azioni negoziate in borsa. Di conseguenza, l’investitore potrebbe esporsi a maggiori rischi, ad esempio a causa della scarsa trasparenza (accesso limitato alle relazioni di bilancio, mancanza di pubblicazione). 178_ Gli investimenti di private equity comportano rischi notevoli e possono tradursi in perdite ingenti; sono basati su un approccio a lungo termine e sono molto meno liquidi delle azioni negoziate in borsa. Di norma, gli investimenti di private equity possono essere liquidati soltanto a distanza di anni dall’investimento originario. L’investitore deve essere consapevole che il suo capitale resterà completamente immobilizzato per lungo tempo, o sarà accessibile soltanto in misura limitata. Prima dell’uscita dall’investimento non vi sono distribuzioni di utili, e di norma non si ha diritto di recesso anticipato. Le società candidate ad un investimento di private equity potrebbero essere caratterizzate da livelli di indebitamento elevati e perciò, rispetto alle imprese consolidate, essere più sensibili alle tendenze negative del mercato, come un aumento dei tassi di interesse. Rispetto alle società quotate, vi è altresì un maggior rischio di insolevenza e fallimento della società destinataria dell’investimento di private equity. 179_ Non è inusuale che, poco dopo l’investimento iniziale, vengano effettuate ulteriori richieste di capitale. Se l’investitore non ottempera a tale richiesta, può perdere tutto il capitale investito fino a quel momento. 180_ Un avvicendamento del gruppo dirigente di un’impresa giovane, nella quale la personalità degli individui nelle funzioni chiave è un fattore particolarmente importante, può avere ripercussioni negative sugli investimenti di private equity. 181_ Nel caso degli investimenti indiretti, non vi è garanzia che il gestore di un fondo di private equity riesca ad effettuare le operazioni necessarie ed a generare profitti in linea con le aspettative di questa forma di investimento. Le capacità del gestore di private equity sono quindi cruciali per il successo di un investimento indiretto. 18/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Real Estate IMMOBILI 182_ Investments in real estate can be made directly or indirectly. Real estate comprises office buildings, retail and industrial premises, residential property and special real estate (such as hotels or hospitals). The variables that determine the value of a property are its location, construction, equipment fittings and the variety of ways in which it can be used. 182_ L’investimento in immobili può essere diretto o indiretto. Per immobili si intendono gli uffici, i locali commerciali e gli stabilimenti industriali, le abitazioni e gli edifici adibiti ad usi speciali (ad es. hotel o ospedali). Le variabili che determinano il valore di un immobile sono l’ubicazione, la costruzione, le dotazioni e la varietà di destinazioni d’uso. 183_ A direct investment involves actually buying property. This will usually require a high capital outlay, a long term investment horizon, in-depth knowledge of the sector, familiarity with the location and often personal involvement, as property needs to be professionally managed. 184_ Indirect investments in real estate generally require a lower capital outlay than direct investments. Indirect investments are divided into those that are exchange-listed and those that are not. Examples of unlisted indirect investments include real estate funds, shares of real estate companies that are not listed for trading on an exchange, and certificates on real estate funds. Real estate funds can reduce risk by diversifying across geographical areas and real estate categories. The main category of exchange-listed indirect investments is real estate investment trusts (REITs). These enable investors to invest in real estate without incurring certain disadvantages, such as illiquidity. 185_ Real estate investments are based on physical assets – land and buildings – that are ultimately unique, and in which trading is not regulated. 186_ Where real estate is concerned, it is therefore often difficult, or even impossible, to spread risks adequately or diversify investments sufficiently. With direct real estate investments especially, the high capital outlay required and the illiquidity of the property market makes diversification difficult or even impossible. 187_ Property markets are also frequently intransparent, and require precise knowledge of local circumstances. It is therefore vital to involve local experts, which hampers access to the market. 188_ Real estate often reacts to interest rate changes in a similar way to bonds: when interest rates are low, for instance, mortgages are cheap and it is easy to generate above-average profits. Conversely, high interest rates cause profits to contract. Fiscal incentives offered by the state to promote home ownership and attractive lending conditions can also lead to excessively high prices. 183_ Un investimento diretto comporta l’acquisto materiale di immobili. A tal fine occorrono un esborso elevato di capitale, un lungo orizzonte di investimento, conoscenze approfondite del settore, familiarità con l’ubicazione e spesso anche un coinvolgimento personale, poiché gli immobili vanno amministrati in maniera professionale. 184_ Gli investimenti indiretti in immobili, che richiedono di norma un esborso di capitale inferiore rispetto agli investimenti diretti, sono distinti in investimenti quotati e investimenti non quotati. Questi ultimi comprendono, ad esempio, i fondi immobiliari, le azioni di società immobiliari non quotate in borsa ed i certificati di fondi immobiliari. I fondi immobiliari possono ridurre i rischi tramite la diversificazione per aree geografiche e per categorie immobiliari. La principale categoria di investimenti indiretti quotati è data dai Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT), che permettono di investire in immobili senza incorrere in alcuni svantaggi, quali il rischio di illiquidità. 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI 185_ Gli investimenti immobiliari sono basati su attività fisiche – terreni ed edifici – con carattere di unicità, la cui compravendita non è regolamentata. 186_ Nel caso dell’investimento immobiliare, quindi, è spesso difficile se non impossibile distribuire adeguatamente i rischi o diversificare gli investimenti in misura sufficiente. Specialmente quando si investe direttamente in immobili, l’elevato esborso di capitale e l’illiquidità del mercato immobiliare rendono la diversificazione difficile o addirittura impossibile. 187_ I mercati immobiliari, inoltre, sono spesso opachi e richiedono conoscenze precise delle particolarità locali. È dunque essenziale avvalersi degli esperti del luogo, e ciò ostacola l’accesso al mercato. 188_ Spesso gli immobili reagiscono a variazioni dei tassi di interesse in maniera analoga alle obbligazioni: ad esempio, se i tassi sono bassi i mutui ipotecari sono convenienti ed è facile realizzare guadagni superiori alla media; viceversa, tassi di interesse elevati comportano una riduzione dei profitti. Anche gli incentivi fiscali offerti dallo Stato per promuovere la proprietà dell’abitazione e condizioni creditizie attraenti possono determinare un aumento eccessivo dei prezzi. METALLI PREZIOSI ED ALTRE MATERIE PRIME Precious metals and other commodities 189_ Commodities are physical goods that are produced via agriculture and mining, for example, and standardised for use as the underlying of a transaction. Derivatives on commodities such as energy sources, precious and other metals, and agricultural products are traded on futures markets. 189_ Le materie prime (commodity) sono merci prodotte, ad esempio, dal settore agricolo e minerario, e standardizzate per l’uso quali sottostanti di una transazione. I derivati su materie prime quali fonti di energia, metalli preziosi e di altra natura, e prodotti agricoli vengono negoziati nei mercati dei future. 190_ Contractual agreements allow investors to buy or sell futures linked to the performance of a particular commodity. This means that they can buy a standardised amount of a commodity at a specific time in the future for a specific price. 190_ Grazie ad appositi accordi contrattuali, gli investitori possono comprare o vendere future collegati all’andamento di una particolare materia prima, ovvero acquistare o vendere una quantità standardizzata di una data materia prima in un determinato momento futuro a un prezzo prestabilito. 191_ The commonest way in which private individuals invest indirectly in commodities is via structured products (see 107 ff. above). There are other alternatives, such as commodity swaps and options that are not listed for trading on an exchange. These are traded directly between the parties concerned and are tailor-made products. More information on how forwards and futures work can be found in a separate section of this brochure (see 86 ff. above). 191_ I prodotti strutturati (si veda §107 e ss.) sono il veicolo più comune mediante il quale i privati investono indirettamente in materie prime; vi sono anche altre alternative, come gli swap e le opzioni su materie prime, che non sono quotati in borsa. Questi strumenti vengono negoziati direttamente tra le parti interessate e costituiscono prodotti su misura. Per ulteriori informazioni sui future e i contratti a termine si rimanda alla sezione rilevante del presente opuscolo (si veda §86 e ss.). D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 19/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 192_ With commodity futures, you may receive physical delivery of the commodity concerned on expiration, while structured products normally provide for cash payment. If you prefer cash settlement, you will have to sell the futures before their expiration date. Such products are therefore more risky than, for instance, equities or collective investments. 192_ Nel caso dei future su materie prime, alla scadenza è prevista di norma la consegna fisica del sottostante, mentre nel caso dei prodotti strutturati si ha un pagamento in contanti. Se si preferisce la liquidazione in contanti, bisogna vendere i future prima della data di scadenza. Tali prodotti sono quindi più rischiosi, ad esempio, delle azioni o degli investimenti collettivi. 193_ The price of commodities is influenced by a number of factors. These include: 193_ Il prezzo della materie prime è influenzato da una molteplicità di fattori. Tra questi: – the relationship between supply and demand – climate and natural disasters – state programmes and regulations, national and international events – state intervention, embargoes and tariffs – movements in interest and exchange rates – trading in commodities and the corresponding contracts – provisions relating to monetary policy, trading, fiscal and currency controls. These variables can lead to additional investment risks. - la relazione tra la domanda e l’offerta - il clima e i disastri naturali - i programmi e le regolamentazioni statali, gli eventi nazionali e internazionali - gli interventi pubblici, gli embargo e i dazi doganali - i movimenti dei tassi di interesse e dei cambi - la compravendita di materie prime e i contratti corrispondenti - le disposizioni relative ai controlli monetari, commerciali, fiscali e valutari Tali variabili possono comportare rischi di investimento addizionali. 194_ Commodities investments are more volatile than conventional investments, and yields on commodities can collapse at short notice. The volatility of commodity prices also affects the value, and hence the price, of a futures contract based on those commodities. Conventional futures on oil, base and precious metals are normally easy to trade, regardless of their term. 194_ Gli investimenti in materie prime sono più volatili di quelli tradizionali, e i rendimenti sulle valute possono crollare con pochissimo preavviso. La volatilità dei prezzi delle materie condiziona anche il valore, e quindi il prezzo, di un contratto future basato su tali materie prime. I future tradizionali su petrolio, metalli di base e preziosi sono di norma facilmente negoziabili, indipendentemente dalla scadenza 195_ When market activity is limited, a contract can become illiquid. Depending on how the yield curve moves, such illiquidity can lead to significant price changes. This is a typical feature of commodities. 195_ Quando l’attività di mercato è limitata, un contratto può facilmente diventare illiquido. A seconda dell’andamento della curva dei rendimenti, tale illiquidità può comportare notevoli variazioni dei prezzi. Questa è una caratteristica tipica delle materie prime. Investments in Emerging Markets 196_ There is no standard definition of the term “emerging markets”. In the broadest sense it includes all economies that are not regarded as “advanced” (see 197 below). Common criteria for defining what is an emerging market are per capita income, the level of development of the financial sector, and the proportion of the total economy that is made up by the service sector. The creditworthiness of countries that fall within this definition can vary widely: from very high to very low, with – in the latter case – very high default risk. Although they can be at very different stages in their economic development, most emerging markets have a political system that is very new (for instance they have only recently become democracies) or is currently changing. This means that the political system and its institutions may be less stable than in an advanced nation. 197_ The list of emerging markets is changing constantly. According to the criteria applied by the International Monetary Fund in October 2007, they include all countries except: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Korea, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Singapore, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, the UK and the US. These nations are classed as having advanced economies. 198_ There are risks linked to investments in emerging markets that are not encountered in their advanced counterparts. This is also the case when the issuer or provider of a product has its headquarters or primary focus of activity in an emerging nation. 199_ Investing in products linked to emerging markets is therefore often speculative. Before investing in emerging markets, you should form an impression of them that allows you to assess the risks involved. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI INVESTIMENTI NEI MERCATI EMERGENTI 196_ Non esiste una definizione convenzionale del termine “mercati emergenti”, che viene usato in senso lato per indicare tutte le economie che non sono considerate “avanzate” (si veda §197 sotto). I criteri più comuni per la definizione di un mercato emergente sono il reddito pro capite, il livello di sviluppo del settore finanziario e la proporzione dell’economia totale rappresentata dal settore dei servizi. L’affidabilità creditizia dei paesi che rispondono a questa definizione può variare ampiamente: si va dai paesi con un’affidabilità molto elevata a quelli con un’affidabilità molto bassa, caratterizzati da rischi di insolvenza molto alti. Benché spesso abbiano raggiunto livelli di sviluppo economico molto diversi, i mercati emergenti presentano per lo più sistemi politici molto nuovi (ad esempio, hanno appena adottato un regime democratico) oppure in transizione. Di conseguenza, il sistema politico e le istituzioni di questi paesi possono essere meno stabili che nelle nazioni avanzate. 197_ L’elenco dei mercati emergenti è in continuo cambiamento. Secondo i criteri applicati dal Fondo Monetario Internazionale nell’ottobre 2007, questa categoria includeva tutti i paesi fuorché: Australia, Austria, Belgio, Canada, Cipro, Corea del Sud, Danimarca, Finlandia, Francia, Germania, Grecia, Hong Kong, Irlanda, Islanda, Israele, Italia, Giappone, Lussemburgo, Norvegia, Nuova Zelanda, Paesi Bassi, Portogallo, Regno Unito, Singapore, Slovenia, Spagna, Stati Uniti, Svezia, Svizzera e Taiwan. Queste nazioni sono classificate tra le economie avanzate. 198_ Gli investimenti nei mercati emergenti comportano rischi non presenti nelle nazioni avanzate. Ciò accade anche se l’emittente o il fornitore di un prodotto hanno la propria sede o svolgono la parte preponderate delle proprie attività in un paese emergente. 199_ Spesso perciò gli investimenti in prodotti collegati ai mercati emergenti sono speculativi. Prima di investire nei mercati emergenti, bisognerebbe acquisire sufficienti informazioni in materia in modo da poter valutare i rischi a cui si va incontro. 20/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari 200_ When investing in emerging markets, the following risks should be taken into account. The list is not exhaustive. Depending on the type of investment product, there may be additional risks involved as described elsewhere in this brochure. 200_ Quando si investe nei mercati emergenti si devono prendere in considerazione i rischi elencati di seguito. L’elenco non è esaustivo: A seconda del tipo di prodotto l’investimento potrebbe comportare ulteriori rischi, come descritto in altre sezioni del presente opuscolo. Political risk 201_ A government’s political inexperience or the instability of the political system increases the risk of short-term, fundamental shifts in a nation’s economy and politics. The consequences for you as an investor can include the confiscation of your assets with no compensation, the restriction of your rights of disposal over your assets, or government- imposed controls. State intervention in specific sectors of industry can result in a dramatic fall in the value of investments in those sectors. Rischio politico 201_ L’inesperienza politica di un governo o l’instabilità del sistema politico accrescono il rischio di mutamenti rapidi e fondamentali del quadro economico e politico di un paese. Tra le conseguenze per gli investitori vi sono la confisca delle attività patrimoniali senza indennizzo, la limitazione del diritto di poter disporre del proprio patrimonio e l’introduzione di controlli pubblici. L’intervento dello Stato in specifici settori industriali può determinare una brusca flessione del valore degli investimenti in tali settori. Economic risk 202_ Emerging market economies are more sensitive to changes in interest and inflation rates, which are in any case subject to greater swings than in the developed nations. The focus of such economies is often relatively narrow, allowing single events to have a magnified impact. In addition, emerging nations generally have a lower capital base. Finally, their financial markets often lack an adequate structure and sufficient supervision. Rischio economico 202_ I mercati emergenti sono più sensibili alle variazioni dei tassi di interesse e di inflazione, che in ogni caso sono soggetti a oscillazioni più ampie che nei paesi avanzati. Tali economie sono spesso relativamente poco differenziate, sicché l’impatto dei singoli eventi risulta talvolta amplificato. Inoltre, le nazioni emergenti presentano di norma una base patrimoniale ridotta. Infine, i mercati finanziari di questi paesi sono spesso privi di una struttura adeguata e di una sorveglianza sufficiente. Credit risk 203_ Investments in debt securities (e.g. bonds, notes) issued by emerging market governments or companies tend to entail higher levels of risk than advanced market debt. This can be due to inferior creditworthiness, a high level of government debt, debt restructuring, a lack of market transparency or a lack of information. It is also much more difficult to assess credit risk due to inconsistent valuation standards and the absence of ratings. Rischio di credito 203_ Gli investimenti in titoli di debito (ad es., obbligazioni, note) emessi da governi o aziende dei mercati emergenti comportano tendenzialmente un grado di rischio maggiore rispetto agli investimenti nel debito dei mercati avanzati; ciò può essere dovuto alla minore affidabilità creditizia, a livelli più elevati di debito pubblico, alla ristrutturazione del debito, alla scarsa trasparenza dei mercati o alla mancanza di informazioni. Inoltre, è molto più difficile valutare il rischio di credito a causa dei criteri di valutazione non uniformi e dell’assenza di rating. Currency risk 204_ The currencies of emerging market nations are subject to unpredictable fluctuations in value that are larger than those of advanced countries. Some countries limit the export of their currency or can impose short-term restrictions, or stop pegging their currency to a reference currency such as the dollar. Hedging can help limit losses resulting from currency swings, but they can never be entirely eliminated. Inflation risk 205_ Large fluctuations in the value of the currency and an insufficiently developed financial market can make it difficult for an emerging market nation’s central bank to stick to its inflation targets. As a result, inflation may fluctuate more than in advanced countries. Market risk 206_ Because there is little or no supervision of financial markets in emerging market nations, regulation, market transparency, liquidity and efficiency are often inadequate. Moreover, high volatility and large price differences are characteristic of these markets. Finally, the inadequacy or absence of regulatory measures gives rise to an increased danger of market manipulation or insider trading. Market liquidity risk 207_ Liquidity is dependent on supply and demand. The impact on the emerging markets of social, economic and political changes or natural disasters can involve a much more rapid and lasting change to this supply and demand equation than would be the case in the advanced markets. In an extreme case, illiquidity can be the result. This can make it impossible for an investor to sell his/her investments. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI Rischio valutario 204_ Rispetto alle valute dei mercati avanzati, quelle dei mercati emergenti vanno soggette ad oscillazioni imprevedibili e di maggiore ampiezza. Alcuni paesi limitano o possono introdurre restrizioni a breve termine sull’esportazione della propria valuta, oppure smettere di ancorare il valore della valuta a quella di una divisa di riferimento, come il dollaro. Le operazioni di copertura (hedging) possono limitare le perdite derivanti dalle fluttuazioni valutarie, ma senza eliminarle del tutto. Rischio di inflazione 205_ Per la banca centrale di un paese emergente può essere difficoltoso perseguire un obiettivo di inflazione, a causa delle ampie fluttuazioni del valore della valuta e di un mercato finanziario non sufficientemente sviluppato. Di conseguenza, l’inflazione può essere più variabile che nei paesi avanzati. Rischio di mercato 206_ A causa della sorveglianza inadeguata o inesistente sui mercati finanziari dei paesi emergenti, la regolamentazione, la trasparenza dei mercati e l’efficienza sono spesso insufficienti. Inoltre, questi mercati sono caratterizzati da una volatilità pronunciata e da ampie differenze di prezzo. Infine, l’inadeguatezza o l’assenza di un quadro normativo accresce il rischio di manipolazione del mercato o di insider trading. Rischio di liquidità del mercato 207_ La liquidità dipende dalla domanda e dall’offerta. L’impatto dei cambiamenti sociali, economici e politici o dei disastri naturali sui mercati emergenti può comportare un mutamento molto più rapido delle condizioni di domanda e offerta di quanto non accadrebbe nei mercati avanzati. Nei casi estremi il risultato può essere l’illiquidità, che impedisce all’investitore di vendere il proprio investimento. 21/22 | Page Pagina Special Risks in Securities Trading / Rischi particolari nella negoziazione di valori mobiliari Legal risk 208_ The absence or inadequacy of financial market supervision can lead to your legal rights being difficult or impossible to enforce. Moreover, legal uncertainty may exist due to the inexperience of the emerging nation’s judiciary. Rischio legale 208_ L’assenza o l’inadeguatezza della vigilanza sui mercati finanziari può impedire all’investitore di far valere in tutto o in parte i propri diritti. Inoltre, l’inesperienza delle autorità giudiziarie nei paesi emergenti può creare condizioni di incertezza legale. Settlement risk 209_ Certain emerging markets have an array of different clearing and settlement systems. These are often outmoded and prone to processing errors as well as considerable delays in settlement and delivery. Some countries do not have any such systems at all (see 14 above). Rischio di adempimento 209_ Alcuni mercati emergenti presentano una molteplicità di sistemi di compensazione e regolamento differenti, i quali sono spesso obsoleti, soggetti ad errori di esecuzione nonché a notevoli ritardi nel regolamento e nella consegna. Alcuni paesi sono del tutto privi di tali sistemi (si veda §14 sopra). Shareholder risk and creditor risk 210_ Legislation to protect the rights of shareholders and creditors (e.g. duties of disclosure, insider trading ban, management responsibilities, minority shareholder protection) may often be inadequate or non-existent. Rischio dell’azionista e del creditore 210_ Nei mercati emergenti le disposizioni a tutela dei diritti degli azionisti e dei creditori (ad es., obblighi di informativa, divieto di insider trading, responsabilità del management, protezione degli azionisti di minoranza) sono spesso inadeguate o inesistenti. D-CLIENT-01-08-EN-IT_v1.0 2. Section Two/ Parte Seconda Additional information / INFORMAZIONI ADDIZIONALI 22/22 | Page Pagina
Scarica