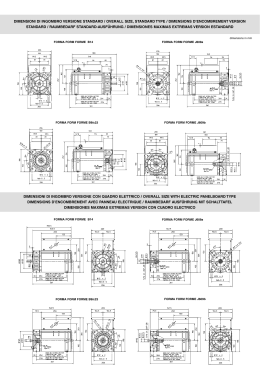
Flameproof motors Moteurs antidéflagrants Explosionsgeschützte Motoren Motores antideflagrantes Motori antideflagranti Aluminium 56 - 80 EEx-d, EEx-de • IIB, IIC Les Ateliers de l’Avre Atav - Les Ateliers de l’Avre Cen - Constructions Electriques Nancy are Cemp SpA trademarks Flameproof motors Moteurs antidéflagrants Explosionsgeschützte Motoren Motores antideflagrantes Motori antideflagranti Aluminium 56 ÷ 80 EEx-d, Catalogue 12 Edition 02-04 EEx-de Catalogue 12 Edition 02-04 • IIB, IIC Katalog 12 Die Auflage 02-04 Catálogo 12 Edición 02-04 Catalogo 12 Edizione 02-04 GB CONTENTS 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 General informations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Series F motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Main characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Main options ............................... Design features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mounting arrangements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Installation and applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Materials, painting and nameplate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bearing seal and mounting interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Terminal box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Connecting diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Three-phase motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Single phase motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Self-braking motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 8 9 9 10 10 12 13 15 17 18 18 20 21 4. 4.1 4.2 4.3 24 24 25 25 26 26 28 29 31 33 34 34 36 37 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5 6 Page Performance data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 Three-phase, 1-speed, ventilated motors . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Three-phase, 1-speed, unventilated motors . . . . . . . . . 90 Three-phase motors, 2 speeds, for general purpose (constant torque) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Three-phase motors, 2 speeds, for centrifugal machines (quadratic torque), . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 Three-phase, 1-speed, self-braking motors . . . . . . . . . 96 Motors driven by inverter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98 Single-phase motors, 1 speed, . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 Overall dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103 Spare parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117 F SOMMAIRE 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 Informations générales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Les moteurs de la série F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Caractéristiques principales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Options principales .......................... Caractéristiques mécaniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Formes de construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Installation et applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Matériaux, peintures et plaque signalétiques . . . . . . . . . . Tenue des paliers et interfaces de montage . . . . . . . . . . Boîte à bornes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Schémas de branchement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Moteurs triphasés . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Moteurs monophasés . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Moteurs-freins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5. 6 Page Données nominales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 Moteurs triphasés, 1 vitesse, ventilés . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Moteurs triphasés, 1 vitesse, non ventilés . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Moteurs triphasés, 2 vitesses, pour usage général (couple constant) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Moteurs triphasés, 2 vitesses, pour machines centrifuges, (couple quadratique) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 Moteurs-freins triphasés, 1 vitesse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96 Moteurs alimentés par inverseur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98 Moteurs monophasés, 1 vitesse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 Dimensions d'encombrement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103 Pièces détachées . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117 D INHALTSVERZEICHNIS 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 Allgemeine Informationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motoren Serie F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hauptmerkmale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hauptausführungen .......................... Mechanische Eigenschaften . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bauformen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Installation und Anwendungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Material, Lackierung und Typenschild . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dichtung der Lager und Montageschnittstellen . . . . . . . . Klemmkasten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Schaltung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Drehstrommotoren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Einphasenmotoren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Selbstbremsende Motoren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 40 41 41 42 42 44 45 47 49 50 50 52 53 4. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5. 6. Seite Betriebsdaten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl, belüftet . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl, unbelüftet . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Drehstrommotoren, 2 Drehzahlen, für allgemeinen Gebrauch (konstantes Gegenmoment), . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Drehstrommotoren, 2 Drehzahlen, für Zentrifugalmaschinen, (quadratisches Gegenmoment), . . 94 Selbstbremsende Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl . . . . . 96 Durch Frequenzwandler betriebene Motoren . . . . . . . . 98 Einphasenmotoren, 1 Drehzahl, . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 Abmessungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103 Ersatzteilliste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117 E ÍNDICE 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 I 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 Informaciones generales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motores serie F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Características principales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Opciones principales ......................... CaracterÍsticas mecánicas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Formas de fabricación . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Instalación y aplicaciones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Materiales, pintado y placa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Resistencia de los cojinetes y piezas para el montaje . . . Caja de bornes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Esquemas de conexión . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motores trifásicos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motores monofásicos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motores con freno . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56 56 57 57 58 58 60 61 63 65 66 66 68 69 4. 4.1 4.2 4.3 72 72 73 73 74 74 76 77 79 81 82 82 84 85 4. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5. 6. Página Données nominales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 Motores trifásicos, 1 velocidad, ventilados . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Motores trifásicos, 1 velocidad, no ventilados . . . . . . . . . 90 Motores trifásicos, 2 velocidades, para uso general (par constante) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Motores trifásicos, 2 velocidades, para máquinas centrífugas (par cuadrático) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 Motores con freno trifásicos, 1 velocidad . . . . . . . . . . . 96 Motores accionados por un variador de frecuencia . . . . 98 Motores monofásicos, 1 velocidad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 Dimensiones de espacio máximo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103 Piezas de repuesto . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117 INDICE Informazioni generali . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motori serie F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Caratteristiche principali . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Principali opzioni ............................ Caratteristiche meccaniche . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Forme costruttive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Installazione e applicazioni . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Materiali, verniciatura e targa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cuscinetti e interfacce di montaggio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Scatola morsettiera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Schemi di collegamento . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motori trifase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motori monofase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motori autofrenanti . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5. 6. Pagina Dati nominali . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87 Motori trifase, 1 velocità, ventilati . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Motori trifase, 1 velocità, non ventilati . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Motori trifase, 2 velocità, per uso generale (coppia costante) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Motori rifase, 2 velocità, per macchine centrifughe (coppia quadratica) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 Motori autofrenanti trifase, 1 velocità . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96 Motori con alimentazione a mezzo inverter . . . . . . . . . . . 98 Motori monofase, 1 velocità . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 Dimensioni d’ingombro . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103 Parti di ricambio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117 Flameproof motors GB 1. General information 1.1 Series F motors 1.1 Series F ATEX motors The motors offered in this catalogue comply with standards concerning equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, in compliance with European Directive 94/9/EC dated 23/3/94, otherwise known as the ATEX directive. GB The ATEX directive states that two different certificates of conformity are to be issued. One is the “EC Standard type” for the homologation of the prototype and the other is for the “Production Quality Assurance”. The production quality Guarantee certificate number is: LCIE 00 ATEX Q8007. The Certificates are issued by the Laboratoire Central des Industries Electriques (L.C.I.E) (Notified Body no. 0081). The conformity certificate numbers are listed in the performance data. Table 1 A - The series F ATEX Version Frame size [mm] Output range (2 pole) [kW] Temperature class (*) IIB IIC Single speed, three phase (2, 4, 6, 8 poles) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,50 T5 / T6 F-BTV F-CTV Three-phase, 1-speed, unventilated (2, 4, 6, 8 poles) 56 - 80 0,06 - 0,55 T4 F-BST F-CST Two speeds, three phase (2/4, 4/6, 4/6, 4/8 poles) (constant-torque) 63 - 80 0,25 - 0,75 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Two speeds, three phase (2/4, 4/8, 4/6, 6/12 poles) (quadratic-torque) 63 - 80 0,25 - 1,10 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Three-phase, 1-speed, with brake (2, 4, 6, 8 pôles) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,10 T4 F-BTVF F-CTVF Single phase, (2, 4, 6 poles) 56 63 - 80 0,06 - 0,08 0,12 - 0,75 T4 F-BM F-BMV F-CM F-CMV (*) For minimum overheating, the temperature class is indicated in chap. 4 (Performance data). Table 1 B - Customizable temperature class (referred to an ambient temperature of 40°C) Frame size 56 - 80 T5 T6 Same power as T4 (*) Power lower (*) For single and three-phase, 2-speed motors: power lower than T4, unless otherwise specified in chap. 4.1. 8 Series 1.2 1.3 1.2 Main characteristics Main options Main characteristics • Explosion-proof motors according to European standard CENELEC EN 50 014, EN 50 018 and EN 50 019 (for terminal box EEx-e). • The European Standards are known and accepted by most Countries world-wide besides CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization) member countries. • Three phase and single phase Squirrel Cage Asynchronous Induction motors. • Totally enclosed, fan cooled, frame IP55 with Terminal box IP65. • The motors dimensions comply with IEC 60072 standard. • Power Supply 400V / 50Hz. Three-phase, 1-speed motors, 2-4-6-8 poles, T4, for sizes between 56 and 80, multi-voltage power supply 380-400-420V/ 50 Hz. • Class F insulation. 1.3 • Noise level (dBA) Noise values measured both loadless and at the rated power supply condition are lower than those set forth by the NF 51-119 Standard (IEC 34-9). We can also provide special applications. • Terminal Box: - available both in a flameproof version, or in an increased safety version - large size - normally installed on the side opposite the feet, can be oriented right- or leftwards frame separation grid - rotating by 90° in 4 positions - frame separation grid. • - Motor frame: cooling fins removable feet pad for direct frame connection removable through hole flange front and back lip seal (IP55) earthing screw. • - Rotor: in pressure cast aluminium alloy shaft mounting by ring nut dynamic balanced with feather key fully seated - insulating paint. • High protection against corrosion: - stainless steel nameplate - anticorrosion plated fasteners. • The following parts are highly resistant to impact: - cast aluminium fan cover. GB • Low friction dust seals. • Vibration level: the dynamic balancing of the rotors (half spline) allows for a level of residual vibrations in three-phase motors which corresponds to the N degree (normal) according to IEC 34-14. • The conformity certificates also cover design characteristics that differ from the basic version, such as: - modification of the maximum installation altitude - modification of the rated voltage and rated frequency - power supply from an inverter - motor protection through temperature detectors - application for operating modes S2 to S9. Main options • Motors protection IP56 - IP65 - IP66. • Terminal box with special cable entries. • Tropicalised motors (relative humidity level H% including between 90 and 98%). • Motors without terminal box, with cable output. • Motors with tacho-generator or encoder. • Special flanges and shafts. • Motors with bi-metallic detector thermistors, PTC thermistors or PT100 resistive sensors (a second cable gland is supplied). • Double ended shafts. • Motors with heaters. • Grade R and S balancing. • Motors for special applications available on request. • Motors with rain cap. • Large motors with special bearings (unidirectional). • Increased safety “e” terminal box, see chap. 2.5. • Non-standard voltages and frequencies (maximum voltage 690V). • Motors with special electrical design. • Motors suitable for frequency inverter drive. • Motors for areas classified as zone 21 and zone 22 (Dust). 9 2. Design features 2.1 Mounting arrangements 2.1 Mounting arrangements The most commonly used mounting arrangements are shown in the table 2 A. Other mounting arrangements are available on request. GB Standard motors ordered in basic mounting arrangements (universal mounting arrangements) IM B3, IM B5 or IM B14 can also be operated in the following different mounting positions: IM B3 in IM B6, IM B7, IM B8, IM V5 or IM V6, IM B5 in IM V1 or IM V3, IM B14 in IM V18 or IM V19. Table 2 A Foot-mounted motor CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II V5 IM V5 IM 1011 B5 IM B5 IM 3001 V1 IM V1 IM 3011 B14 IM B14 IM 3601 V18 IM V18 IM 3611 Flange-mounted motor: large flange, clearance fixing holes According to the restrictions for explosion-proof electrical machinery it is forbidden that foreing bodies be allowed to fall into the fan cowl. Therefore vertically mounted shaft down motors are fitted with a protective hood over te fan cowl. Foot and flange-mounted motor: large flange, clearance fixing holes In case of vertical arrangement with shaft end up the protection against foreign bodies must be ensured by the working machine or by a suitable cover. However, the cooling air access may not be hindered by this cover. Flange-mounted motor: small flange, tapped fixing holes CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II Foot and flange-mounted motor: with small flange, tapped fixing holes CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II 10 B3 IM B3 IM 1001 2.1 GB V6 IM V6 IM 1031 B6 IM B6 IM 1051 B7 IM B7 IM 1061 B8 IM B8 IM 1071 V3 IM V3 IM 3031 B35 IM B35 IM 2001 V15 IM V15 IM 2011 V36 IM V36 IM 2031 V19 IM V19 IM 3631 B3/B14 IM B34 IM 2101 V5/V18 IM V58 IM 2111 V6/V19 IM V69 IM 2131 11 2.2 Installation and application 2.2.1 Thermal and environmental specifications 2.2.2 Harsh industrial environments 2.2.1 Thermal and environmental specifications GB Operating conditions Except for some particular notes, the specifications of the motors of chap. 4 (Performance data) correspond to the operating condition S1 (uninterrupted operation according to IEC 34-1). Special requirements for other approved conditions of use can be met. Explosion groups and temperature classes Except for some particular notes, motors are available in Group IIB or IIC. The standard temperature class with which motors are supplied is T4, unless otherwise specified in chap. 4.1 (Performance data). Motors class T5 or T6 are also available on request. Ambient temperature and altitude The control of surface temperatures within the limits set forth by the temperature class entails the use at an ambient temperature which should be less than or equal to 40° C and at an altitude lower than or equal to 1000 m (according to NF C 51-111). The minimum ambient temperature for using the standard motors of the choice chart is of -20° C. Further information on operating conditions not complying with these limits is available on request. Winding overheating The overheating of motor winding described in chap. 4 (Performance data) is less than or equal to 80 K. 2.2.2 Harsh industrial environments For harsh industrial environments (among which chemical industry, raw materials industry, and energy production), proposes a hardened model according to the German standard VIK (Vereinigung Industrielle Kraft wirschaft). The corresponding option, called “VIK”, relates to EEx-de IIC motors. 12 Compared to the standard, the construction differences are: - improved safety EEx-e large-sized terminal box, provided with screw studs, with adjustable cable output that prevents having to move the board. - PTC thermal protection included, - stainless steel nuts, bolts and nameplate, - two-layer epoxy resin outside finish, 2 x 40 µm, - inside finish: insulating paint on rotor and winding coil heads, - additional nameplate in the terminal box, - rain cap. Thermal limits of the winding insulators The winding insulators are made with class F materials. Humidity The standard motors of the choice chart can be used up to a relative humidity of H% = 90. 2.3 Materials, painting and nameplate 2.3.1 Materials and painting 2.3.1 Materials and painting Materials Table 2 B - Materials of the main components Frame size 56 - 80 Frame Endshields Terminal box Fan cover Standard aluminium alloy Fan Antistatic composite plastic material or aluminium Shaft Acier XC 48 Stator Rigidly assembled low-loss metal sheets Winding Class of insulation F or H Bolts and screws Galvanized steel; stainless steel is also available on request Cable gland Aluminium, nickel-plated brass or stainless steel Surface treatment specifications Standard finish: No treatments, natural aluminium-coloured motor. Recommended for use: - in damp places or with water vapour - in chemical or not very aggressive environments - with motor surface temperatures from -20° C to +130° C. Optional finish: • Primer: - degreasing - one phosphating layer of about 20 µm (compatible with any further finish, except for epoxy resin) • Polyurethane finish - degreasing - one modified vinyl wash primer layer of about 10 µm - one glossy of blue (RAL 5010) two-component polyurethane layer (of about 30 µm) - nuts and bolts in stainless steel. Recommended for use: - in wet places, with water vapour or with poorly saline air - in fairly harsh industrial environment with occasional ejection of aggressive chemical products. - with motor surface temperatures from -20° C to +130° C. GB • Epoxy resin finish - degreasing - one modified vinyl wash primer layer of about 10 µm - one glossy of blue (RAL 5010) two-component polyamide epoxy resin (of about 25 µm) - stainless steel nuts and bolts. Recommended for use: - in wet places, with water vapour or with saline air - in harsh industrial environment with aggressive chemical products. - with motor surface temperatures from -20° C to +130° C. • Special finishes can be provided. 13 2.3 2.3.2 Nameplate 2.3.2 Nameplate Identification Motors are identified by a nameplate with the markings described below: GB Table 2 C - Markings prescribed by the current regulation Markings Meaning EEx d de II B-C T4 - T5 - T6 LCIE N° ... CE mark Specific explosion protection related mark Symbol of safety equipment meeting a protection class “Flameproof enclosure” protection class “d” motor and “e” terminal box Explosion group Enclosure group Ignition temperature class CE type certificate no Table 2 D - Other markings Markings Meaning ATAV CEMP FRANCE NONANCOURT FRANCE Type ... N° ./. kg ... kW ... Volts ... Amp ... Cos. ... Hz ... min-1 ... S ... CI. IP °C amb ... Vis: Cl. Commercial mark Manufacturer's name and address Motor's commercial reference Serial no./Year of manufacture Motor's weight Motor's power Delta voltage / star voltage Delta current / star current Power factor Rated frequency Rpm Operating conditions Insulation class Protection class Maximum ambient temperature Nuts and bolts resistance class Nameplate The nameplate, made of stainless steel, is secured to the frame with grooved nails. Les Ateliers de l’Avre SA N° II T IP L.C.I.E. 2613 Type: EExd II2G 0081 Fabriqué par: Cemp France F 27320 NONANCOURT ATEX Vis/screw Schraube : cl. kW S Hz cl. V±10% Date: min-1 °C max A cos ϕ Fig. 2 A - Nameplate 14 kg IEC 34-1 2.4 Bearing seal and mounting interfaces 2.4.1 Bearings 2.4.2 Mechanical specifications 2.4.1 Bearings Standard motors are provided with ball bearings with deep and sealed grooves. Bearings on the driving end are locked. Bearings used: Frame size (mm) Bearing, driving end, type Bearing, non driving end, type 56 63-71 80 6202 ZZ 6203 2RS 6005 2RS 6200 ZZ 6203 2RS 6004 2RS GB 2.4.2 Mechanical specifications Loads applicable on the shaft end The maximum dynamic loads that can be applied (N) for an operating cycle of L10h = 25,000 hours are as follows: Table 2 E Stress (N) 2 poles Frame size Stress direction 4 poles Frame size 6 poles Frame size 8 poles Frame size 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 350 480 510 460 610 650 540 710 740 600 780 820 240 350 370 330 440 470 370 510 540 420 560 590 220 330 330 310 420 430 350 490 500 400 540 550 250 370 410 340 460 510 400 530 580 440 580 630 IMB... ; IMV... IMB... IMV... 15 2.4 2.4.3 Special manufactures 2.4.3 Special manufactures Motor mounting interfaces Special flanges In addition to the standard mounting arrangements shown in chapter 2.1, motors are also available mounted with pads for anchorage to a pipe or ventilation system. Motors are available with flanges other than standard flanges which comply with NFC 51-120 regulations, with through holes (B5) or threaded holes (B14). The table below, in addition to the figures given in chapter 5 (Overall dimensions), gives the measurements of the available flanges. GB Table 2 F Frame size 16 Structural form Flange Dimensions [mm] ØM ØN ØP Ø TLB Ø TTB 56 B5 B5 B14 FF85 FF115 FT75 85 115 75 70 95 60 105 140 90 7.0 9.0 --- ----M5 63 B5 B14 B5 B14 FF100 FT65 FF130 FT85 100 65 130 85 80 50 110 70 120 85 160 105 7.0 --9.0 --- --M5 --M6 71 B5 B14 B5 B14 B5 FF100 FT65 FF115 FT75 FF165 100 65 115 75 165 80 50 95 60 130 120 85 140 90 200 7.0 --9.0 --11.0 --M5 --M5 --- 80 B5 B5 B14 B5 FF115 FF130 FT85 FF215 115 130 85 215 95 110 70 180 140 160 105 250 9.0 9.0 --13.5 ----M6 --- 2.5 2.5 Terminal box Terminal box Wiring with “d” terminal box Options for cable gland “d” Options for terminal box “e” • Terminal box is arranged according to the feet (for IM1... or IM2... mounting). The terminal box axis is normally perpendicular to the laying surface. Optionally, it can be supplied for “right” or “left” mount according to a front view of the motor, main shaft end side (without surcharge). Note: the terminal box position can only be changed at the factory. - terminal box supplied without cable gland, with threaded hole ISO M - gasket Ø 9 or 13 mm for cable gland - additional cable gland (standard model) or additional hole - cable gland with shielding extension - cable gland for armoured cable or special cable gland. • Increased safety EEx-e terminal box: - available for ventilated three-phase motors with 63 to 80 HA - IP55 (IP65 optional); maximum voltage 690V, waterproof connection system, removable between terminal box and frame supplied with an EEx-e cable gland for a non-armoured cable with 7.5 to 13 mm diameter (M20 ISO). Cable gland option: contact us for further information. Other options • Cable output position In standard executions, the cable output is on the right (looking at the motor from the shaft side). • • - Motors without terminal board. Motor with cable output: available for the three-phase series power supply cable (4 or 7 wires) connected at the factory - small overall dimensions, thanks to the elimination of the terminal box on the ventilated three-phase motors - dimensions and further features: contact us for further information. Standard All other options must be requested at the time of the order using the same reference (upper, lower, left, right, front and rear cable output). • “d” cable gland In “EEx-d” motors, the cable gland aids the flameproof enclosure closing. The user MUST choose a cable with a diameter on the sealing membrane side corresponding to the cable gland specification, as well as use a device for hooking the cable on the cable external diameter side. In standard conditions, motors are supplied with an EEx-d cable gland with cable hook. On the sealing membrane side, the cable must have a diameter of 11 ± 0.5 mm (Figure 2 C). In standard conditions, 2-speed motors have two cable glands. Left (option) Right (option) • Manual control on/off switch built in the terminal box (only HA 63-71-80). Fig. 2 B Cable hooking Gasket Cable gland Standard aluminium cable gland for frame size 56 to 80, (sides in max mm) Sealing membrane Outer diameter Fig. 2 C 17 GB 3. Connecting diagrams 3.1 Three-phase motors 3.1 Three-phase motors The winding of standard motors can be connected together to form two different connections: - star connection - delta connection Star connection GB Connecting together the W2, U2, V2 terminals (star point) and connecting to the mains the U1, V1, W1 terminals a star connection is obtained. The phase current Iph and the phase voltage Uph are the following: Iph = In Uph = Un / ED 3 where In the line current and Un is the line voltage. U2 V2 Star point W2 U ph I ph U1 L1 V1 In U2 V2 W2 I ph I ph U ph U1 L1 Iph = In / ED 3 Fig. 3 B V1 W1 L3 L2 Un Star - Delta starting Two speed motors The star-delta starting is an easy way to reduce the starting current and starting torque. Standard two speed motors are designed for only one rated voltage and for direct starting. When the speed ratio is 1/2 the standard motors have one winding (Dahlander connection). For the other ratios motors have two different windings. 18 L3 Un Fig. 3 A Connecting the end of each winding to the beginning of the next winding a delta connection is obtained. The phase current Iph and the phase voltage Uph are the following: Motors can be started with the star-delta starting method whenever the supply voltage correspond to the rated voltage of the motors in delta connections. L2 L1 Un Delta connection Uph = Un U ph W1 L3 L2 U ph I ph L1 L2 U ph Un L3 3.1 Connection for single speed motors: U1 U1 U2 W2 U1 W1 V1 V2 W2 U2 V2 W1 U1 V1 W1 W1 V1 L1 Y-Connection L2 L2 L1 ∆-Connection L3 GB V1 L3 Number of pole: 2, 4, 6, 8 ...... Synchronous speed at 50 Hz: 3000, 1500, 1000, 750 ..... Two separate windings for two speed motors: L1 W2 V2 L2 L3 U1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W1 U2 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 V1 Low Speed High Speed L2 L1 Number of pole: 2/6, 2/8, 4/6, 6/8 Synchronous speed at 50 Hz: 3000/1000, 3000/750, 1500/1000, 1000/750. L3 Dahlander system for two speed motors, constant torque: L1 W2 L2 L3 U1 U1 W2 U2 U1 V1 V2 V2 W1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W2 W1 V1 V2 High Speed W1 U2 V1 U2 L2 L1 Low Speed L3 Number of pole: 2/4, 4/8 Synchronous speed at 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Dahlander system for two speed motors, quadratic torque: L1 W2 U1 L2 L3 W2 U2 U1 V1 U1 V2 W2 W1 V1 V2 V2 U2 High Speed W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 U2 W1 V1 W1 Low Speed L1 L2 L3 Number of pole: 2/4, 4/8 Synchronous speed at 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Fig. 3 C - Three phase motors connecting diagrams. 19 3.2 3.2 Single phase motors Single phase motors Red cable Brown cable Black cable Red cable Brown cable Black cable GB U1 U1 W1 V1 L2 L1 W1 V1 L2 L1 capacitor capacitor 220V / 240V 220V / 240V Fig. 3 D - Single-phase motor wiring diagrams F56 Green cable Green cable W2 U1 U2 V1 L1 V2 W2 W1 U1 V2 V1 L1 L2 W1 L2 220V / 240V 110V / 120V Green cable Green cable W2 U2 V2 W2 U1 V1 W1 U1 L2 L1 110V / 120V Fig. 3 E - Single-phase motor wiring diagrams F63-80 20 U2 U2 V2 V1 L1 W1 L2 220V / 240V 3.3 Self-braking motors - Groups IIB and IIC (BTVF and CTVF) 3.3.1 Brake power supply 3.3.2 Brake operating limits 3.3.3 Adjustments 3.3.1 Brake power supply Figures show the various power supply diagrams of the brake, with or without the “reduced response time” option. L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 GB CONTACTOR CONTACTOR EARTHING TERMINAL BOX BRAKE BRAKE W1 V1 U1 TERMINAL HOLDER PLATE V2 U2 W2 Vdc EARTHING TERMINAL BOX W1 V2 V1 U1 TERMINAL HOLDER PLATE U2 W2 Vdc Vac Vac RECTIFIER RECTIFIER Fig. 3 F - Standard response time Brake power supply parallel with the motor power supply Fig. 3 G - Reduced response time Brake power supply parallel with the motor power supply L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Rectifier power supply: Rectifier power supply: Vac Vac CONTACTOR CONTACTOR EARTHING TERMINAL BOX BRAKE W1 V2 V1 U1 TERMINAL HOLDER PLATE U2 W2 Vdc EARTHING TERMINAL BOX BRAKE W1 V2 V1 U1 TERMINAL HOLDER PLATE U2 W2 Vdc Vac RECTIFIER RECTIFIER Fig. 3 H - Standard response time Independent brake power supply Vac Fig. 3 I - Reduced response time Independent brake power supply 21 3.3 3.3.1 Brake power supply 3.3.2 Brake operating limits 3.3.3 Adjustments 3.3.1 Brake power supply In all cases, the brake works with uninterrupted voltage supplied by a rectifier installed on the terminal box of the motor supplied. Two options are available for the alternative sinusoidal power supply of the rectifier: GB Power supply parallel with the motor power supply phases This is the simplest and most common way of using a brake. In this configuration, it is not possible to set up two-speed motors or use a motor with a frequency converter. Typical response times for the beginning of the lock are: F63-71 : 32 ms ; F80 :140 ms Option: reduced response time. Typical response times for the beginning of the lock are: F63-71 : 10 ms ; F80 : 35 ms. 3.3.2 Brake operating limits The energy dissipated in the gasket over successive braking cycles should neither cause the brake to exceed the motor temperature class nor lead to early wear. Braking/hour, driving shaft inertia and motor speed should be indicated when a motor has to be chosen. 3.3.3 Adjustments Unless otherwise stated, motors are supplied with one of the braking torque values specified in Chapter 4.5 (Performance Data). However we have a procedure for adjusting or replacing the gasket if this is required during the use of the brake. 22 Independent power supply The user must provide for an alternative sinusoidal power supply (230 or 400V ± 10%). This connection also allows using the motor with a frequency converter, but it requires an additional cable gland. Option: reduced response time. Moteurs antidéflagrants F 23 1. Informations générales 1.1 Les moteurs de la série F 1.1 Les moteurs de la série F Les moteurs présentés dans ce catalogue respectent les normes relatives aux appareils et aux systèmes de protection à utiliser en atmosphères potentiellement explosives, conformément à la directive européenne n° 94/9/CE du 23/3/94, plus connue sous l’appellation “directive ATEX”. La directive ATEX prévoit la délivrance de deux certificats de conformité différents. L’un “Attestation CE de Type” pour l’homologation du prototype, l’autre pour la “Notification de lévolution relative à la qualite de produit”. Le numéro de la notofication relative à la qualité de produit est: LCIE 00 ATEX Q8007. Les certificats sont délivrés par le Laboratoire Central des Industries Electriques (L.C.I.E) (Organisme Notifié n° 0081). Les numéros de certificats de conformité sont indiques dans les données Nominales. Tableau 1 A - La série F ATEX F Version Hauteur d’axe [mm] Puissance (2 pôles) [kW] Classe de température standard (*) IIB IIC Série Triphasé, 1 vitesse (2, 4, 6, 8 pôles) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,50 T5 / T6 F-BTV F-CTV Triphasé, 1 vitesse non ventilés (2, 4, 6, 8 pôles) 56 - 80 0,06 - 0,55 T4 F-BST F-CST Triphasé, 2 vitesses (2/4, 4/6, 4/6, 4/8 pôles) (couple constant) 63 - 80 0,25 - 0,75 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Triphasé, 2 vitesses (2/4, 4/8, 4/6, 6/12 pôles) (couple quadratique) 63 - 80 0,25 - 1,10 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Triphasé, 1 vitesse avec frein (2, 4, 6, 8 pôles) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,10 T4 F-BTVF F-CTVF Monophasé, (2, 4, 6 pôles) 56 63 - 80 0,06 - 0,08 0,12 - 0,75 T4 F-BM F-BMV F-CM F-CMV (*) La classe de température réalisable à puissance nominale pour un échauffement minimal est indiquée dans le ch. 4 (Données Nominales). Tableau 1 B - Classe de température sur demande Hauteur d’axe 56 - 80 T5 T6 Mêmes Puissances que T4 (*) Puissances réduites (*) Pour les moteurs monophasés et triphasés à 2 vitesses: puissances réduites par rapport à T4, sauf pour les moteurs indiques dans le ch. 4.1 (Données Nominales). 24 1.2 1.3 1.2 Caractéristiques principales Options principales Caractéristiques principales • Moteurs antidéflagrants à l’épreuve des explosions conformément aux normes européennes CENELEC EN 50 014, EN 50 018 et EN 50 019 (pour boîte à bornes EEx-e). • Les normes européennes sont reconnues et acceptées par toutes les nations appartenant au CENELEC (Commission européenne pour la standardisation électrotechnique) et par presque toutes les autres nations du monde. • Moteurs asynchrones triphasés et monophasés à cage d'écureuil. • Complètement fermé, autoventilé, carcasse IP55 avec boîte à bornes IP55. • Dimensions conformes aux normes IEC 60072. • Alimentation 400V/ 50Hz. Moteurs triphasés à 1 vitesse, 2-4-6-8 pôles, T4, pour des hauteurs d’axe de 56 à 80, alimentation multi-tension 380-400-420V/ 50 Hz. • Classe d'isolation F. 1.3 • Niveau de bruit (dBA) Les bruits acoustiques mesurés à vide, et dans les conditions nominales d’alimentation, sont inférieurs à ceux définis par la norme NF 51-119 (idem IEC 34-9). Nous consulter pour applications spéciales. • Haute protection contre la corrosion: - plaque signalétique en acier inoxydable - visserie anticorrosion. • Boîte à bornes: - disponible tant dans la version antidéflagrante que dans la version à sécurité augmentée - de grandes dimensions - normalement installée du côté opposé aux pattes, orientable à gauche ou à droite - pivotant de 90° dans les 4 positions - grille de séparation avec la carcasse. • Bagues d’étanchéité à faible coefficient de frottement. • - • Les certificats de conformité valent également pour des caractéristiques de projet différentes de celles de la version de base, telles que: - altitude supérieure à 1.000 m au-dessus du niveau de la mer - autres tensions et fréquences - alimentation par variateur électronique de fréquence - moteur protégé par des sondes de température - régimes d'utilisation de S2 à S9. Carcasse du moteur: ailettes de refroidissement pattes amovibles bossage pour fixation directe sur carcasse bride à trous lisses amovible joint à lèvres à l’avant et à l’arrière (IP55) vis de masse. • Rotor: - coulé sous pression en alliage d’aluminium - montage fretté sur arbre - équilibré dynamiquement clavette entière - vernis d’isolation. • Haut niveau de protection contre les chocs: - capot de ventilateur en fonderie d’aluminium. • Niveau de vibration: l’equilibrage dynamique des rotors (demi-clé) confère en standard pour les moteurs triphasés, on niveau de vibration résiduel correspondant à la classe N (normale) selon CEI 34-14. F Options principales • Tensions et fréquences d'alimentation spéciales (tension maximum 690 V). • Moteurs avec protection IP56 - IP65 IP66. • Boîte à bornes avec entrée de câble spéciale. • Moteurs avec caractéristiques électriques selon spécifications client. • Moteurs tropicalisés (taux d'humidité relative H% comprise entre 90 et 98%). • Moteurs sans boîte à bornes avec sortie câble. • Moteurs pour alimentation avec variateur électronique de fréquence. • Moteurs avec thermoprotecteurs bimétalliques, thermistance PTC ou sonde résistive PT100 (le deuxième presse-étoupe est fourni). • Moteurs avec dynamo tachymétrique ou codeur. • Brides et arbres spéciaux. • 2 bouts d'arbre. • Equilibrage classe R et S. • Moteurs avec roulements spéciaux (unidirectionnels) taille augmentée. • Moteurs avec résistance anticondensation et/ou protection contre les basses températures. • Moteurs pour zones classées zone 21 et zone 22 (Poussières). • Moteurs pour applications spécifiques sur demande. • Moteurs avec capots protecteurs contre la pluie. • Boîte à bornes sécurité augmentée “e” voir ch. 2.5. 25 2. Caractéristiques mécaniques 2.1 Formes de construction 2.1 Formes de construction Les formes de construction communément utilisées sont représentées au tableau 2 A. Sur demande, d'autres formes de construction peuvent être fournies. Les moteurs commandés avec les formes de construction IM B3, IM B5 ou IM B14 peuvent également être utilisés dans d'autres positions de montage: - IM B3 en IM B6, IM B7, IM B8, IM V5 ou IM V6, - IM B5 en IM V1 ou IM V3, - IM B14 en IM V18 ou IM V19. F La norme pour les machines électriques de sécurité prescrit que la chute de corps étrangers à l'intérieur du moteur doit être impossible. A cette fin, les moteurs installés verticalement avec l'arbre orienté vers le bas doivent être munis d'un élément de protection placé au-dessus du capot de ventilateur. En cas de montage vertical avec l'arbre orienté vers le haut, la protection contre les corps étrangers est assurée par la machine accouplée ou bien par un élément monté par l'utilisateur final. Cette protection ne doit pas gêner le flux d'air pour le refroidissement. Tableau 2 A Moteurs à pattes CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II V5 IM V5 IM 1011 B5 IM B5 IM 3001 V1 IM V1 IM 3011 B14 IM B14 IM 3601 V18 IM V18 IM 3611 Moteurs à bride trous lisses Moteurs à pattes et brides trous lisses CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II Moteurs à bride trous taraudés Moteurs à pattes et brides trous taraudés CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II 26 B3 IM B3 IM 1001 2.1 V6 IM V6 IM 1031 B6 IM B6 IM 1051 B7 IM B7 IM 1061 B8 IM B8 IM 1071 F V3 IM V3 IM 3031 B35 IM B35 IM 2001 V15 IM V15 IM 2011 V36 IM V36 IM 2031 V19 IM V19 IM 3631 B3/B14 IM B34 IM 2101 V5/V18 IM V58 IM 2111 V6/V19 IM V69 IM 2131 27 2.2 Installation et applications 2.2.1 Spécification thermiques et environnementales 2.2.2 Ambiances industrielles sévères 2.2.1 Spécification thermiques et environnementales Régime d’utilisation Sauf mention particulière, les spécifications des moteurs présentées au ch. 4 (Donnés Nominales) correspondent au régime d’utilisation S1 (régime de fonctionnement permanent selon CEI 34-1). Néanmoins d’autres régimes d’utilisation sont autorisés, nous consulter pour vos besoins particuliers. F Groupes d’explosions et classes de température Sauf mention particulière, les moteurs sont livrables en Groupe IIB ou IIC. La classe de température standard, avec laquelle les moteurs sont fournis est T4, sauf pour les moteurs indiques dans le ch. 4.1 (Données Nominales). Sur demande, peuvent être construits des moteurs classe T5 ou T6. Température ambiante et altitude La maîtrise des températures de surface dans les limites imposées par la classe de température implique une utilisation à une température ambiante ≤ a 40 °C et une altitude ≤ 1000 m (selon NFC 51-111). La température ambiante minimale d'utilisation des moteurs standards du guide de sélection est de -20 °C. Nous consulter pour toute utilisation en dehors de ces limites. Echauffement du bobinage L’échauffement du bobinage des moteurs présenté au ch. 4 (Données Nominales) est ≤ 80 degrés K. 2.2.2 Ambiances industrielles sévères Pour les ambiances sévères (dont industrie chimique, industrie des matières premières, production d’énergie) propose une variante de construction durcie selon le standard allemand VIK (Vereinigung Industrielle Kraft wirschaft). L’option correspondante, dite “VIK”, concerne les moteurs EEx-de IIC. 28 Les différences de construction par rapport au standard sont: - boîte à bornes sécurité augmentée EEx-e largement dimensionnée, équipée de vis imperdables, avec sortie de câble orientable sans mouvement de la plaquette à bornes. - protection thermique PTC incluse, - visserie et plaque signalétique acier inoxydable, - finition externe epoxy 2 couches 2 x 40 µm, - finition interne: vernis d’isolation sur rotor et chignons de bobinage, - plaque signalétique supplémentaire dans boîte à bornes, - capot de protection parapluie. Limites thermiques des isolants de bobinage Les isolants de bobinage sont réalises dans des matériaux Classe F. Humidité Les moteurs standards du guide de sélection sont utilisables jusqu’à une humidité relative H% ≤ 90. 2.3 Matériaux, peinture et plaque signalétique 2.3.1 Matériaux et peinture 2.3.1 Matériaux et peinture Matériaux Tableau 2 B - Matériaux des composants principaux: Hauteur d’axe 56 - 80 Carcasse Flasques Boîte a bornes Capot du ventilateur Alliage d’aluminium normalisé Ventilateur Aluminium ou matériau plastique composite antistatique Arbre Acier XC 48 Stator Tôles à faibles pertes assemblées rigidement Bobinage Classe d’isolation F ou H Visserie Acier galvanisé, inoxydable sur demande Presse-etoupe Aluminium, laiton nickelé ou acier inoxydable F Spécifications de traitement de surface Finition standard: Aucun traitement, moteur couleur aluminium naturel. Préconisée pour utilisation: - en présence d’humidité ou de vapeur d’eau - en environnement chimique peu agressif - dans le domaine de température de surface moteur de -20 °C à +130 °C. Finitions optionelles: • Finition apprêt - dégraissage - 1 couche apprêt phosphatant 20 µm environ (compatible de toute finition ultérieure, sauf époxy) • Finition polyuréthane - dégraissage - 1 couche wash primaire vinyl modifié 10 µm environ - 1 couche polyuréthane bi-composants bleu RAL 5010 (30 µm environ) - visserie inoxydable. Préconisée pour utilisation: - en présence d’eau, de vapeur d’eau, d’air faiblement salin - en atmosphère industrielle moyennement sévère avec projections occasionnelles de produits chimiques agressifs. - dans le domaine de température de surface moteur de -20 °C à +130 °C. • Finition époxy - dégraissage - 1 couche wash primaire vinyl modifié 10 µm environ - 1 couche époxy polyamide bi-composants bleu RAL 5010 (25 µm environ) - visserie inoxydable. Préconisée pour utilisation: - en présence d’eau, de vapeur d’eau, d’air salin - en atmosphère industrielle sévère avec présence de produits chimiques agressifs - dans le domaine de température de surface moteur de -20 °C à +130 °C. • Autres finitions nous consulter. 29 2.3 2.3.2 Plaque signalétique 2.3.2 Plaque signalétique Identification Les moteurs sont identifiés par un plaquage portant les marquages décrits ci-dessous: Tableau 2 C - Marquages imposés par la législation en viguer Marquages Signification EEx d de II B-C T4 - T5 - T6 LCIE N° ... Marque CE Marque spécifique pour la protection contre les explosions Symbole des appareils de sécurité répondant à un mode de protection Mode de protection “à enveloppe antidéflagrante” Moteur “d” et boîte à bornes “e” Groupe d’explosion Subdivison de pression d’explosion Classe de température d’inflammation N° de l’attestation CE de type F Tableau 2 D - Autre indications de marquage Marquages Signification ATAV CEMP FRANCE NONANCOURT FRANCE Type ... N° ./. kg ... kW ... Volts ... Amp ... Cos. ... Hz ... min-1 ... S ... CI. IP °C amb ... Vis: Cl. Marque commerciale Nom et adresse constructeur Référence commerciale moteur N° de série/année de fabrication Masse du moteur Puissance du moteur Tension triangle / tension étoile Courant triangle / courant étoile Facteur de puissance Fréquence nominale Nombre de tours par minute Regime d’utilisation Classe d’isolation Indice de protection Température ambiante maximale Classe de résistance de la visserie Plaque signalétique Les Ateliers de l’Avre Type: EExd II2G 0081 Fabriqué par: Cemp France F 27320 NONANCOURT SA N° II IP T L.C.I.E. 2613 La plaque signalétique, en acier inoxydable, est fixée sur la carcasse par des clous cannelés. ATEX Vis/screw Schraube : cl. kW S Hz cl. V±10% Date: min-1 °C max A cos ϕ Figure 2 A - Plaque signalétique 30 kg IEC 34-1 2.4 Tenue des paliers et interfaces de montage 2.4.1 Paliers 2.4.2 Spécifications mécaniques 2.4.1 Paliers Les moteurs standards sont munis de roulements à billes à gorges profondes et étanches. Les roulements avant sont bloqués. Roulements utilisés Hauteur d’axe (mm) Type roulement avant Type roulement arrière 56 63-71 80 6202 ZZ 6203 2RS 6005 2RS 6200 ZZ 6203 2RS 6004 2RS F 2.4.2 Spécifications mécaniques Charges applicables sur le bout d’arbre Les charges dynamiques maximales applicables (N) pour une durée de vie L10h=25 000 heures sont les suivantes: Tableau 2 E Effort (N) Direction effort 2 pôles Hauteurs d’axe 4 pôles Hauteurs d’axe 6 pôles Hauteurs d’axe 8 pôles Hauteurs d’axe 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 350 480 510 460 610 650 540 710 740 600 780 820 240 350 370 330 440 470 370 510 540 420 560 590 220 330 330 310 420 430 350 490 500 400 540 550 250 370 410 340 460 510 400 530 580 440 580 630 IMB... ; IMV... IMB... IMV... 31 2.4 2.4.3 Exécutions spéciales 2.4.3 Exécutions spéciales Interfaces de montage des moteurs Brides spéciales Au-delà des formes de construction standard présentées au Par. 2.1, il existe des moteurs que l'on monte à l'aide de bossages pour la fixation à un tube ou à un système de ventilation. Il existe de moteurs à brides qui, bien qu’elles diffèrent des modèles standard, sont conformes à la normative NFC 51-120. Ces brides sont à trous lisses (B5) ou à trous filetés (B14). Le tableau ci-dessous complète les données présentées au Chap. 5 (Dimensions) et présente les mesures des brides disponibles. Tableau 2 F F Hauteur d’axe 32 Forme de construction Bride Dimensions [mm] ØM ØN ØP Ø TLB Ø TTB 56 B5 B5 B14 FF85 FF115 FT75 85 115 75 70 95 60 105 140 90 7.0 9.0 --- ----M5 63 B5 B14 B5 B14 FF100 FT65 FF130 FT85 100 65 130 85 80 50 110 70 120 85 160 105 7.0 --9.0 --- --M5 --M6 71 B5 B14 B5 B14 B5 FF100 FT65 FF115 FT75 FF165 100 65 115 75 165 80 50 95 60 130 120 85 140 90 200 7.0 --9.0 --11.0 --M5 --M5 --- 80 B5 B5 B14 B5 FF115 FF130 FT85 FF215 115 130 85 215 95 110 70 180 140 160 105 250 9.0 9.0 --13.5 ----M6 --- 2.5 2.5 Boîte à bornes Boîte à bornes Cablage avec boîte a bornes “d” Options pour presse-étoupe “d” Options boîte à bornes “e” • Orientation de la boîte à bornes par rapport aux pattes (pour montage IM1... ou IM2...). En standard, l’axe de la boîte à bornes est perpendiculaire au plan de pose. En option il peut-être livré “à droite” ou “à gauche” vue face au moteur côté bout d’arbre principal (sans incidence financière). Remarque: la modification du positionnement de boîte à bornes n’est réalisable qu’en usine. - boîte à bornes livrée sans presse-étoupe, avec trou fileté ISO M - garniture Ø 9 ou 13 mm pour presse-étoupe - presse-étoupe supplémentaire (modèle standard) ou trou supplémentaire - presse-étoupe avec reprise de blindage - presse-étoupe pour câble armé ou presse-étoupe spécial. • Boîte à bornes sécurité augmentée EEx-e: - disponible pour moteurs triphasés ventilés HA 63 à 80 - IP55 (IP65 optional) tension maximum 690V, traversée étanche démontable entre boîte et carcasse - livrée équipée d’un presse-étoupe EEx-e pour câble non armé diamètre 7,5 à 13 mm (M20 ISO). Option de presse-étoupe: nous consulter. Autres options Standard • • - Moteurs sans borniers. Moteur à sortie câble: disponible pour les gammes triphasées câble d’alimentation (4 ou 7 fils) raccordé en usine - encombrement réduit par suppression de la boîte à bornes sur moteurs triphasés ventilés - dimensions et autres caractéristiques: nous consulter. • Position de sortie de câble Dans le modèle standard, la sortie du câble se trouve à droite (quand on regarde le moteur du côté de l’arbre). Toutes les autres options doivent être demandées au moment de la commande, en utilisant la même référence (sortie du câble vers le haut, vers le bas, vers la gauche, vers la droite, antérieure, postérieure). • Presse-étoupe “d” Le presse-étoupe participe dans les moteurs “EEx-d” à la fermeture de l’enveloppe antidéflagrante. L’utilisateur doit impérativement choisir un câble dont le diamètre sur gaine d’étanchéité correspond à la spécification du presse-étoupe et utiliser un dispositif d’amarrage de câble serré sur le diamètre extérieur du câble. En standard, les moteurs sont livrés équipés d’un presse-étoupe EEx-d avec amarrage de câble. Le câble doit présenter un diamètre sur gaine d’étanchéité de 11 ± 0,5mm (Figure 2 C). En standard les moteurs bi-vitesse sont équipés de 2 presse-étoupe. A gauche (option) Figure 2 B A droite (option) • Interrupteur marche-arrêt à commande manuelle, intégré dans la boîte à bornes (HA 63-71-80 seulement). Amarrage de câble Garniture Presse-etoupe Figure 2 C Presse-étoupe standard en aluminium pour hauteur d’axe 56 à 80 (côtes en mm max) Gaine d’étancheité Diamètre extérieur 33 F 3. Schémas de branchement 3.1 Moteurs triphasés 3.1 Moteurs triphasés Les enroulements des moteurs standard peuvent être reliés de deux façons: - connexion en étoile - connexion en triangle Connexion en étoile F La connexion en étoile est obtenue en reliant ensemble les bornes W2, U2, V2 et en alimentant les bornes U1, V1, W1. Le courant et la tension de phase sont: Iph = In Uph = Un / ED 3 où In est le courant de ligne et Un est la tension de ligne. U2 V2 Centre étoile W2 U ph I ph U1 L1 V1 U ph I ph U ph W1 L2 L1 L3 L2 Un L3 Un Figure 3 A Connexion en triangle La connexion en triangle s'obtient en reliant la fin d'une phase au début de la phase successive. Le courant de phase Iph et la tension de phase Uph sont: Iph = In / ED 3 In U2 V2 W2 I ph U1 L1 Uph = Un Figure 3 B V1 W1 L3 L2 Un Démarrage étoile-triangle Moteurs à deux vitesses Le démarrage étoile-triangle est le moyen le plus facile pour réduire le courant et le couple de démarrage. Les moteurs reliés en triangle et dont la tension nominale correspond à la tension de réseau peuvent être mis en marche avec la méthode étoile-triangle. Les moteurs standards à deux vitesses sont conçus pour une seule tension et pour un démarrage direct. Lorsque le rapport entre les deux vitesses est de 1 à 2 les moteurs standards ont un seul enroulement (couplage Dahlander). Pour les autres vitesses les moteurs possédent deux enroulements différents. 34 I ph U ph L1 L2 U ph Un L3 3.1 Connexions en étoile et en triangle pour les moteurs à une vitesse: U1 U1 U2 W2 U1 W1 Connexion-Y V1 V2 W2 U2 V2 W1 U1 V1 W1 W1 V1 L1 L2 V1 L2 L1 Connexion-∆ L3 L3 Nombre de pôles: 2, 4, 6, 8 ...... Vitesse de synchronisme à 50 Hz: 3000,1500,1000, 750 ..... F Connexion pour les moteurs à deux vitesses, deux enroulements séparés: L1 W2 V2 L2 L3 U1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W1 U2 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 V1 Petite vitesse Grande vitesse L2 L1 L3 Nombre de pôles: 2/6, 2/8, 4/6, 6/8 Vitesse de synchronisme à 50 Hz: 3000/1000, 3000/750, 1500/1000, 1000/750. Connexion pour les moteurs à deux vitesses, couple constant (Dahlander): L1 W2 L2 L3 U1 U1 W2 U2 U1 V1 V2 V2 W1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W2 W1 V1 V2 W1 U2 Grande vitesse V1 U2 L2 L1 Petite vitesse L3 Nombre de pôles: 2/4, 4/8 Vitesse de synchronisme à 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Connexion pour les moteurs à deux vitesses, couple quadratique (Dahlander): L1 W2 U1 L2 L3 W2 U2 U1 V1 U1 V2 W2 W1 V1 V2 V2 Grande vitesse U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 U2 W1 U2 W2 V1 W1 Petite vitesse L1 L2 L3 Nombre de pôles: 2/4, 4/8 Vitesse de synchronisme à 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Figure 3 C - Schémas de branchement des moteurs triphasés. 35 3.2 3.2 Moteurs monophasés Moteurs monophasés Câble rouge Câble marron U1 Câble rouge Câble marron U1 W1 V1 W1 L2 L1 condensateur Câble noir V1 L2 L1 F Câble noir condensateur 220V / 240V 220V / 240V Figure 3 D - Schémas de branchement de moteurs monophasés F56 Câble vert Câble vert W2 U1 U2 V1 L1 V2 W2 W1 U1 V2 V1 L1 L2 W1 L2 220V / 240V 110V / 120V Câble vert Câble vert W2 U2 V2 W2 U1 V1 W1 U1 L2 L1 110V / 120V Figure 3 E - Schémas de branchement de moteurs monophasés F63-80 36 U2 U2 V2 V1 L1 W1 L2 220V / 240V 3.3 Moteur-freins - Groupes IIB et IIC (BTVF et CTVF) 3.3.1 Alimentation du frein 3.3.2 Limites fonctionnelles du frein 3.3.3 Réglages 3.3.1 Alimentation du frein Le figure montrent les différents schémas d’alimentation de frein avec ou sans l’option “temps de réponse réduit”. L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 CONTACTEUR CONTACTEUR MASSE BOITE A BORNES FREIN W1 V1 FREIN U1 MASSE BOITE A BORNES F W1 U1 PLAQUE A BORNES PLAQUE A BORNES V2 V1 U2 W2 Vdc Vac V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac REDRESSEUR REDRESSEUR Figure 3 F - Temps de réponse standard Alimentation du frein en parallele sur l’alimentation moteur Figure 3 G - Temps de réponse reduit Alimentation du frein en parallele sur l’alimentation moteur L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Alimentation redresseur: Alimentation redresseur: Vac Vac CONTACTEUR CONTACTEUR MASSE BOITE A BORNES FREIN W1 V1 U1 MASSE BOITE A BORNES FREIN W1 V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac REDRESSEUR Figure 3 H - Temps de réponse standard Alimentation du frein indépendante V1 U1 PLAQUE A BORNES PLAQUE A BORNES V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac REDRESSEUR Figure 3 I - Temps de réponse reduit Alimentation du frein indépendante 37 3.3 3.3.1 Alimentation du frein 3.3.2 Limites fonctionnelles du frein 3.3.3 Réglages 3.3.1 Alimentation du frein Dans tous les cas le frein fonctionne sous une tension continue délivrée par un redresseur implanté dans la boîte du moteur livré. Deux possibilités sont offertes à l’alimentation alternative sinusoïdale du redresseur: F Alimentation indépendante Une alimentation alternative sinusoîdale doit être prévue par l’utilisateur (230 ou 400V ± 10%). Ce branchement permet entre autre l'utilisation du moteur avec un variateur de fréquence mais nécessite un presse-étoupe supplémentaire. Option: temps de réponse réduit. Alimentation en parallèle sur les phases d’alimentation moteur C'est la manière la plus simple et également la plus courante d'utiliser un frein. Sous cette configuration, il n'est cependant pas possible de réaliser des moteurs à deux vitesses ou d’utiliser le moteur avec un variateur de fréquence. Les temps de réponse typiques pour le début de serrage sont: F63-71 : 32 ms ; F80 :140 ms Option: temps de réponse réduit. Les temps de réponse typiques pour le début de serrage sont: F63-71 : 10 ms ; F80 : 35 ms. 3.3.2 Limites fonctionnelles du frein L'énergie dissipée au cours de freinages répétés ne doit pas provoquer une élévation excessive de la température ou réduire la durée de vie moyenne prévue pour le frein. Quand on choisit le moteur, il est donc fondamental d’indiquer le nombre de freinages à l’heure, l'inertie à l'arbre et la vitesse. 3.3.3 Réglages Le moteur est livré avec le couple de freinage qui est indiqué dans les tableaux figurant dans le chapitre 4.5 (Données nominales). Cependant, on dispose de la possibilité de recourir à une procédure permettant le réglage du couple de freinage ou le remplacement des garnitures de frein au cas où de telles opérations se révéleraient nécessaires. 38 Explosionsgeschützte Motoren D 39 1. Allgemeine Informationen 1.1 Motoren Serie F 1.1 Motoren Serie F Die in diesem Katalog vorgestellten Motoren entsprechen den Bestimmungen für Geräte und Schutzsysteme, die in potentiell explosionsgefährdeter Atmosphäre eingesetzt werden, in Entsprechung der europäischen Richtlinie N° 94/9/CE vom 23/3/94, auch als Richtlinie ATEX bekannt. Die Richtlinie ATEX sieht die Ausstellung von zwei Konformitätserklärungen vor. Tabelle 1 A - Die Serie F ATEX Ausführung D Eine “CE – Markierung” als Baumusterbescheinigung, die andere als „Garantie der Produktionsqualität“. Die Nummer des Zertifikats für die Qualitätssicherung in der Produktion ist: LCIE 00 ATEX Q8007. Die Bescheinigungen werden durch das Laboratoire Central des Industries Electriques L.C.I.E. (Zentrallabor der Elektroindustrie) ausgestellt, das unter der Nummer 0081 gemeldet ist. Die Nummern der KonformitätsBescheinigungen sind in den Betriebsdaten wiedergegeben. Größe [mm] Leistung (2-polig) [kW] Temperaturklasse Standard (*) IIB IIC Serie Drehstrommotor, 1 Drehzahl (2, 4, 6, 8 Pole) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,50 T5 / T6 F-BTV F-CTV Drehstrommotor, 1 Drehzahl, unbelüftet (2, 4, 6, 8 Pole) 56 - 80 0,06 - 0,55 T4 F-BST F-CST Drehstrommotor, 2 Drehzahlen (2/4, 4/6, 4/6, 4/8 Pole) (konstantes Gegenmoment) 63 - 80 0,25 - 0,75 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Drehstrommotor, 2 Drehzahlen (2/4, 4/8, 4/6, 6/12 Pole) (quadratisches Gegenmoment) 63 - 80 0,25 - 1,10 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Drehstrom, 1 Drehzahl, mit Bremse (2, 4, 6, 8 Pole) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,10 T4 F-BTVF F-CTVF Einphasenmotor, (2, 4, 6 Pole) 56 63 - 80 0,06 - 0,08 0,12 - 0,75 T4 F-BM F-BMV F-CM F-CMV (*) Die Temperaturklasse für die Mindestwicklungserwärmung wird in Kapitel 4 (Betriebsdaten) angegeben. Tabelle 1 B - Temperaturklasse auf Anfrage (bezogen auf Umgebungstemperatur von 40 °C) Größe T5 T6 56 - 80 Gleiche Leistungen T4 (*) Reduzierte Leistungen (*) Für Einphasen- und Drehstrommotoren mit Drehzahlen: Reduzierte Leistungen im vergleich zu T4, vorbehaltlich der Angaben in Kapitel 4.1. 40 1.2 1.3 1.2 Hauptmerkmale Hauptausführungen Hauptmerkmale • Explosionsgeschützte Motoren gemäß den europäischen Normen CENELEC EN 50 014, EN 50 018 und EN 50 019 (für den Klemmkasten EEx-e). • Die europäischen Normen werden von allen Mitgliedsländern von CENELEC (Europäisches Komitee für elektrotechnische Normung) und fast allen Nationen der Welt anerkannt. • Asynchrone Drehstrom- und Einphasenmotoren mit Käfigläufer. • Komplett geschlossen, eigenbelüftet, Gehäuse IP55 mit Klemmkasten IP65. • Abmessungen gemäß den Normen IEC 60072. • Stromversorgung 400V/ 50Hz. Drehstrommotoren ,1 Drehzahl, 2-4-6-8 Pole, T4, für Baugrößen von 56 bis 80, Stromversorgung mit Mehrbereichsspannung 380-400-420V/ 50 Hz. • Isolationsklasse F. • Geräuschpegel (dBA) Die Werte des Geräuschpegels, der sowohl bei Leerlauf als auch unter Nennspannung gemessen wurde, sind niedriger als die in der Norm NF 51-119 (IEC 34-9) festgelegten Werte. Kontaktieren Sie uns für Sonderanwendungen. 1.3 • Klemmkasten: - verfügbar sowohl in der druckfester Ausführung als auch in der Ausführung in erhöhter Sicherheit - verfügbar in vergrößerter Ausführung - normalerweise auf der den Stützfüßen entgegengesetzten Seite installiert, nach links oder rechts ausrichtbar - um 90° in 4 Positionen drehbar. - Trenngitter vom Motorgehäuse. • - Motorgehäuse: Kühlrippen abnehmbare Stützfüße Montageplatte für Direktanschluss an das Motorgehäuse - abnehmbarer Flansch mit glatten Bohrungen - Dichtring mit Lippe A-Seite und B-Seite (IP55) - Masseschraube. • Rotor: - bei Unterdruck in Aluminiumlegierung gegossen - Montage mit Nutmutter auf Welle - dynamische Auswuchtung mit ganzer Passfeder - Isolierlack. • Hoher Korrosionsschutz: - Typenschild aus Edelstahl - Schrauben aus korrosionsbeständigem Material. • Hohe Stoßfestigkeit: - Lüfterhaube in Aluminiumschmelze. • Dichtungsring mit niedrigem Reibungskoeffizienten. • Schwingungshöhe: Die dynamische Auswuchtung der Rotoren (kurzer Schlüssel) gewährleistet für den Standard der Drehstrommotoren eine verbleibende Schwingungshöhe vom Grad N (normal) entsprechend IEC 34-14. • Die Konformitätszertifikate sind auch für Einsatzbedingungen, die sich von der Basisversion unterscheiden gültig, wie: - Höhe von mehr als 1000 m ü.d.M. - unterschiedliche Spannungen und Frequenzen. - Stromversorgung durch den Frequenzwandler - von Temperaturfühlern geschützter Motor. - Betriebsart von S2 bis S9. D Hauptausführungen • Sonder-Spannungen und –frequenzen (max. Spannung 690V). • Motoren mit elektrischen Eigenschaften gemäß Kundenspezifikationen. • Motoren für die Versorgung durch elektronischen Frequenzwandler (FU). • Sonder-Flansche und-Wellen. • Motoren mit Schutzart IP56 - IP65 - IP66. • Tropenfeste Motoren (Relative Feuchtigkeit H% zwischen 90 und 98%). • Motoren mit bimetallischem Wärmeschutz, Thermistoren PTC oder Widerstandssonde PT100 (es wird eine zweite Kabelpresse geliefert). • Graduelle Auswuchtung R und S. • Motoren mit Heizung gegen Kondenswasser und/oder Schutz gegen tiefe Temperaturen. • Verzinkter Edelstahl auf Anfrage. • Motoren mit Regenschutzdach. • Zweites Wellenenden (BS). • Klemmkasten mit speziellen Kabeleinführungen. • Motoren ohne Klemmbrett mit Kabelverschraubung und herausgeführtem Kabel. • Motoren mit Tacho-Dynamo oder Encoder. • Motoren für die Sicherheitsbereiche 21 und 22 (Stäube). • Motoren für Sonderanwendungen auf Anfrage. • Klemmbrett in erhöhter Sicherheit “e”, siehe Kap. 2.5. 41 2. Mechanische Eigenschaften 2.1 Bauformen 2.1 Bauformen Die gewöhnlich verwendeten Bauformen werden in der Tabelle 2 A dargestellt. Auf Wunsch können auch andere Bauformen geliefert werden. Die mit den Bauformen IM B3, IM B5 oder IM B14 bestellten Motoren können auch für andere Montagepositionen verwendet werden: - IM B3 als IM B6, IM B7, IM B8, IM V5 oder IM V6, - IM B5 als IM V1 oder IM V3, - IM B14 als IM V18 oder IM V19. Die Vorschriften für elektrische Maschinen sehen vor, daß keine Fremdkörper in den Motor fallen dürfen. Um dies zu verhindern, sind vertikale Motoren, deren Welle nach unten gerichtet ist, mit einem Schutzdach über der Lüfterhaube ausgestattet. D Im Falle der vertikalen Montage mit nach oben gerichteter Welle wird der Motor entweder von der daran angeschlossenen Maschine oder durch ein von Endnutzer montiertes Schutzdach gegen Fremdkörper geschützt. Eine solche Schutzabdeckung darf den Fluß der Luft für den Kühlkreislauf nicht einschränken. Tabelle 2 A Motoren mit Stützfüßen CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II V5 IM V5 IM 1011 B5 IM B5 IM 3001 V1 IM V1 IM 3011 B14 IM B14 IM 3601 V18 IM V18 IM 3611 Motoren mit Flansch: normaler Flansch, Durchgangslöcher zur Befestigung Motoren mit Stützfüßen und Flansch: normaler Flansch, Durchgangslöcher zur Befestigung CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II Motoren mit Flansch: reduzierter Flansch, gewindegeschnittene Befestigungslöcher Motoren mit Stützfüßen und Flansch: reduzierter Flansch, gewindegeschnittene Befestigungslöcher CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 code I IEC 34-7 code II 42 B3 IM B3 IM 1001 2.1 V6 IM V6 IM 1031 B6 IM B6 IM 1051 B7 IM B7 IM 1061 B8 IM B8 IM 1071 V3 IM V3 IM 3031 B35 IM B35 IM 2001 V15 IM V15 IM 2011 V36 IM V36 IM 2031 V19 IM V19 IM 3631 B3/B14 IM B34 IM 2101 V5/V18 IM V58 IM 2111 V6/V19 IM V69 IM 2131 D 43 2.2 Installation und Anwendungen 2.2.1 Thermische und Umgebungsbedingte Eigenschaften 2.2.2 Erschwerte Einsatzbedingungen 2.2.1 Thermische und Umgebungsbedingte Eigenschaften Betriebsart Bis auf einige Ausnahmen bzgl. der Einzelheiten, entsprechen die Merkmale der in Kap. 4 aufgeführten Motoren (Betriebsdaten) der Betriebsart S1 (Dauerbetriebsart gemäß IEC 34-1). Kontaktieren Sie uns bei Sonderanfragen hinsichtlich anderer zugelassener Betriebsarten. Explosionsgruppen und Temperaturklassen Bis auf einige Ausnahmen bzgl. der Einzelheiten, sind die Motoren in der Gruppe IIB oder IIC erhältlich. Die Standardtemperaturklasse, mit der die Motoren geliefert werden, ist T4, vorbehaltlich der Angaben in Kapitel 4.1 (Betriebsdaten). Auf Anfrage können auch Motoren der Klasse T5 oder T6 gebaut werden. Raumtemperatur und Höhe Die Kontrolle der Oberflächentemperatur innerhalb der durch die Temperaturklasse gesetzten Grenzen impliziert einen Maschinengebrauch bei einer Raumtemperatur und Aufstellhöhe oder gleich 40° C und einer Höhe von weniger oder gleich 1000 m (gemäß NFC 51-111). Die Mindestraumtemperatur für den Betrieb der zur Auswahl stehenden StandardMotoren liegt bei -20° C. Für Informationen hinsichtlich der Nutzungsbedingungen außerhalb dieser Grenzwerte stehen wir Ihnen zur Verfügung. Überhitzung der Wicklung Die in Kap. 4 beschriebene Überhitzung der Motorwicklung (Betriebsdaten) ist niedriger oder gleich 80 K. D 2.2.2 Erschwerte Einsatzbedingungen Bei erschwerten Einsatzbedingungen (darunter die chemische Industrie, die Rohstoffindustrie und die Energieproduktion) wird eine Motorausführung nach dem deutschen Standard VIK (Vereinigung Industrielle Kraftwirtschaft) vorgeschlagen. Die entsprechende Ausführung, genannt “VIK”, betrifft die Motoren des Typs EEx-de IIC. 44 Die Konstruktionsunterschiede gegenüber dem Standard sind: - großzügig dimensioniertes Klemmbrett in erhöhter Sicherheit EEx-e, ausgestattet mit Halteschrauben und speziellen Wicklungs-Ableitungen, sodass das Klemmbrett nicht versetzt werden muss. - Temperaturüberwachung PTC inbegriffen, - Schrauben und Typenschild in rostfreiem Stahl, - Außenanstrich mit Epoxydharz in zwei Schichten 2 x 40 µm, - Innenanstrich: Isolierlack auf dem Rotor und den Köpfen der Aufwickelspule, - zusätzliches Typenschild im Klemmkasten, - Regenschutzdach. Thermische Grenzwerte für die Wicklungsisolierungen Die Isolierungen für die Wicklungen werden aus Materialien der Klasse F hergestellt. Feuchtigkeit Die zur Auswahl stehenden Standardmotoren können bis zu einer Feuchtigkeit von H% = 90 benutzt werden. 2.3 Material, Lackierung und Typenschild 2.3.1 Materialien und Lackierung 2.3.1 Materialien und Lackierung Material Tabelle 2 B - Material der Hauptbauteile: Größe Motorgehäuse Lagerschild Anschlusskasten Lüfterhaube 56 - 80 Lüfterrad Aluminium oder antistatisches Plastikverbundmaterial Welle Stahl XC 48 Statorpaket steif montierte Bleche mit geringem Verlustfaktor Wicklung Isolierungen Klasse F oder H Schrauben Verzinkter Edelstahl auf Anfrage Kabelschuh Aluminium, vernickeltes Messing oder rostfreier Stahl Legierung aus genormtem Aluminium Spezifikationen zur Oberflächenbehandlung Standardausführung: Keine Behandlung, Motor Farbe Aluminium Natur. Empfehlung für den Einsatzbei: - für Feuchtigkeit oder Wasserdampf geeignet - in geringfügig aggressiver chemischer Umgebung - im Bereich der Motoroberflächentemperaturen zwischen 20° C und +130° C. D Ausführung optional • Grundanstrich: - Entfettung - eine Schicht phosphatiert ca. 20 µm (mit allen anderen Anstrichen kompatibel, mit Ausnahme des Epoxydharzes). • Polyurethan-Anstrich: - Entfettung - eine Schicht wash primer modifiziertes Vinyl ca. 10 µm - eine Schicht zweilagiges Polyurethan blau RAL 5010 (ca. 30 µm) - rostfreien Schrauben. Empfehlungen für den Gebrauch: - bei Umgebung mit hoher Feuchtigkeit, Wasserdampf und etwas salzhaltiger Luft geeignet - bei relativ schweren Einsatzbedingungen, verbunden mit gelegentlichem Vorhandensein aggressiver Chemikalien. - im Bereich der Motoroberflächentemperaturen zwischen -20° C und +130° C. • Ausführung in Epoxydharz: - Entfettung - eine Schicht wash primer modifiziertes Vinyl ca. 10 µm - eine Schicht zweilagiges Epoxydharz Polyamid blau RAL 5010 (ca. 25 µm) - rostfreien Schrauben. Empfehlungen für den Gebrauch: - bei Umgebung mit hoher Feuchtigkeit, Wasserdampf, und stark salzhaltiger Luft - bei schweren Einsatzbedingungen, verbunden mit Vorhandensein aggressiver Chemikalien. - im Bereich der Motoroberflächentemperaturen zwischen 20° C und +130° C. • Andere Ausführungen. 45 2.3 2.3.2 Typenschild 2.3.2 Typenschild Kennzeichnung Die Motoren werden mit einem Typenschild versehen, auf dem die folgenden Kennzeichnungen aufgeführt sind: Tabelle 2 C - durch das geltende Gesetz vorgeschriebene Kennzeichnungen Kennzeichnung Bedeutung EEx d de II B-C T4 - T5 - T6 LCIE N° ... EG-Kennzeichnung spezifische Kennzeichnung bzgl. des Explosionsschutzes Symbol für Sicherheitsvorrichtungen entsprechend der Ex-Schutzart Ex-Schutz “druckfeste Kapselung” Motor “d” und Klemmbrett “e” Explosionsgruppe Gasgruppe Zünd-Temperaturklasse Nummer der EG-Bescheinigung des Typs Tabelle 2 D - Andere Kennzeichnungsangaben Kennzeichnung ATAV CEMP FRANCE NONANCOURT FRANCE Typ ... Nr ./. kg ... kW ... Volt ... Amp ... Cos. ... Hz ... min-1 ... S ... CI. IP °C amb ... Vis: Cl. D Bedeutung Handelsmarke Name und Anschrift des Herstellers Handelsbezeichnung des Motors Maschinennummer/Herstellungsjahr Gewicht des Motors Leistung des Motors Spannung für Dreieckschaltung/ Spannung für Sternschaltung Strom für Dreieckschaltung/ Strom für Sternschaltung Leistungsfaktor Nennfrequenz Anzahl der Umdrehungen pro Minute Betriebsart Isolationsklasse Schutzindex maximale Raumtemperatur Festigkeitsklasse des Schraubwerks Typenschild Das Typenschild aus rostfreiem Stahl ist mit Kerbnägeln am Motorgehäuse befestigt. Les Ateliers de l’Avre SA N° II IP T L.C.I.E. 2613 Type: EExd II2G 0081 Fabriqué par: Cemp France F 27320 NONANCOURT ATEX Vis/screw Schraube : cl. kW S Hz cl. V±10% Date: min-1 °C max A cos ϕ Abbildung 2 A - Typenschild 46 kg IEC 34-1 2.4 Dichtung der Lager und Montageschnittstellen 2.4.1 Lager 2.4.2 Mechanische Eigenschaften 2.4.1 Lager Die Standardmotoren sind mit Rillenkugellagen ausgestattet. Das antriebsseitige Lager ist als Festlager ausgeführt. Verwendete Lager: Achsenhöhe (mm) Art des Lagers A-Seite Art des Lagers B-Seite 56 63-71 80 6202 ZZ 6203 2RS 6005 2RS 6200 ZZ 6203 2RS 6004 2RS 2.4.2 Mechanische Eigenschaften Zulässige Belastung am Wellenende Die maximal zugelassenen dynamischen Belastungen (N) für die Lebensdauer L10h = 25.000 Stunden sind folgende: D Tabelle 2 E Beanspruchung (N) Richtung der Beanspruchung 2 Pole Größe 4 Pole Größe 6 Pole Größe 8 Pole Größe 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 350 480 510 460 610 650 540 710 740 600 780 820 240 350 370 330 440 470 370 510 540 420 560 590 220 330 330 310 420 430 350 490 500 400 540 550 250 370 410 340 460 510 400 530 580 440 580 630 IMB... ; IMV... IMB... IMV... 47 2.4 2.4.3 Spezialausführungen 2.4.3 Spezialausführungen Spezialflansche Schnittstellen für die Montage der Motoren Außer den Standardbauformen, die im Kapitel 2.1 illustriert werden, sind Motoren mit Montage mit Beschlägen für den Anschluss an ein Rohr oder ein Lüftungssystem verfügbar. Es sind Motoren mit vom Standard verschiedenen Flanschen verfügbar, die jedoch der Norm NFC 51-120 entsprechen, mit Durchgangsbohrungen (B5) oder mit Gewindebohrungen (B14). Die folgende Tabelle gibt zur Vervollständigung der in Kapitel 5 (Abmessungen) angegebenen Abmessungen die Maße der verfügbaren Flansche an. Tabelle 2 F Größe Flansch Abmessungen [mm] ØM ØN ØP Ø TLB Ø TTB 56 B5 B5 B14 FF85 FF115 FT75 85 115 75 70 95 60 105 140 90 7.0 9.0 --- ----M5 63 B5 B14 B5 B14 FF100 FT65 FF130 FT85 100 65 130 85 80 50 110 70 120 85 160 105 7.0 --9.0 --- --M5 --M6 71 B5 B14 B5 B14 B5 FF100 FT65 FF115 FT75 FF165 100 65 115 75 165 80 50 95 60 130 120 85 140 90 200 7.0 --9.0 --11.0 --M5 --M5 --- 80 B5 B5 B14 B5 FF115 FF130 FT85 FF215 115 130 85 215 95 110 70 180 140 160 105 250 9.0 9.0 --13.5 ----M6 --- D 49 Bauform 2.5 2.5 Klemmenkasten Klemmenkasten Verkabelung mit Anschlußkasten “d” Optionen für Kabelpresse “d” • Ausrichtung des Anschlußkasten im Verhältnis zu den Stützfüßen (für die Montage IM1... oder IM2...). In der Standardversion ist die Achse des Anschlußkasten senkrecht zur Stellfläche ausgerichtet. Optional kann der Anschlußkasten “rechts” oder “links”, gesehen von der Frontansicht des Motors, vom Hauptwellenende aus positioniert werden (ohne zusätzliche Kosten). Hinweis: Die Position des Klemmbretts kann nur in der Fabrik geändert werden. - Klemmbrett geliefert ohne Kabelpresse, mit Gewindebohrung ISO M - Dichtung Ø 9 oder 13 mm für Kabelpresse - zusätzliche Kabelpresse (Standardmodell) oder zusätzliche Bohrung - Kabelpresse mit Wiederaufnahme der Abschirmung - Kabelpresse für armiertes Kabel oder Spezialkabelpresse: Kontaktieren Sie uns. • Position der Kabelausführung kann Bei der Standardausführung befindet sich der Ausgang des Kabels rechts (bei Betrachtung des Motors von der Seite der Welle). Alle weiteren Optionen müssen bei der Bestellung unter Verwendung der gleichen Angabe (Ausgang des Kabels nach oben, nach unten, nach links, nach links, vorne, hinten) erfragt werden. • Kabelpresse “d” Bei den Motoren “EEx-d” trägt die Kabelpresse zur Schließung der druckfesten Kapselung bei. Der Bediener muss unbedingt ein Kabel verwenden, dessen Durchmesser auf der Dichtmembran der Größe der Kabelpresse entspricht, sowie eine Kabeleinhängevorrichtung am äußeren Durchmesser des Kabels. Standard Links (option) Abbildung 2 B Rechts (option) Optionen bei Ansclußkasten erhöhte Sicherheit “e” • Anschlußkasten in erhöhter Sicherheit EEx-e: - verfügbar für Drehstrommotoren, belüftet durch HA von 63 bis 80 - IP55 (IP65 als Sonderausstattung) max. Spannung 690V, absolut dichtes Verbindungssystem, zwischen Klemmbrett und Motorgehäuse abmontierbar Lieferung mit Kabelpresse EEx-e für ein nicht armiertes Kabel mit einem Durchmesser zwischen 7,5 und 13 mm (M20 ISO). Option Kabelpresse: Kontaktieren Sie uns. Weitere Optionen • Motoren ohne Klemmenkasten. • Motor mit Kabelausgang: - verfügbar für Drehstromserien - Netzkabel (4- oder 7-adrig) angeschlossen in der Fabrik - reduzierte Abmessungen dank der Beseitigung des Klemmbretts auf den belüfteten Drehstrommotoren - Abmessungen und andere Eigenschaften: Kontaktieren Sie uns. • Schalter an/aus durch manuelle Steuerung, integriert in das Klemmbrett (nur HA 63-71-80). Kabeleinhängung Bei der Standardversion sind die gelieferten Motoren mit einer Kabelpresse EEx-d mit Kabeleinhängung ausgestattet. Auf der Dichtmembran muss der Kabel einen Durchmesser von 11 ± 0,5 mm aufweisen (Abbildung 2 C). Bei der Standardversion sind die Motoren mit zwei Drehzahlen mit 2 Kabelpressen ausgestattet. Dichtung Kabelpresse Dichtmembran Kabelpresse Standard in Aluminium für Größe Außendurchzwischen 56 und 80 messer (Seiten in mm max) Abbildung 2 C 49 D 3. Schaltung 3.1 Drehstrommotoren 3.1 Drehstrommotoren Die Wicklungen der Standardmotoren können auf zwei Arten angeschlossen werden: - Sternschaltung - Dreieckschaltung Sternschaltung Für eine Sternschaltung müssen die Klemmen W2, U2 und V2 zusammengeschlossen und die Stellen U1, V1 und W1 gespeist werden. Der Phasenstrom und die Phasenspannung sind: Iph = In Uph = Un / ED 3 wobei In der Netzstrom und Un die Netzspannung ist. V2 U2 Sternpunkt W2 U ph I ph V1 U1 L1 U ph I ph U ph W1 L2 L1 L3 L2 Un L3 Un Abbildung 3 A D Dreieckschaltung Für eine Dreieckschaltung muß das Ende einer Phase an den Beginn der nächsten Phase angeschlossen werden. Der Phasenstrom Iph und die Phasenspannung Uph sind: Iph = In / ED 3 Uph = Un In V2 U2 W2 I ph V1 U1 L1 Abbildung 3 B W1 L3 L2 Un Stern-Dreieck-Anlauf Motoren mit zwei Drehzahlen Der Stern-Dreieck-Anlauf ist die einfachste Art, den Strom und das Anlaufdrehmoment zu reduzieren. Standardmotoren mit zwei Drehzahlen sind für eine Spannung und einen direkten Anlauf konstruiert. Die Motoren, deren Nennspannung bei Dreieckschaltung der Netzspannung entspricht, können mit der Stern-DreieckMethode angelassen werden. Wenn das Verhältnis zwischen den zwei Drehzahlen 1 zu 2 ist, dann haben die Standardmotoren eine Wicklung (DahlanderSchaltung). Für andere Drehzahlen haben die Motoren zwei getrennte Wicklungen. 50 I ph U ph L1 L2 U ph Un L3 3.1 Stern- und Dreieckschaltung für Motoren mit einer Drehzahl: U1 U1 U2 W2 U1 W1 Y-Schaltung V1 V2 W2 U2 V2 W1 U1 V1 W1 W1 V1 L1 L2 V1 L2 L1 ∆-Schaltung L3 L3 Pole: 2, 4, 6, 8 ...... Nenndrehzahl bei 50 Hz: 3000, 1500, 1000, 750 ..... Schaltung für Motoren mit zwei Drehzahlen und zwei getrennten Wicklungen: L1 W2 V2 L2 L3 U1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W1 U2 Hohe Drehzahl W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 D V1 Niedrige Drehzahl L2 L1 L3 Pole: 2/6, 2/8, 4/6, 6/8 Nenndrehzahl bei 50 Hz: 3000/1000, 3000/750, 1500/1000, 1000/750. Dahlander-Schaltung für Motoren mit zwei Drehzahlen und konstantem Drehmoment: L1 W2 L2 L3 U1 U1 W2 U2 U1 V1 V2 V2 W1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W2 W1 V1 V2 W1 U2 Hohe Drehzahl V1 U2 L2 L1 Niedrige Drehzahl L3 Pole: 2/4, 4/8 Nenndrehzahl bei 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Dahlander-Schaltung für Motoren mit zwei Drehzahlen und quadratischem Drehmoment: L1 W2 U1 L2 L3 W2 U2 U1 V1 U1 V2 W2 W1 V1 V2 V2 U2 Hohe Drehzahl W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 U2 W1 V1 W1 Niedrige Drehzahl L1 L2 L3 Pole: 2/4, 4/8 Nenndrehzahl bei 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Abbildung 3 C - Schaltungsschema für Drehstrommotoren 51 3.2 Einphasenmotoren 3.1.2 Einphasenmotoren Rotes Kabel Braun Kabel U1 Schwarz Kabel Rotes Kabel Braun Kabel U1 W1 V1 W1 V1 L2 L1 Schwarz Kabel L2 L1 Kondensator Kondensator 220V / 240V 220V / 240V Abbildung 3 D - Schaltungen der Einphasenmotoren F56 D Grünes Kabel Grünes Kabel W2 U1 U2 V1 L1 V2 W2 W1 U1 V2 V1 L1 L2 W1 L2 220V / 240V 110V / 120V Grünes Kabel Grünes Kabel W2 U2 V2 W2 U1 V1 W1 U1 L2 L1 110V / 120V Abbildung 3 E - Schaltungen der Einphasenmotoren F63-80 52 U2 U2 V2 V1 L1 W1 L2 220V / 240V 3.3 Selbstbremsende Motoren - Gruppen IIB und IIC (BTVF und CTVF) 3.2.1 Stromversorgung der Bremse 3.2.2 Funktionale Grenzen der Bremse 3.2.3 Einstellungen 3.2.1 Stromversorgung der Bremse Die Abbildungen zeigen die verschiedenen Schaltungen der Bremse mit und ohne die Option “Ansprechzeit reduziert”. L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 KONTAKTGEBER KONTAKTGEBER MASSE KLEMMKASTEN BREMSE W1 V1 BREMSE U1 MASSE KLEMMKASTEN W1 V2 V1 U1 KLEMMHALTERPLATTE KLEMMHALTERPLATTE U2 W2 Vdc Vac V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac D GLEICHRICHTER GLEICHRICHTER Abbildung 3 F - Ansprechzeit Standard Stromversorgung der Bremse parallel zur Stromversorgung des Motors Abbildung 4 G - Ansprechzeit reduziert Stromversorgung der Bremse parallel zur Stromversorgung des Motors L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Stromversorgung Gleichrichter: Stromversorgung Gleichrichter: Vac Vac KONTAKTGEBER KONTAKTGEBER MASSE KLEMMKASTEN BREMSE W1 V1 U1 MASSE KLEMMKASTEN BREMSE W1 V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac GLEICHRICHTER Abbildung 5 H - Ansprechzeit Standard Stromversorgung der Bremse unabhängig V1 U1 KLEMMHALTERPLATTE KLEMMHALTERPLATTE V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac GLEICHRICHTER Abbildung 6 I - Ansprechzeit reduziert Stromversorgung der Bremse unabhängig 53 3.3 3.3.1 Stromversorgung der Bremse 3.3.2 Funktionale Grenzen der Bremse 3.3.3 Einstellungen 3.3.1 Stromversorgung der Bremse Im Standard wird die Bremse mit Gleichspannung betrieben, die durch einen Gleichrichter auf dem Klemmbrett des gelieferten Motors zugeführt wird. Für die alternative Sinusspannung des Gleichrichters sind zwei Möglichkeiten vorgesehen: D Stromversorgung parallel zu den Versorgungsphasen des Motors Dies ist die einfachste sowie die üblichste Art der Benutzung einer Bremse. In dieser Konfigurierung ist es nicht möglich, Motoren mit zwei Geschwindigkeiten zu realisieren oder den Motor mit Frequenzvariator einzusetzen. Die für den Blockierungsbeginn typischen Ansprechzeiten sind: F63-71 : 32 ms ; F80 :140 ms Option: Ansprechzeit reduziert. Die für den Blockierungsbeginn typischen Ansprechzeiten sind: F63-71 : 10 ms ; F80 : 35 ms. Stromversorgung unabhängig Der Bediener muss eine alternative Sinusstromversorgung gewährleisten (230 oder 400V ± 10%). Dieser Anschluss ermöglicht unter anderem die Verwendung des Motors mit einem Frequenzwandler, erfordert aber eine zusätzliche Kabelpresse. Option: Ansprechzeit reduziert. 3.3.2 Funktionale Grenzen der Bremse Die Energieabgabe während der nachfolgenden Bremsung darf nicht zu einem übermäßigen Anstieg der Temperatur oder zu einer Reduzierung der vorgesehenen durchschnittlichen Lebensdauer der Bremse führen. Bei der Wahl des Motors ist es daher von wesentlicher Bedeutung, die Anzahl dr Bremsungen pro Stunde, die auf die Welle übertragene Trägheit und die Drehzahl anzugeben. 3.3.3 Einstellungen Der Motor wird mit dem Bremsmoment geliefert, das in den Tabellen in Kapitel 4.5 (Betriebsdaten) angegeben wird. Es ist jedoch ein Verfahren zur Einstellung des Bremsmoments oder zur Ersetzung der Bremsdichtung vorhanden, falls diese Eingriffe erforderlich sind. 54 Motores antideflagrantes E 55 1. Informaciones generales 1.1 Motores serie F 1.1 Motores serie F ATEX Los motores presentados en este catálogo respetan las normas, relativas a los aparatos y a los sistemas de protección a utilizar en atmósferas potencialmente explosivas, en conformidad con la directiva europea n° 94/9/CE del 23/3/94, conocida como directiva ATEX. La directiva ATEX tiene prevista la expedición de dos diferentes certificados de conformidad. Uno “CE del Tipo” para la homologación del prototipo, el otro para la “Garantía de Calidad de la Producción”. El número del certificado di Garantía de calidad de la producción es: LCIE 00 ATEX Q8007. Los certificados son expedidos por el Laboratoire Central des Industries Electriques (L.C.I.E) (Organismo notificado n° 0081). Los números de los certificados de conformidad se indican en los datos nominales. Tabla1 A - La serie F ATEX Versión E Tamaño [mm] Potencias (2 polos) [kW] Clase de temperatura standard (*) IIB IIC Serie Trifásico, 1 velocidad (2, 4, 6, 8 polos) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,50 T5 / T6 F-BTV F-CTV Trifásicos, 1 velocidad, no ventilados (2, 4, 6, 8 polos) 56 - 80 0,06 - 0,55 T4 F-BST F-CST Trifásico, 2 velocidades (2/4, 4/6, 4/6, 4/8 polos) (par constante) 63 - 80 0,25 - 0,75 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Trifásico, 2 velocidades (2/4, 4/8, 4/6, 6/12 polos) (par cuadrático) 63 - 80 0,25 - 1,10 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Trifásicos, 1 velocidad, con freno (2, 4, 6, 8 polos) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,10 T4 F-BTVF F-CTVF Monofásico, (2, 4, 6 polos) 56 63 - 80 0,06 - 0,08 0,12 - 0,75 T4 F-BM F-BMV F-CM F-CMV (*) La clase de temperatura realizable, con potencia nominal, se indica en el capítulo 4 (Datos nominales). Tabla 1 B - Clase de temperatura a demanda (referida a una temperatura ambiente de 40 °C) Tamaño T5 T6 56 - 80 Mismas Potencias T4 (*) Potencias reducidas (*) Para los motores monofásicos y trifásicos de 2 velocidades: potencias reducidas respecto a T4, salvo cuanto indicado en el capítulo 4.1. 56 1.2 1.3 1.2 Características principales Opciones principales Características principales • Motores antideflagrantes a prueba de explosión según las Normas europeas CENELEC EN 50 014, EN 50 018 ed EN 50 019 (para caja de bornes EEx-e). • Las Normas europeas son reconocidas y aceptadas por los países pertenecientes al CENELEC (Comisión europea para la estandarización electrotécnica) y por la mayoría de los países del mundo. • Motores asíncronos trifásicos y monofásicos de jaula de ardilla. • Completamente cerrados, con ventilación autónoma, carcasa IP55 con caja de bornes IP65. • Dimensiones según normas IEC 60072. • Alimentación 400V/ 50Hz. Motores trifásicos 1 velocidad, 2-4-6-8 polos, T4, para alturas del eje de 56 a 80, alimentación multi-tensión 380-400-420V/ 50 Hz. • Clase de aislamiento F. 1.3 • Nivel de ruido (dBA) El nivel de ruido, medido en vacío y en las condiciones nominales de alimentación, es inferior al contemplado por la norma NF 51-119 (IEC 34-9). Estamos a su disposición para aplicaciones especiales. • Caja de bornes: - disponibles ya sea en versión antideflagrante como en versión con seguridad aumentada - de grandes dimensiones - generalmente instalada en la parte opuesta respecto a los pies, orientable tanto hacia la derecha como hacia la izquierda - giratoria hasta 90° en las 4 posiciones - rejilla de separación del armazón. • - Armazón del motor: aspas de enfriamiento pies removibles bullón para la unión directa al armazón brida con orificios lisos removible anillo de retención con reborde delantero y trasero (IP55) - tornillo de masa. • - Rotor: fundido a presión en aleación de aluminio montaje con virola en el eje equilibrado dinámico con lengüeta entera pintura aislante • Alta protección contra la corrosión: - pintado interior y exterior con polvo de - tornillos anticorrosión. • Alta protección contra los golpes: - casquete cubre ventilador en fundición de aluminio. • Anillos de retención con bajo coeficiente de roce. • Nivel de vibraciones: El equilibrado dinámico de los rotores (media chaveta) confiere al estándar de los motores trifásicos un nivel de vibraciones residuales que corresponde al grado N (normal) según IEC 34-14. • Los certificados de conformidad son válidos incluso para características de proyecto diferentes con respecto a la versión base, como por ejemplo: - altitud superior a los 1000 m s. n. m. - varias tensiones y frecuencias - alimentación desde inverter - motor protegido por detectores de temperatura - servicio de S2 a S9. E Opciones principales • Tensiones y frecuencias de alimentación especiales (tensión máxima 690V). • Motores con características eléctricas según demandas del cliente. • Motores preparados para la alimentación por medio de un variador electrónico de frecuencia (inverter). • Bridas y ejes especiales. • Ejes de doble extremo. • Equilibrado de grados R y S. • Motores con cojinetes especiales (unidireccionales) aumentados. • Motores tropicalizados (Grado de humedad relativa H% comprendido entre 90 y 98%). • Motores con protectores térmicos bimetálicos, termistores PTC o sonda resistiva PT100 (se suministra otro prensacables) • Motores con resistencias contra la condensación y protección contra las bajas temperaturas. • Motores con techo protector contra la lluvia. • Caja de bornes con entradas para cables especialesi. • Motores sin caja de bornes con salida de cable • Motores con dínamo tacométrica o encoder. • Motores para áreas clasificadas zona 21 y zona 22 (Polvos). • Motores para aplicaciones epeciales a petición. • Caja de bornes con seguridad aumentada “e”, véase cap. 2.5 • Motores con protección IP56 - IP65 - IP66. 57 2. Características mecánicas 2.1 Formas de fabricación 2.1 Formas de fabricación Las formas de fabricación utilizadas corrientemente están descritas en la tabla 2 A. Sobre pedido se proporcionan otras formas de fabricación. Los motores requeridos en las formas de fabricación IM B3, IM B5 o IM B14 pueden ser utilizados incluso para otras posiciones de montaje: - IM B3 in IM B6, IM B7, IM B8, IM V5 o IM V6, - IM B5 in IM V1 o IM V3, - IM B14 in IM V1 o IM V3, La normativa para las máquinas eléctricas de seguridad prescribe que hay que impedir la caída de impurezas en el interior del motor. Con este fin los motores instalados en vertical con el eje hacia abajo tiene que tener una tapa de protección por encima del cubre ventilador. E En caso de montaje en vertical con el eje colocado hacia arriba la protección contra las impurezas está garantizada por la máquina acoplada o por una tapa de protección montado por el usuario final. Esta protección no debe obstaculizar el flujo de aire para la refrigeración. Tabla 2 A Motores con patas CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 código I IEC 34-7 código II V5 IM V5 IM 1011 B5 IM B5 IM 3001 V1 IM V1 IM 3011 B14 IM B14 IM 3601 V18 IM V18 IM 3611 Motores con brida: brida normal, orificios de fijación de los pasadores Motores con patas y brida: brida normal, orificios de fijación de los pasadores CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 código I IEC 34-7 código II Motores con brida: brida reducida, orificios de fijación fileteados Motores con patas y brida: brida reducida, orificios de fijación fileteados CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 código I IEC 34-7 código II 58 B3 IM B3 IM 1001 2.1 V6 IM V6 IM 1031 B6 IM B6 IM 1051 B7 IM B7 IM 1061 B8 IM B8 IM 1071 V3 IM V3 IM 3031 B35 IM B35 IM 2001 V15 IM V15 IM 2011 V36 IM V36 IM 2031 E V19 IM V19 IM 3631 B3/B14 IM B34 IM 2101 V5/V18 IM V58 IM 2111 V6/V19 IM V69 IM 2131 59 2.2 Instalación y aplicaciones 2.2.1 Características térmicas y ambientales 2.2.2 Ambientes industriales agresivos 2.2.1 Características térmicas y ambientales Régimen de utilización A excepción de algunas especificaciones concretas, las características de los motores presentados en el cap. 4 (Datos nominales) corresponden al régimen de utilización S1 (régimen de funcionamiento permanente según IEC 34-1). Estamos a su disposición para resolver especiales requisitos relativos a otras condiciones de utilización aprobadas. Grupos de explosiones y clases de temperatura: A excepción de algunas especificaciones concretas, los motores están disponibles en el Grupo IIB o IIC. La clase de temperatura standard, con la cual son suministrados nuestros motores, es la T4, salvo cuanto indicado en el capítulo 4.1 (Datos nominales). A petición, es posible construir motores de clase T5 o T6. Temperatura ambiente y altitud El control de las temperaturas superficiales en los límites impuestos por la clase de temperatura implica una utilización a una temperatura ambiente igual o inferior a 40° C y a una altitud igual o inferior a 1000 m (según NFC 51-111). La temperatura ambiente mínima de utilización de los motores estándar presentados en la guía para la elección es de -20° C. Estamos a su disposición para informaciones sobre las condiciones de utilización que no cumplan dichos límites. Recalentamiento del devanado El recalentamiento del devanado de los motores descrito en el cap. 4 (Datos nominales) es igual o inferior a 80 K. E 2.2.2 Ambientes industriales agresivos Para los ambientes agresivos (entre los cuales: industria química, de materias primas y de producción de energía) propone una variante de fabricación basada en el estándar alemán VIK (Vereinigung Industrielle Kraft wirschaft). La opción correspondiente, denominada “VIK”, concierne a los motores de tipo EEx-de IIC. 60 Las diferencias de fabricación respecto al estándar son: - caja de bornes con seguridad aumentada EEx-e ampliamente dimensionada, dotada de tornillos retenidos, con salida del cable orientable que evita el movimiento del tablero. - protección térmica PTC incluida, - tornillería y placa de acero inoxidable - acabado externo de resina epoxídica en dos capas 2 x 40 µm, - acabado interno pintura aislante para el rotor y las cabezas de las bobinas de devanado, - placa suplementaria en la caja de bornes, - tapa de protección contra la lluvia. Límites térmicos de los aislantes del devanado Los aislantes del devanado se realizan con materiales de clase F. Humedad: Los motores estándar presentados en la guía para la elección se pueden utilizar con una humedad relativa (H%) de hasta un 90 % . 2.3 Materiales, pintado y placa 2.3.1 Materiales y barnizado 2.3.1 Materiales y barnizado Materiales Tabla 2 B - Materiales de los principales componentes: Tamaño 56 - 80 Carcasa Escudos Caja de bornes Protección ventilador Aleación de aluminio normalizado Ventilador Aluminio o material plástico compuesto antiestático Eje Acero XC 48 Estator Chapas de bajo nivel de pérdida rígidamente ensambladas Devanado Aislamientos clase F o H Tornillos Acero galvanizado, inoxidable a petición Prensacables Aluminio, latón niquelado o acero inoxidable Características de los tratamientos de superficie Acabado estándar: Sin tratamiento, motor de color aluminio natural. Aconsejado para su utilización - en presencia de humedad o de vapor de agua - en ambientes químicos poco agresivos - en el sector de temperaturas de superficie del motor comprendidas entre -20° C y +130° C. Acabado opcional: • Acabado de fondo - desengrase - una capa de tratamiento de fosfatación 20 µm aprox. (compatible con todos los acabados posteriores, a excepción de la resina epoxídica). • Acabado poliuretánico - desengrase - una capa de wash primer vinílico modificado de 10 µm aprox. - una capa de poliuretano bicomponente azul RAL 5010 (30 µm aprox.) - tornillería inoxidable. Aconsejado para utilización: - en presencia de agua, vapor de agua, ambiente de baja salinidad - en atmósfera industrial discretamente agresiva con proyecciones ocasionales de productos químicos agresivos. - en el sector de temperaturas de superficie motor comprendidas entre -20° C y +130° C. • Acabado en resina epoxídica - desengrase - una capa de wash primer vinílico modificado de 10 µm aprox. - una capa de resina epoxídica poliamídica bicomponente azul RAL 5010 (25 µm aprox.) - tornillería inoxidable. Aconsejado para utilización - en presencia de agua, vapor de agua, aire salino - en atmósfera industrial agresiva con presencia de productos químicos agresivos - en el sector de temperaturas de superficie del motor comprendidas entre -20° C y +130° C. • Otros acabados estamos a su disposición. 61 E 2.3 2.3.2 Placa 2.3.2 Placa Identificación Los motores se identifican mediante una placa de características en la que se indican las marcas que se describen a continuación: Tabla 2 C - Marcados impuestos por la legislación en vigor Marcado Significado EEx d de II B-C T4 - T5 - T6 LCIE N° ... Marcado CE Marcado específico relativo a la protección contra las explosiones Símbolo de los aparatos de seguridad que cumplen una modalidad de protección Modalidad de protección “con envolvente antideflagrante” Motor “d” y caja de bornes “e” Grupo de explosión Grupo antideflagrante Clase de temperatura de ignición N° de certificado CE del tipo Tabla 2 D - Otras indicaciones de marcado: E Marcado Significado ATAV CEMP FRANCE NONANCOURT FRANCE Type ... N° ./. kg ... kW ... Volts ... Amp ... Cos. ... Hz ... min-1 ... S ... CI. IP °C amb ... Vis: Cl. Marca comercial Nombre y dirección del Fabricante Referencia comercial del motor N° de matrícula/año de fabricación Masa del motor Potencia del motor Tensión triángulo / tensión estrella Corriente triángulo / corriente estrella Factor de potencia Frecuencia nominal Número de revoluciones por minuto Régimen de funcionamiento Clase de aislamiento Indice de protección Temperatura ambiente máxima Clase de resistencia de la tornillería Placa La placa, de acero inoxidable, está fijada al armazón con clavos estriados. Les Ateliers de l’Avre SA N° II T IP L.C.I.E. 2613 Type: EExd II2G 0081 Fabriqué par: Cemp France F 27320 NONANCOURT ATEX Vis/screw Schraube : cl. kW S Hz cl. V±10% Date: min-1 °C max A cos ϕ Figura 2 A - Placa 62 kg IEC 34-1 2.4 Resistencia de los cojinetes y piezas de montaje 2.4.1 Cojinetes 2.4.2 Características mecánicas 2.4.1 Cojinetes Los motores estándar están dotados de cojinetes de bolas con collares profundos y herméticos. Los cojinetes delanteros están bloqueados. Cojinetes utilizados Altura del eje (mm) Tipo de cojinete delantero Tipo de cojinete trasero 56 63-71 80 6202 ZZ 6203 2RS 6005 2RS 6200 ZZ 6203 2RS 6004 2RS 2.4.2 Características mecánicas Cargas aplicables en la extremidad del eje Las cargas dinámicas máximas aplicables (N) para una duración de servicio L10h = 25.000 ore son las siguientes: Tabla 2 E E Esfuerzo (N) 2 polos Tamaño Dirección del esfuerzo 4 polos Tamaño 6 polos Tamaño 8 polos Tamaño 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 350 480 510 460 610 650 540 710 740 600 780 820 240 350 370 330 440 470 370 510 540 420 560 590 220 330 330 310 420 430 350 490 500 400 540 550 250 370 410 340 460 510 400 530 580 440 580 630 IMB... ; IMV... IMB... IMV... 63 2.4 2.4.3 Ejecuciones especiales 2.4.3 Ejecuciones especiales Interfaces de montaje de los motores Bridas especiales Además de las formas de fabricación estándar, que se describen en el capítulo 2.1, están disponibles unos motores con montaje por medio de bullones para su unión a un tubo o a un sistema de ventilación. Están disponibles unos motores con unas bridas, diferentes del estándar, pero que cumplen con la normativa NFC 51-120 con orificios lisos (B5) o con orificios con rosca (B14). El cuadro que sigue y que integra las cotas que se indican en el capítulo 5 (Dimensiones totales) indica las medidas de las bridas disponibles. Tabla 2 F Tamaño Brida Dimensiones [mm] ØM ØN ØP Ø TLB Ø TTB 56 B5 B5 B14 FF85 FF115 FT75 85 115 75 70 95 60 105 140 90 7.0 9.0 --- ----M5 63 B5 B14 B5 B14 FF100 FT65 FF130 FT85 100 65 130 85 80 50 110 70 120 85 160 105 7.0 --9.0 --- --M5 --M6 71 B5 B14 B5 B14 B5 FF100 FT65 FF115 FT75 FF165 100 65 115 75 165 80 50 95 60 130 120 85 140 90 200 7.0 --9.0 --11.0 --M5 --M5 --- 80 B5 B5 B14 B5 FF115 FF130 FT85 FF215 115 130 85 215 95 110 70 180 140 160 105 250 9.0 9.0 --13.5 ----M6 --- E 64 Forma de fabricación 2.5 2.5 Caja de bornes Caja de bornes Cableado con caja de bornes “d” Opciones para prensacables “d” Opciones para caja de bornes “e” • Orientación de la caja de bornes con relación a los pies (para montaje IM1... o IM2...). En el estándar, el eje de la caja de bornes es perpendicular a la superficie de emplazamiento. Como opción, se puede entregar “a derecha” o “a izquierda” vista frontal al motor por el lado de la extremidad del eje principal (sin repercusión sobre su costo). Nota: Solamente en fábrica se puede modificar la posición de la caja de bornes. - caja de bornes entregada sin prensacables, con orificio de rosca ISO M - junta Ø 9 o 13 mm para prensacables - prensacables suplementario (modelo estándar) u orificio suplementario - prensacables con continuidad de blindaje - prensacables para cable armado o prensacables especial. • Caja de bornes con seguridad aumentada Eex-e - disponible para motores trifásicos ventilados por HA de 63 a 80 - IP55 (IP65 opcional) tensión máxima 690V, sistema de conexión hermética, desmontable entre la caja de bornes y el armazón entregada con dotación de un prensacables EEx-e para un cable no armado con diámetro de 7,5 a 13 mm (M20 ISO).Opción prensacables:estamos a su disposición. • Prensacables “d” En los motores “EEx-d” el prensacables contribuye al cierre del envolvente antideflagrante. El usuario deberá terminantemente elegir un cable cuyo diámetro en la membrana de retención corresponda a las características del prensacables además de usar un dispositivo de enganche del cable en el diámetro externo del cable. En el estándar, los motores entregados están dotados de un prensacables EEx-d con enganche del cable. En la membrana de retención el cable debe presentar un diámetro igual a 11 ± 0,5 mm (Figura 2 C). En el estándar los motores a dos velocidades, están dotados de 2 prensacables. Otras opciones Estándar • Posición de la salida del cable En la ejecución standard la salida del cable es por la parte derecha (mirando el motor por el lado del eje). Todas las demás opciones son a solicitar en el momento de presentar el pedido, utilizando la misma referencia (salida del cable por la parte alta, la parte baja, por la izquierda, por la derecha, por delante, por detrás). • • - Motores sin caja de bornes. Motor con salida de cable: disponible para las series trifásicas cable de alimentación (4 o 7 hilos) conectado en fábrica - dimensiones reducidas gracias a la eliminación de la caja de bornes en los motores trifásicos ventilados - dimensiones y otras características: estamos a su disposición. A la izquierda (opción) Figura 2 B A la derecha (opción) • Interruptor encendido/apagado de accionamiento manual, integrado en la caja de bornes (sólo HA 63-71-80). E Enganche de los cables Junta Prensacables Prensacables estándar en aluminio para tamaño de 56 a 80 (lados en mm máx.) Membrana de retención Diámetro exterior Figura 2 C 65 3. Esquemas de conexión 3.1 Motores trifásicos 3.1 Motores trifásicos Los devanados de los motores estándar pueden ser conectados en dos formas: - conexión de estrella - conexión de triángulo Conexión de estrella La conexión de estrella se obtiene conectando a la vez los bornes terminales W2, U2, V2 y alimentando los bornes terminales U1, V1, W1. La corriente y la tensión de fase son: Iph = In Uph = Un / ED 3 en que In es la corriente de línea y Un es la tensión de línea. V2 U2 Centro estrella W2 U ph I ph U1 L1 V1 U ph I ph U ph W1 L2 L1 L3 L2 Un L3 Un Figura 3 A Conexión de triángulo E La conexión de triángulo se lleva a cabo conectando el final de una fase al principio de la fase sucesiva. In U2 V2 W2 I ph La corriente de fase Iph y la tensión de fase I ph U ph Uph son: U1 3 Iph = In / ED Uph = Un L1 Figura 3 B V1 W1 L3 L2 Un Arranque de estrella-triángulo Motores con dos velocidades El arranque estrella-triángulo es el modo más fácil para reducir la corriente y el par de arranque. Los motores cuya tensión nominal con el motor conectado en triángulo corresponde a la tensión de red pueden ponerse en marcha con el método estrella-triángulo. Los motores estándar de dos velocidades están proyectados para una única tensión, con arranque directo. Cuando la relación entre las dos velocidades es de 1 a 2 los motores estándar tienen un único devanado (conexión Dahlander). Para los otras velocidades los motores tienen dos devanados diferentes. 66 L1 L2 U ph Un L3 3.1 Conexiones de estrella y triángulo para motores de una velocidad: U1 U1 U2 W2 U1 W1 V1 V2 W2 U2 V2 W1 U1 V1 W1 W1 V1 Conexión-Y L1 L2 V1 L2 L1 Conexión-∆ L3 L3 Número de polos: 2, 4, 6, 8 ...... Velocidad de sincronismo de 50 Hz: 3000, 1500, 1000, 750 .... Conexión para motores de dos velocidades, dos devanados separados: L1 W2 V2 L2 L3 U1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W1 U2 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 V1 Velocidad baja Velocidad alta L2 L1 L3 Número de polos: 2/6, 2/8, 4/6, 6/8 Velocidad de sincronismo de 50 Hz: 3000/1000, 3000/750, 1500/1000, 1000/750. E Conexión Dahlander para motores de dos velocidades, par constante: L1 W2 L2 L3 U1 U1 W2 U2 U1 V1 V2 V2 W1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W2 W1 V1 V2 Velocidad alta W1 U2 V1 U2 L2 L1 Velocidad baja L3 Número de polos: 2/4, 4/8 Velocidad de sincronismo de 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Conexión Dahlander para motores de dos velocidades, par cuadrático: L1 W2 U1 L2 L3 W2 U2 U1 V1 U1 V2 W2 W1 V1 V2 V2 Velocidad alta U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 U2 W1 U2 W2 V1 W1 Velocidad baja L1 L2 L3 Número de polos: 2/4, 4/8 Velocidad de sincronismo de 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Figura 3 C - Esquemas de conexión de los motores trifásicos. 67 3.2 3.2 Motores monofásicos Motores monofásicos Cable rojo Cable marrón U1 Cable negro Cable rojo U1 W1 V1 W1 V1 L2 L1 Cable negro Cable marrón L2 L1 condensador condensador 220V / 240V 220V / 240V Figura 3 D - Esquemas de conexión de los motores monofásicos F56 Cable verde Cable verde E W2 U1 U2 V1 L1 V2 W2 W1 U1 V2 V1 L1 L2 W1 L2 220V / 240V 110V / 120V Cable verde Cable verde W2 U2 V2 W2 U1 V1 W1 U1 L2 L1 110V / 120V Figura 3 E - Esquemas de conexión de los motores monofásicos F63-80 68 U2 U2 V2 V1 L1 W1 L2 220V / 240V 3.3 Motores con freno - Grupos IIB y IIC (BTVF y CTVF) 3.3.1 Alimentación del freno 3.3.2 Limites funcionales del freno 3.3.3 Regulaciones 3.3.1 Alimentación del freno Las figuras muestran los diferentes esquemas de alimentación del freno con o sin la opción “tiempo de respuesta reducido”. L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 CONTACTOR CONTACTOR MASA CAJA DE BORNES FRENO W1 V1 MASA CAJA DE BORNES FRENO U1 W1 V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac V1 U1 PLACA PORTA BORNES PLACA PORTA BORNES V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac RECTIFICADOR RECTIFICADOR Figura 3 F - Tiempo de respuesta estándar Alimentación del freno en paralelo en la alimentación del motor Figura 3 G - Tiempo de respuesta reducido Alimentación del freno en paralelo en la alimentación del motor L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Alimentación rectificador: Alimentación rectificador: Vac Vac CONTACTOR CONTACTOR MASA CAJA DE BORNES FRENO W1 V1 U1 MASA CAJA DE BORNES FRENO W1 U2 W2 Vdc Vac RECTIFICADOR Figura 3 H - Tiempo de respuesta estándar Alimentación del freno independiente V1 U1 PLACA PORTA BORNES PLACA PORTA BORNES V2 E V2 U2 W2 Vdc Vac RECTIFICADOR Figura 3 I - Tiempo de respuesta reducido Alimentación del freno independiente 69 3.3 3.3.1 Alimentación del freno 3.3.2 Limites fonctionnelles du frein 3.3.3 Réglages 3.3.1 Alimentación del freno En todos los casos, el freno funciona con una tensión continua proporcionada por un rectificador instalado en la caja de bornes del motor entregado. Para la alimentación alternativa sinusoidal del rectificador hay disponibles dos posibilidades: Alimentación en paralelo en las fases de alimentación del motor Es la manera más simple, además que la más habitual, de utilizar un freno. En esta configuración no es posible realizar motores con dos velocidades ni utilizar el motor con un variador de frecuencia. Los tiempos de respuesta típicos para el inicio del bloqueo son: F63-71 32 ms ; F80 :140 ms Opción: tiempo de respuesta reducido Los tiempos de respuesta típicos para el inicio del bloqueo son: F63-71 10 ms ; F80 : 35 ms. Alimentación independiente El usuario debe preparar una alimentación alternativa sinusoidal (230 o 400V ± 10%). Dicha conexión permite, entre otras cosas, utilizar el motor con un variador de frecuencia pero necesita un prensacables suplementario. Opción: tiempo de respuesta reducido. 3.3.2 Limites funcionales del freno E La energía disipada en el curso de sucesivos frenados no debe producir una subida excesiva de la temperatura ni reducir la vida media prevista para el freno. Cuando se elige el motor es pues fundamental indicar el número de frenados por hora, la inercia transmitida al eje motor y la velocidad. 3.3.3 Regulaciones El motor se suministra con el par de frenado que se indica en los cuadros del capítulo 4.5 (Datos nominales). De todas formas se dispone de un procedimiento para la regulación del par de frenado o la sustitución de la junta en caso de que resultaran necesarias dichas operaciones. 70 Motori antideflagranti I 71 1. Informazioni generali 1.1 Motori serie F 1.1 Motori serie F I motori presentati in questo catalogo rispettano le norme, relative agli apparecchi e ai sistemi di protezione da utilizzare in atmosfere potenzialmente esplosive, in conformità alla direttiva europea n° 94/9/CE del 23/3/94, conosciuta come direttiva ATEX. La direttiva ATEX prevede il rilascio di due diversi certificati di conformità. Uno “CE del Tipo” per l’omologazione del prototipo, l’altro per la “Garanzia di Qualità della Produzione”. Il numero del certificato di “Garanzia di Qualità della Produzione” è: LCIE 00 ATEX Q8007. I certificati sono stati rilasciati dal Laboratoire Central des Industries Electriques (L.C.I.E) (Organismo notificato n° 0081). I numeri dei certificati di conformità sono indicati nel capitolo 4 (Dati nominali). Tabella 1 A - La serie F ATEX Versione I Altezza d’asse [mm] Potenze (2 poli) [kW] Classe di temperatura standard (*) IIB IIC Serie Trifase, 1 velocità (2, 4, 6, 8 poli) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,50 T5 / T6 F-BTV F-CTV Trifase, 1 velocità non ventilati (2, 4, 6, 8 poli) 56 - 80 0,06 - 0,55 T4 F-BST F-CST Trifase, 2 velocità (2/4, 4/6, 4/6, 4/8 poli) (coppia costante) 63 - 80 0,25 - 0,75 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Trifase, 2 velocità (2/4, 4/8, 4/6, 6/12 poli) (coppia quadratica) 63 - 80 0,25 - 1,10 T4 F-BTV F-CTV Trifase, 1 velocità con freno (2, 4, 6, 8 poli) 63 - 80 0,12 - 1,10 T4 F-BTVF F-CTVF Monofase, (2, 4, 6 poli) 56 63 - 80 0,06 - 0,08 0,12 - 0,75 T4 F-BM F-BMV F-CM F-CMV (*) La classe di temperatura realizzabile a potenza nominale è indicata nel capitolo 4 (Dati nominali). Tabella 1 B - Classe di temperatura su richiesta (riferita a temperatura ambiente di 40 °C). Altezza d’asse 56 - 80 T5 T6 Stesse potenze T4 (*) Potenze ridotte (*) Per i motori monofase e trifase a 2 velocità: potenze ridotte rispetto T4, salvo quanto indicato nel capitolo 4.1. 72 1.2 1.3 1.2 Caratteristiche principali Principali opzioni Caratteristiche principali • Motori antideflagranti a prova di esplosione secondo le norme europee CENELEC EN 50 014, EN 50 018 ed EN 50 019 (per scatola morsettiera EEx-e). • Livello di rumorosità (dBA) I rumori acustici, misurati a vuoto nonché nelle condizioni nominali di alimentazione, sono inferiori a quelli definiti dalla norma NF 51-119 (IEC 34-9). • Le norme europee sono riconosciute e accettate dalle nazioni appartenenti al CENELEC (Commissione europea per la standardizzazione elettrotecnica) e da quasi tutte le nazioni del mondo. • Scatola morsettiera: - disponibile sia in versione antideflagrante sia in versione a sicurezza aumentata - di grandi dimensioni - in genere installata sul lato opposto rispetto ai piedi, su richiesta può essere installata a destra o a sinistra - ruotabile di 90° nelle 4 posizioni - griglia di separazione dalla carcassa. • Motori asincroni trifase e monofase a gabbia di scoiattolo. • Completamente chiusi, carcassa IP55 con scatola morsettiera IP65 ventilati o non ventilati. • Dimensioni a norme IEC 60072. • Alimentazione 400V/ 50Hz. Motori trifase 1 velocità, 2-4-6-8 poli, T4, per altezze d’asse da 56 a 80, alimentazione multitensione 380-400-420V/ 50 Hz. • Classe di isolamento F. 1.3 • Carcassa del motore: - alette di raffreddamento - piedi rimovibili - borchia per attacco diretto alla carcassa - flangia a fori lisci rimovibile - anello di tenuta a labbro anteriore e posteriore (IP55) - vite di massa. • - Rotore: in lega di alluminio pressofuso montaggio con ghiera su albero bilanciatura dinamica con linguetta intera vernice isolante. • Alta protezione contro la corrosione: - targa in acciaio inossidabile - viteria anticorrosione. • Alta protezione contro gli urti: - calotta copriventola in fusione d’alluminio. • Anelli di tenuta a basso coefficiente d'attrito. • Livello di vibrazioni: la bilanciatura dinamica dei rotori (mezza chiavetta) conferisce allo standard dei motori trifase un livello di vibrazioni residue corrispondente al grado N (normale) secondo IEC 34-14. • I certificati di conformità sono validi anche per caratteristiche di progetto diverse dalla versione base, quali: - altitudine superiore ai 1000 m s. l. m. - varie tensioni e frequenze - alimentazione da inverter - motore protetto da rilevatori di temperatura - servizio da S2 a S9. Principali opzioni • Tensioni e frequenze di alimentazione speciali (massima tensione 690V). • Motori con caratteristiche elettriche su specifica cliente. • Motori predisposti per alimentazione tramite variatore elettronico di frequenza (inverter). • Flange e alberi speciali. • Alberi a doppia sporgenza. • Bilanciatura di grado R e S. • Motori con cuscinetti speciali (unidirezionali, maggiorati). I • Motori con protezione IP56 - IP65 - IP66. • Motori tropicalizzati (tasso di umidità relativa H% incluso tra 90 e 98%). • Motori con termoprotettori bimetallici, termistori PTC o sonda resistiva PT100 (viene fornito un secondo pressacavo). • Motori con resistenze per anticondensa e/o protezione contro le basse temperature. • Motori con tettuccio parapioggia. • Scatola morsettiera con entrate cavi speciali. • Motori privi di morsettiera con uscita cavo. • Motori con dinamo tachimetrica o encoder. • Motori per aree classificate zona 21 e zona 22 (Polveri). • Motori per applicazioni speciali su richiesta. • Morsettiera a sicurezza aumentata “e” (vedi cap. 2.5). 73 2. Caratteristiche meccaniche 2.1 Forme costruttive 2.1 Forme costruttive Le forme costruttive comunemente utilizzate sono raffigurate nella tabella 2 A. Su richiesta sono fornite altre forme costruttive. I motori ordinati nelle forme costruttive IM B3, IM B5 o IM B14 possono essere utilizzati anche per altre posizioni di montaggio: - IM B3 in IM B6, IM B7, IM B8, IM V5 o IM V6, - IM B5 in IM V1 o IM V3, - IM B14 in IM V18 o IM V19. La normativa per le macchine elettriche a sicurezza prescrive che debba essere impedita la caduta di corpi estranei all'interno del motore. A tale scopo i motori montati in verticale con albero rivolto verso il basso devono avere un tettuccio di protezione sopra il copriventola. In caso di montaggio in verticale con albero rivolto verso l'alto la protezione contro corpi estranei viene assicurata dalla macchina accoppiata o da un tettuccio montato dall'utilizzatore finale. Tale protezione non deve impedire il flusso d'aria per il raffreddamento. Tabella 2 A Motori con piedi CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 codice I IEC 34-7 codice II 74 V5 IM V5 IM 1011 B5 IM B5 IM 3001 V1 IM V1 IM 3011 B14 IM B14 IM 3601 V18 IM V18 IM 3611 Motori con flangia: flangia normale, fori di fissaggio passanti Motori con piedi e flangia: flangia normale, fori di fissaggio passanti CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 codice I IEC 34-7 codice II Motori con flangia: flangia ridotta, fori di fissaggio filettati Motori con piedi e flangia: flangia ridotta, fori di fissaggio filettati CEI 2-14 IEC 34-7 codice I IEC 34-7 codice II I B3 IM B3 IM 1001 2.1 V6 IM V6 IM 1031 B6 IM B6 IM 1051 B7 IM B7 IM 1061 B8 IM B8 IM 1071 V3 IM V3 IM 3031 B35 IM B35 IM 2001 V15 IM V15 IM 2011 V36 IM V36 IM 2031 V19 IM V19 IM 3631 B3/B14 IM B34 IM 2101 V5/V18 IM V58 IM 2111 V6/V19 IM V69 IM 2131 I 75 2.2 Installazione e applicazioni 2.2.1 Specifiche termiche e ambientali 2.2.2 Ambienti industriali gravosi 2.2.1 Specifiche termiche e ambientali Regime di utilizzo Le specifiche dei motori presentati nel cap. 4 (Dati nominali) corrispondono al regime di utilizzo S1 (regime di funzionamento permanente secondo IEC 34-1) ad eccezione di alcune note particolari. Gruppi di esplosioni e classi di temperatura I motori sono disponibili nel Gruppo IIB o IIC. La classe di temperatura standard, con la quale i motori sono forniti è T4, salvo quanto indicato nel capitolo 4.1 (Dati nominali). Su richiesta possono essere costruiti motori classe T5 o T6. Temperatura ambiente e altitudine Il controllo delle temperature di superficie, nei limiti imposti dalla classe di temperatura, implica un utilizzo dei motori a una temperatura ambiente inferiore o pari a 40° C e a un'altitudine inferiore o pari a 1000 m (secondo NFC 51-111). La temperatura ambiente minima di utilizzo dei motori standard è pari a -20° C. Sopraelevazione di temperatura dell'avvolgimento La sopraelevazione di temperatura dell'avvolgimento dei motori descritto nel cap. 4 (Dati nominali) è inferiore o pari a 80 K. 2.2.2 Ambienti industriali gravosi I Per gli ambienti gravosi (fra i quali l'industria chimica, delle materie prime e della produzione di energia) si propone una variante costruttiva basata sullo standard tedesco VIK (Vereinigung Industrielle Kraft wirschaft). Tale variante riguarda i motori di tipo EEx-de IIC. 76 Le differenze costruttive in rapporto allo standard sono: - morsettiera a sicurezza aumentata EEx-e ampiamente dimensionata, dotata di viti antiallentanti e di dispositivo che evita il movimento del cavo, - protezione termica PTC compresa, - bulloneria e targa in acciaio inossidabile, - finitura esterna in resina epossidica a due strati 2 x 40 µm, - vernice isolante su rotore e testate dell’avvolgimento, - targa supplementare nella scatola morsettiera, - tettuccio parapioggia. Limiti termici degli isolanti dell'avvolgimento L’avvolgimento è realizzato con materiali di classe F. Umidità I motori standard sono utilizzabili sino a un'umidità relativa di H% = 90. 2.3 Materiali, verniciatura e targa 2.3.1 Materiali e verniciatura 2.3.1 Materiali e verniciatura Materiali Tabella 2 B - Materiali dei componenti principali: Altezza d’asse 56 - 80 Carcassa Scudi Scatola morsettiera Copriventola Lega di alluminio normalizzato Ventola Alluminio o materiale plastico composito antistatico Albero Acciaio XC 48 Statore Lamiere a bassa perdita rigidamente assemblate Avvolgimento Isolamenti classe F o H Viteria Acciaio zincato, inossidabile su richiesta Pressacavo Alluminio, ottone nichelato o acciaio inossidabile Note relative ai trattamenti di superficie Finitura standard: Nessun trattamento, motore non verniciato colore alluminio naturale. Consigliata per l'uso: - in presenza di umidità o di vapore acqueo - in ambiente chimico poco aggressivo - con temperature di superficie motore da -20° C a +130° C. Finiture opzionali: • Finitura di fondo - sgrassaggio - uno strato trattamento di fosfatazione 20 µm circa (compatibile con tutte le finiture ulteriori, fatta eccezione per la resina epossidica). • Finitura poliuretanica - sgrassaggio - uno strato wash primer vinilico modificato 10 µm circa - uno strato di poliuretano bi-componente blu RAL 5010 (30 µm circa) - bulloneria inossidabile. Consigliata per l'uso: - in presenza di acqua, vapore acqueo, aria scarsamente salina - in atmosfera industriale discretamente gravosa con presenza occasionale di prodotti chimici aggressivi - con temperature di superficie motore da -20° C a +130° C. • Finitura in resina epossidica - sgrassaggio - uno strato wash primer vinilico modificato 10 µm circa - uno strato di resina epossidica poliammidica bi-componente blu RAL 5010 (25 µm circa). - bulloneria inossidabile. Consigliata per l'uso: - in presenza di acqua, vapore acqueo, aria salina - in atmosfera industriale gravosa con presenza di prodotti chimici aggressivi - con temperature di superficie motore da -20° C a +130° C. • Altre finiture su richiesta. 77 I 2.3 2.3.2 Targa 2.3.2 Targa Identificazione I motori vengono identificati tramite una targhetta che riporta le marcature descritte qui di seguito: Tabella 2 C - Marcature imposte dalla legislazione in vigore Marcature Significato EEx d de II B-C T4 - T5 - T6 LCIE N° ... Marchio CE Marchio specifico relativo alla protezione contro le esplosioni Simbolo degli apparecchi di sicurezza che soddisfa una modalità di protezione Modalità di protezione “a involucro antideflagrante” Motore “d” e scatola morsettiera “e” Gruppo di esplosione Gruppo di custodia Classe di temperatura d'accensione N° di attestazione CE del tipo Tabella 2 D - Altre indicazioni di marcatura I Marcature Significato ATAV CEMP FRANCE NONANCOURT FRANCE Tipo ... N° ./. kg ... kW ... Volts ... Amp ... Cos. ... Hz ... min-1 ... S ... CI. IP °C amb ... Vis: Cl. Marchio commerciale Nome e indirizzo del costruttore Riferimento commerciale del motore N° di matricola/anno di fabbricazione Massa del motore Potenza del motore Tensione triangolo / tensione stella Corrente triangolo / corrente stella Fattore di potenza Frequenza nominale Numero di giri al minuto Regime di utilizzo Classe d’isolamento Indice di protezione Temperatura ambiente massima Classe di resistenza della bulloneria Targa La targa, in acciaio inossidabile, è fissata alla carcassa con rivetti. Les Ateliers de l’Avre SA N° II T IP L.C.I.E. 2613 Type: EExd II2G 0081 Fabriqué par: Cemp France F 27320 NONANCOURT ATEX Vis/screw Schraube : cl. kW S Hz cl. V±10% Date: min-1 °C max A cos ϕ Figura 2 A - Targa 78 kg IEC 34-1 2.4 Cuscinetti e interfacce di montaggio 2.4.1 Cuscinetti 2.4.2 Specifiche meccaniche 2.4.1 Cuscinetti I motori sono dotati di cuscinetti a sfera largamente dimensionati. I cuscinetti anteriori sono bloccati. Cuscinetti utilizzati: Altezza d'asse (mm) Tipo di cuscinetto anteriore Tipo di cuscinetto posteriore 56 63-71 80 6202 ZZ 6203 2RS 6005 2RS 6200 ZZ 6203 2RS 6004 2RS 2.4.2 Specifiche meccaniche Carichi applicabili sull'estremità dell'albero I carichi dinamici massimi applicabili (N) per una durata di servizio L10h = 25.000 ore sono i seguenti: Tabella 2 E Carico (N) Direzione del carico 2 poli Altezza d’asse 4 poli Altezza d’asse 6 poli Altezza d’asse 8 poli Altezza d’asse 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 56 63-71 80 350 480 510 460 610 650 540 710 740 600 780 820 240 350 370 330 440 470 370 510 540 420 560 590 220 330 330 310 420 430 350 490 500 400 540 550 250 370 410 340 460 510 400 530 580 440 580 630 I IMB... ; IMV... IMB... IMV... 79 2.4 2.4.3 Esecuzioni speciali 2.4.3 Esecuzioni speciali Interfacce di attacco dei motori Flange speciali Oltre alle forme costruttive standard, illustrate nel capitolo 2.1, sono disponibili motori con montaggio a mezzo di borchie per l’attacco a un tubo o a un sistema di ventilazione. Sono disponibili motori con flange, diverse dallo standard, ma conformi alla normativa NFC 51-120 con fori lisci (B5) o con fori filettati (B14). La tabella che segue, ad integrazione delle quote riportate nel capitolo 5 (Dimensioni d’ingombro), riporta le misure delle flange disponibili. Tabella 2 F Altezza d’asse I 80 Forma costruttiva Flangia Dimensioni [mm] ØM ØN ØP Ø TLB Ø TTB 56 B5 B5 B14 FF85 FF115 FT75 85 115 75 70 95 60 105 140 90 7.0 9.0 --- ----M5 63 B5 B14 B5 B14 FF100 FT65 FF130 FT85 100 65 130 85 80 50 110 70 120 85 160 105 7.0 --9.0 --- --M5 --M6 71 B5 B14 B5 B14 B5 FF100 FT65 FF115 FT75 FF165 100 65 115 75 165 80 50 95 60 130 120 85 140 90 200 7.0 --9.0 --11.0 --M5 --M5 --- 80 B5 B5 B14 B5 FF115 FF130 FT85 FF215 115 130 85 215 95 110 70 180 140 160 105 250 9.0 9.0 --13.5 ----M6 --- 2.5 2.5 Scatola morsettiera Scatola morsettiera Esecuzione con scatola morsettiera “d” Opzioni Esecuzione con scatola morsettiera “e” • Di serie la scatola morsettiera è opposta ai piedi di appoggio. In opzionze può essere sul lato destro o sinistro (Figura 2 B). É possibile modificare la posizione della morsettiera solamente in fabbrica. - scatola morsettiera priva di pressacavo, con foro filettato ISO M - pressacavo per cavo Ø 9 o 13 mm - pressacavo supplementare (modello standard) o foro supplementare - pressacavo con ripresa della schermatura - pressacavo per cavo armato o pressacavo speciale. • Scatola morsettiera a sicurezza aumentata EEx-e: - disponibile per motori trifase ventilati altezza asse da 63 a 80 - IP55 (IP65 opzionale) tensione massima 690V, sistema di connessione a tenuta stagna, smontabile tra la morsettiera e la carcassa consegnata dotata di un pressacavo EEx-e per un cavo non armato con diametro da 7,5 a 13 mm (M20 ISO). • Posizione dell'uscita del cavo. Nell’esecuzione standard l'uscita del cavo è a destra (guardando il motore dal lato albero). Tutte le altre opzioni sono da richiedere al momento dell'ordine utilizzando lo stesso riferimento (uscita del cavo verso l'alto, verso il basso, verso sinistra, verso destra, anteriore, posteriore). • Pressacavo “d” Nei motori “EEx-d” il pressacavo contribuisce alla chiusura dell'involucro antideflagrante. L’utente deve tassativamente scegliere un cavo il cui diametro sulla guaina di tenuta corrisponda alla specifica del pressacavo oltre che usare un dispositivo di serraggio del cavo sul suo diametro esterno. Di serie, i motori sono dotati di un pressacavo EEx-d idoneo per il serraggio del cavo. Guaina diametro 11 ± 0,5 mm (Figura 2 C). Altre opzioni Standard • • - Motori senza scatola morsettiera. Motore con uscita cavo: disponibile per le serie trifase cavo di alimentazione (4 o 7 fili) collegato in fabbrica - dimensioni di ingombro ridotte grazie all’eliminazione della scatola scatola morsettiera sui motori trifase ventilati. A sinistra (opzione) A destra (opzione) • Interruttore acceso/spento a comando manuale, integrato nella scatola morsettiera (solo altezza d’asse 63-71-80). Figura 2 B I motori a due velocità sono dotati di 2 pressacavi. Serraggio del cavo I Guarnizione Pressacavo Pressacavo standard in alluminio per altezza d’asse da 56 a 80 (valori in mm max) Guaina di tenuta Diametro esterno Figura 2 C 81 3. Schemi di collegamento 3.1 Motori trifase 3.1 Motori trifase Gli avvolgimenti dei motori standard possono essere collegati in due modi: - collegamento a stella - collegamento a triangolo Collegamento a stella Il collegamento a stella si ottiene collegando insieme i terminali W2, U2, V2 e alimentando i terminali U1, V1, W1. La corrente e la tensione di fase sono: Iph = In U2 Centro stella W2 U ph I ph Uph = Un / ED 3 dove In è la corrente di linea e Un è la tensione di linea. V2 U1 L1 V1 U ph W1 L2 L1 L3 L2 U ph I ph Un L3 Un Figura 3 A Collegamento a triangolo Il collegamento a triangolo si ottiene collegando la fine di una fase al principio della fase successiva. La corrente di fase Iph e la tensione di fase In U2 V2 W2 I ph Uph sono: 3 Iph = In / ED Uph = Un U1 L1 Figura 3 B V1 W1 L3 L2 Un I Avviamento stella-triangolo Motori a due velocità L'avviamento stella-triangolo è il modo più facile per ridurre la corrente e la coppia di avviamento. I motori la cui tensione nominale con motore collegato a triangolo corrisponde alla tensione di rete possono avviarsi con il metodo stella-triangolo. I motori standard a due velocità sono progettati per una sola tensione, avviamento diretto. Quando il rapporto tra le due velocità è di 1 a 2 i motori standard hanno un unico avvolgimento (collegamento Dahlander). Per le altre velocità i motori hanno due differenti avvolgimenti. 82 I ph U ph L1 L2 U ph Un L3 3.1 Collegamenti stella e triangolo per motori ad una velocità: U1 U1 U2 W2 U1 W1 V1 V2 W2 U2 V2 W1 U1 V1 W1 W1 V1 Collegamento-Y L1 L2 V1 L2 L1 Collegamento-∆ L3 L3 Numero di poli: 2, 4, 6, 8 ...... Velocità di sincronismo a 50 Hz: 3000, 1500, 1000, 750 ..... Collegamento per motori a due velocità, due avvolgimenti separati: L1 W2 V2 L2 L3 U1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W1 U2 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 V1 Velocità bassa Velocità alta L2 L1 L3 Numero di poli: 2/6, 2/8, 4/6, 6/8 Velocità di sincronismo a 50 Hz: 3000/1000, 3000/750, 1500/1000, 1000/750. Collegamento Dahlander per motori a due velocità, coppia costante: L1 W2 L2 L3 U1 U1 W2 U2 U1 V1 V2 V2 W1 W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 W2 W1 I V1 V2 Velocità alta W1 U2 V1 U2 L2 L1 Velocità bassa L3 Numero di poli: 2/4, 4/8 Velocità di sincronismo a 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. Collegamento Dahlander per motori a due velocità, coppia quadratica: L1 W2 U1 L2 L3 W2 U2 U1 V1 U1 V2 W2 W1 V1 V2 V2 U2 Velocità alta Numero di poli: 2/4, 4/8 Velocità di sincronismo a 50 Hz: 3000/1500,1500/750. W2 U2 V2 U1 V1 W1 U2 W1 V1 W1 Velocità bassa L1 L2 L3 Figura 3 C - Schemi di collegamento dei motori trifase. 83 3.2 3.2 Motori monofase Motori monofase cavo rosso cavo marrone U1 cavo nero cavo rosso U1 W1 V1 cavo marrone W1 V1 L2 L1 cavo nero L2 L1 condensatore condensatore 220V / 240V 220V / 240V Figura 3 D - Schemi di collegamento dei motori monofase F56 cavo verde cavo verde W2 U1 U2 V1 L1 V2 W2 W1 U1 W1 L2 220V / 240V cavo verde cavo verde W2 U2 V2 W2 U1 V1 W1 U1 L2 L1 110V / 120V Figura 3 E - Schemi di collegamento dei motori monofase F63-80 84 V2 V1 L1 L2 110V / 120V I U2 U2 V2 V1 L1 W1 L2 220V / 240V 3.3 Motori autofrenanti - Gruppi IIB e IIC (BTVF e CTVF) 3.3.1 Alimentazione del freno 3.3.2 Limiti funzionali del freno 3.3.3 Regolazioni 3.3.1 Alimentazione del freno Le figure mostrano i diversi schemi di alimentazione del freno con o senza l'opzione “tempo di risposta ridotto”. L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 CONTATTORE CONTATTORE MASSA SCATOLA MORSETTIERA FRENO MASSA SCATOLA MORSETTIERA W1 V2 V1 PIASTRA PORTA MORSETTI U2 Vdc FRENO U1 W1 W2 V2 V1 PIASTRA PORTA MORSETTI U2 W2 Vdc Vac Vac RADDRIZZATORE U1 RADDRIZZATORE Figura 3 F - Tempo di risposta standard Alimentazione del freno in parallelo all’alimentazione del motore Figura 3 G - Tempo di risposta ridotto Alimentazione del freno in parallelo all’alimentazione del motore L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Alimentazione raddrizzatore: Alimentazione raddrizzatore: Vac Vac I CONTATTORE CONTATTORE MASSA SCATOLA MORSETTIERA FRENO W1 V2 V1 PIASTRA PORTA MORSETTI U2 Vdc RADDRIZZATORE Figura 3 H - Tempo di risposta standard Alimentazione del freno indipendente U1 W2 SCATOLA MORSETTIERA FRENO W1 V2 V1 PIASTRA PORTA MORSETTI U2 W2 Vdc Vac Vac U1 RADDRIZZATORE Figura 3 I - Tempo di risposta ridotto Alimentazione del freno indipendente 85 3.3 3.3.1 Alimentazione del freno 3.3.2 Limiti funzionali del freno 3.3.3 Regolazioni 3.3.1 Alimentazione del freno Il freno funziona con una tensione continua fornita da un raddrizzatore installato all’interno della scatola morsettiera. Per l'alimentazione del raddrizzatore sono disponibili due possibilità: Alimentazione in parallelo sulle fasi di alimentazione motore É il modo più semplice oltre che il più comune di utilizzare un freno. In questa configurazione non è possibile realizzare motori a due velocità o utilizzare il motore con variatore di frequenza. I tempi di risposta tipici per l'inizio del bloccaggio sono: F63-71 : 32 ms ; F80 :140 ms Opzione: tempo di risposta ridotto. I tempi di risposta tipici per l'inizio del bloccaggio sono: F63-71 : 10 ms ; F80 : 35 ms. 3.3.2 Limiti funzionali del freno L’energia dissipata nel corso di frenate successive non deve produrre un innalzamento eccessivo della temperatura o ridurre la vita media prevista per il freno. Quando si sceglie il motore, è quindi fondamentale indicare il numero di frenate per ora, l'inerzia all’albero e la velocità. I 3.3.3 Regolazioni Il motore viene fornito con coppia frenante indicata nelle tabelle di cui al capitolo 4.5 (Dati nominali). Tuttavia è disponibile una procedura per la regolazione della coppia frenante o la sostituzione della guarnizione frenante nel caso in cui tali operazioni risultassero necessarie. 86 Alimentazione indipendente L'utente deve prevedere un'alimentazione supplementare in corrente alternata (230 o 400V ± 10%). Tale allacciamento permette, tra l'altro, di utilizzare il motore con un variatore di frequenza ma necessita di un pressacavo supplementare. Opzione: tempo di risposta ridotto. GB F D 4. Performance data 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 E Three-phase, 1-speed, ventilated motors Three-phase, 1-speed, unventilated motors Three-phase motors, 2 speeds, for general purpose (constant torque) Three-phase motors, 2 speeds, for centrifugal machines (quadratic torque) Three-phase, 1-speed, self-braking motors Motors driven by inverter Single-phase motors, 1 speed I 4. Données nominales 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Moteurs triphasés, 1 vitesse, ventilés Moteurs triphasés, 1 vitesse, non ventilés Moteurs triphasés, 2 vitesses, pour usage général (couple constant) Moteurs triphasés, 2 vitesses, pour machines centrifuges (couple quadratique) Moteurs-freins triphasés, 1 vitesse Moteurs avec alimentation par inverseur Moteurs monophasés, 1 vitesse 4. Betriebsdaten 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl, belüftet Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl, unbelüftet Drehstrommotoren, 2 Drehzahlen, für allgemeinen Gebrauch (konstantes Gegenmoment) Drehstrommotoren, 2 Drehzahlen, für Zentrifugalmaschinen (quadratisches Gegenmoment) selbstbremsende Drehstrommotoren, 1 Drehzahl Motoren für die Versorgung durch elektronische Frequenzumrichter Einphasenmotoren, 1 Drehzahl 4. Datos nominales 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Motores trifásicos, 1 velocidad, ventilados Motores trifásicos, 1 velocidad, no ventilados Motores trifásicos, 2 velocidades, para uso general (par constante) Motores trifásicos, 2 velocidades, para máquinas centrifugas (par cuadrático) Motores con freno trifásicos, 1 velocidad Motores con alimentación por medio de inverter Motores monofásicos, 1 velocidad 4. Dati nominali 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Motori trifase, 1 velocità, ventilati Motori trifase, 1 velocità, non ventilati Motori trifase, 2 velocità, per uso generale (coppia costante) Motori trifase, 2 velocità, per macchine centrifughe (coppia quadratica) Motori autofrenanti trifase, 1 velocità Motori con alimentazione a mezzo inverter Motori monofase, 1 velocità 87 GB Three-phase ventilated motors Speed Rated data at F Moteurs triphasés ventilés Vitesse D Drehstrommotoren belüftet Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Velocidad Datos nominales E I 4. Motores trifásicos ventilados 1 4.1 Motori trifase ventilati Velocità Dati nominali a démarrage direct 400 V 50 Hz Direkteinschaltung arranque directo avviamento diretto rpm GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Certificato LCIE Classe T Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] IIB - IIC EEx-d EEx-de IIC EEx-d EEx-de Velocità Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] cos ϕ F F F F F F F F F F 63 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV A2 A2 A2 B2 C2 A2▲ A2▲ A2 B2 C2▲ F F F F F F F F F F 63 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV A2 A2 A2 B2 C2 A2▲ A2▲ A2 B2 C2▲ 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 1.50 2850 2780 2840 2820 2790 2945 2920 2925 2885 2905 0.40 0.56 0.70 0.95 1.35 0.95 1.20 1.80 2.30 3.40 54 53 63 65 67 74 80 79 81 80 0.89 0.88 0.89 0.90 0.90 0.79 0.85 0.77 0.86 0.82 0.40 0.61 0.84 1.24 1.88 1.20 1.80 2.40 3.60 4.90 5.3 4.0 5.7 5.0 4.7 10.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 7.9 2.6 2.2 3.0 2.3 2.1 5.0 4.0 4.0 2.8 3.6 2.8 2.4 3.3 2.4 2.3 5.4 4.3 4.4 3.0 3.8 62 62 62 64 64 66 66 66 66 66 0.0007 0.0011 0.0011 0.0011 0.0012 0.0013 0.0013 0.0013 0.0013 0.0018 7.5 7.5 7.5 9.5 10.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 17.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 5 F F F F F F F F 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV A4 A4 B4 B4 A4▲ A4 B4 C4▲ F F F F F F F F 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV A4 A4 B4 B4 A4▲ A4 B4 C4▲ 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 1435 1405 1425 1430 1450 1445 1415 1430 0.55 0.65 0.75 1.15 1.30 1.45 1.85 2.70 54 60 65 66 64 78 80 77 0.58 0.73 0.77 0.70 0.67 0.70 0.82 0.76 0.80 1.20 1.60 2.40 2.40 3.60 5.00 7.30 4.5 3.9 4.6 4.8 6.3 5.7 4.7 4.9 4.7 3.0 2.8 2.6 4.4 3.3 2.2 2.6 4.9 3.2 3.0 2.8 4.6 3.6 2.4 2.8 55 55 56 56 56 56 56 56 0.0007 0.0007 0.0011 0.0011 0.0023 0.0023 0.0023 0.0029 7.5 7.5 9.0 9.0 12.0 12.0 12.0 14.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 F F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV A6 B6 B6 A6▲ A6 B6 C6▲ F F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV A6 B6 B6 A6▲ A6 B6 C6▲ 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.75 930 925 890 950 930 920 880 0.55 0.90 0.90 0.90 1.10 1.75 2.15 50 49 53 60 65 68 64 0.61 0.60 0.77 0.62 0.74 0.70 0.78 1.20 1.90 2.70 2.50 3.80 5.60 8.10 2.7 2.3 2.5 4.0 3.0 3.8 2.9 1.6 1.5 1.4 2.4 1.6 2.2 1.5 1.7 1.6 1.5 2.6 1.8 2.4 1.7 52 52 52 54 54 54 54 0.0011 0.0012 0.0014 0.0023 0.0023 0.0029 0.0029 7.5 9.5 10.0 12.0 12.0 14.0 14.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 6 6 6 6 6 6 5 F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV B8 C8 C8▲ A8 B8 C8▲ F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV B8 C8 C8▲ A8 B8 C8▲ 0.075 0.12 0.18 0.18 0.25 0.37 660 675 660 705 690 705 0.35 0.60 1.05 0.95 1.05 1.40 47 45 50 54 57 64 0.57 0.63 0.50 0.50 0.60 0.59 1.10 1.70 2.60 2.40 3.40 5.00 2.0 2.5 2.2 3.0 2.6 3.0 1.3 2.2 1.8 2.4 1.7 2.2 1.3 2.3 1.9 2.5 1.8 2.3 44 46 46 48 48 48 0.0008 0.0014 0.0014 0.0023 0.0023 0.0029 9.0 10.0 10.0 12.0 12.0 14.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 6 6 6 6 6 6 non-standard power puissance non normalisée nicht genormte Leistung potencia no normalizada potenza non normalizzata 88 Données nominales à 3000 1500 1000 750 Motor type IIB EEx-d EEx-de ▲ direct on line start ❊ I'n = In · 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); 2 ▼ J = PD 4 (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 89 GB F D 4. E Three-phase unventilated motors Speed Moteurs triphasés non ventilés Vitesse Drehstrommotoren unbelüftet Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Motores trifásicos no ventilados Velocidad Datos nominales 4.2 Motori trifase non ventilati I 90 1 direct on line start Velocità 3000 1500 1000 750 démarrage direct 400 V 50 Hz Dati nominali a Direkteinschaltung arranque directo avviamento diretto rpm GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Motor type Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Certificato LCIE Classe T IIB EEx-d ▲ Rated data at Données nominales à Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] cos ϕ Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] IIB - IIC EEx-d 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.37 0.55 2825 2760 2850 2780 2840 2880 2945 2920 0.27 0.31 0.40 0.56 0.70 0.95 0.95 1.20 53 60 54 53 63 71 71 78 0.69 0.76 0.89 0.88 0.89 0.80 0.79 0.85 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.60 0.84 1.20 1.20 1.80 4.0 3.5 5.3 4.0 5.7 6.0 8.0 8.0 5.0 4.0 2.6 2.2 3.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 5.2 4.2 2.8 2.4 3.2 4.2 4.2 4.2 51 51 55 55 55 58 60 60 0.00012 0.00012 0.00060 0.00060 0.00070 0.00070 0.0012 0.0012 4.5 4.5 6.5 6.5 7.5 8.0 12.0 12.0 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37◆ 0.37 0.55 0.75 1420 1370 1450 1430 1425 1390 1450 1445 1410 0.37 0.40 0.50 0.58 0.75 1.00 1.30 1.50 1.90 50 57 60 65 65 68 61 74 75 0.50 0.62 0.64 0.73 0.77 0.78 0.67 0.72 0.78 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.20 1.60 2.50 2.40 3.60 5.00 3.5 3.0 5.7 5.0 5.0 4.5 6.6 5.5 5.0 4.0 3.5 5.4 3.5 2.8 2.3 4.0 2.8 3.4 4.2 3.7 5.6 3.7 2.9 2.5 4.2 3.0 3.5 51 51 55 55 55 58 60 60 60 0.0002 0.0002 0.0006 0.0006 0.0007 0.0008 0.0021 0.0021 0.0027 4.5 4.5 6.5 6.5 7.5 8.0 11.0 11.0 14.0 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 F 80 CST A6▲ F 80 CST B6 F 80 CST C6 0.06 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 890 930 925 950 930 920 0.35 0.55 0.90 0.90 1.10 1.75 43 55 48 65 65 66 0.72 0.63 0.60 0.62 0.74 0.70 0.60 1.20 1.80 2.50 3.80 5.60 2.6 2.7 2.7 3.6 3.0 3.3 2.9 1.6 2.5 2.4 1.6 2.2 2.9 1.7 2.6 2.6 1.7 2.4 51 55 55 60 60 60 --0.0007 0.0009 0.0021 0.0021 0.0027 --7.5 8.0 11.0 11.0 12.0 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 F 80 CST B8 F 80 CST B8 F 80 CST C8▲ 0.075 0.012 0.18 0.25 0.37 650 675 705 690 705 0.40 0.60 0.95 1.05 1.40 45 46 55 57 66 0.60 0.63 0.50 0.60 0.59 1.10 1.70 2.40 3.50 5.00 2.0 2.0 3.0 2.6 3.0 1.3 1.6 2.5 1.7 1.8 1.4 1.7 2.7 1.9 1.9 51 55 60 60 60 0.0007 0.0011 0.0021 0.0021 0.0027 6.5 7.5 11.0 11.0 12.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 IIC EEx-d F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 63 71 80 80 BST BST BST BST BST BST BST BST A2 A2 A2 A2 B2 C2 A2▲ A2▲ F 56 CST A2 F 56 CST A2 F F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 BST BST BST BST BST BST BST BST BST A4 A4 A4 A4 B4 C4 A4▲ B4 C4 F 56 CST A4 F 56 CST A4 F F F F F F 56 63 71 80 80 80 BST BST BST BST BST BST A6 B6 B6 A6▲ B6 C6 F 56 CST A6 F F F F F 63 71 80 80 80 BST BST BST BST BST B8 C8 B8 B8 C8▲ non-standard power puissance non normalisée nicht genormte Leistung potencia no normalizada potenza non normalizzata F 80 CST A2▲ F 80 CST A2▲ F 80 CST A4▲ F 80 CST B4 F 80 CST C4 ◆ Velocità S1 service only in ambient air flow at 40° C Service S1 uniquement dans un flux d'air ambiant à 40°C Service S1 nur bei Raumluftstrom von 40° C Servicio S1 únicamente en flujo de aire ambiente a 40° C Servizio S1 unicamente in flusso d'aria ambiente a 40° C Short Court Kurz Corto Corto Long Long Lang Largo Lungo ❊ I'n = In · 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); 2 ▼ J = PD 4 (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 91 GB Three-phase motors Speed Rated data at F Moteurs triphasés Vitesse D Drehstrom Motoren Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Velocidad Datos nominales E I 4. Motores trifásicos 2 4.3 Motori trifase direct on line start Données nominales à Velocità Dati nominali a 400 V 50 Hz démarrage direct pour usage général (couple constant) Direkteinschaltung für allgemeinen Gebrauch (konstantes Gegenmoment) arranque directo para uso general (par constante) avviamento diretto per uso generale (coppia costante) 3000/1500 1500/1000 1500/750 rpm GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Motor type Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Certificato LCIE Classe T IIB EEx-d EEx-de IIC EEx-d EEx-de F 63 BTV C2-4 F 63 CTV C2-4 F 80 BTV B2-4 F 80 CTV B2-4 F 80 BTV C2-4 F 80 CTV C2-4 F 71 BTV C4-6 F 71 CTV C4-6 F 80 BTV B4-6 F 80 CTV B4-6 F 80 BTV B4-6 F 80 CTV B4-6 F 80 BTV C4-6 F 80 CTV C4-6 F 71 BTV C4-8 F 71 CTV C4-8 F 80 BTV B4-8 F 80 CTV B4-8 F 80 BTV C4-8 F 80 CTV C4-8 Frame size 56: contact us for further information Hauteur d’axe 56 : nous consulter Achsenhöhe 56: Kontaktieren Sie uns. Velocità Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] cos ϕ Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] IIB - IIC EEx-d EEx-de 0.25 0.18 0.55 0.37 0.75 0.55 2720 1440 2905 1465 2815 1440 0.80 1.05 1.80 1.25 2.80 1.80 56 47 64 66 58 64 0.90 0.58 0.70 0.65 0.70 0.72 0.88 1.19 1.81 2.41 2.55 3.65 3.3 3.4 5.0 5.6 3.7 5.2 2.5 3.0 2.9 3.5 3.9 3.6 2.7 3.2 3.1 3.7 4.1 3.8 64 56 66 56 66 56 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.18 0.12 0.37 0.25 0.55 0.30 0.75 0.37 1440 685 1460 940 1450 950 1410 940 0.65 0.80 1.20 0.95 1.70 1.00 2.00 1.15 55 39 76 54 73 60 71 65 0.76 0.57 0.72 0.78 0.71 0.70 0.85 0.73 1.19 1.67 2.42 2.54 3.62 3.02 5.08 3.76 4.5 2.1 5.0 2.3 5.0 3.0 4.5 3.1 3.0 2.2 2.7 1.0 2.6 2.1 2.0 1.3 3.3 2.3 2.8 1.2 2.7 2.2 2.2 1.4 56 52 56 54 56 54 56 54 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.18 0.12 0.55 0.25 0.75 0.37 1430 675 1405 710 1380 710 0.65 0.80 1.45 1.45 1.80 2.10 53 37 62 46 71 55 0.78 0.63 0.87 0.54 0.87 0.50 1.20 1.70 3.74 3.36 5.19 4.98 4.0 2.0 5.0 2.2 4.4 2.8 2.3 2.1 2.0 1.8 2.2 2.5 2.5 2.2 2.1 1.9 2.4 2.7 56 46 56 48 56 48 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 ❊ I'n = In · 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); Altura de eje 56 estamos a su disposición (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); Altezza d'asse 56: su richiesta (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 92 for general purpose (constant torque) 2 ▼ J = PD 4 93 GB Three-phase motors Speed Rated data at F Moteurs triphasés Vitesse D Drehstrom Motoren Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Velocidad Datos nominales E 4. I 4.4 Motores trifásicos 2 Motori trifase Données nominales à Velocità Dati nominali a 400 V 50 Hz direct on line start for centrifugal machines (quadratic torque) démarrage direct pour machines centrifuges (couple quadratique) Direkteinschaltung für Zentrifugalmaschinen (quadratisches Gegenmoment) arranque directo para máquinas centrífugas (par cuadrático) avviamento diretto per macchine centrifughe (coppia quadratica) rpm GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Motor type Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Certificato LCIE Classe T Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] IIB - IIC EEx-d EEx-de IIB EEx-d EEx-de IIC EEx-d EEx-de F 63 BTV B2-4 F 63 CTV B2-4 F 71 BTV C2-4 F 71 CTV C2-4 F 80 BTV B2-4 F 80 CTV B2-4 F 80 BTV B2-4 F 80 CTV B2-4 F 80 BTV C2-4 F 80 CTV C2-4 F 63 BTV B4-8 F 63 CTV B4-8 F 71 BTV C4-8 F 71 CTV C4-8 F 80 BTV C4-8 F 80 CTV C4-8 F 80 BTV B4-8 F 80 CTV B4-8 F 80 BTV B4-8 F 80 CTV B4-8 F 80 BTV C4-8 F 80 CTV C4-8 F 63 BTV B4-6 F 63 CTV B4-6 F 71 BTV C4-6 F 71 CTV C4-6 F 80 BTV A4-6 F 80 CTV A4-6 F 80 BTV B4-6 F 80 CTV B4-6 F 80 BTV C4-6 F 80 CTV C4-6 F 71 BTV C6-12 F 71 CTV C6-12 F 80 BTV B6-12 F 80 CTV B6-12 F 80 BTV C6-12 F 80 CTV C6-12 Frame size 56: contact us for further information Hauteur d’axe 56: nous consulter Achsenhöhe 56: Kontaktieren Sie uns. Velocità Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] 0.25 0.06 0.37 0.09 0.55 0.13 0.75 0.18 1.10 0.28 2810 1435 2835 1440 2905 1445 2840 1420 2760 1420 0.90 0.40 1.05 0.50 1.80 0.45 2.10 0.55 4.10 0.75 56 38 62 39 66 57 67 62 63 67 0.76 0.66 0.85 0.69 0.70 0.76 0.78 0.83 0.65 0.81 0.85 0.45 1.25 0.60 1.80 0.85 2.50 1.20 3.80 1.90 4.60 3.70 5.70 3.70 4.40 5.00 4.60 4.60 4.00 4.00 4.60 2.40 3.60 2.00 2.00 3.00 2.20 2.20 2.00 2.10 4.80 2.50 3.80 2.20 2.30 3.10 2.40 2.30 2.30 2.20 62 55 64 56 66 56 66 56 66 56 0.0011 9.0 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0012 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.18 0.03 0.25 0.06 0.37 0.09 0.55 0.13 0.75 0.18 1.10 0.28 1440 695 1430 670 1430 675 1440 700 1430 670 1425 690 0.70 0.30 1.05 0.45 1.30 0.50 1.40 0.65 2.10 1.20 3.10 1.20 51 32 56 34 69 45 71 50 73 50 71 52 0.75 0.78 0.63 0.57 0.70 0.59 0.79 0.60 0.77 0.62 0.72 0.64 1.20 0.40 1.70 0.85 2.50 1.27 3.60 1.77 5.00 2.50 7.30 3.80 4.77 2.30 3.90 2.60 6.00 2.80 5.20 2.60 4.80 2.50 5.00 4.60 3.60 2.40 2.80 2.00 3.00 2.40 2.20 1.90 2.00 2.40 2.40 2.20 3.80 2.50 3.00 2.20 3.20 2.50 2.40 2.00 2.20 2.50 2.60 2.30 55 44 56 46 56 48 56 48 56 48 56 48 0.0011 9.0 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0012 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0023 12.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.18 0.06 0.25 0.08 0.37 0.12 0.55 0.18 0.75 0.25 1450 970 1420 955 1460 975 1450 965 1450 960 0.70 0.55 0.85 0.55 1.20 0.75 1.70 0.90 2.00 0.95 54 30 58 38 64 41 73 58 73 64 0.84 0.55 0.81 0.62 0.72 0.59 0.71 0.63 0.74 0.60 1.19 0.59 1.68 0.80 2.42 1.18 3.62 1.78 4.94 2.49 3.50 2.50 3.00 2.40 5.20 3.00 5.50 3.60 5.00 3.40 1.60 2.80 1.20 2.50 1.60 3.00 2.50 2.30 2.40 2.20 1.80 2.90 1.40 2.60 1.80 3.20 2.70 2.50 2.50 2.20 55 52 56 52 56 54 56 54 56 54 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 16.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 16.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.12 0.03 0.37 0.06 0.65 0.10 950 430 960 470 900 450 0.80 0.35 1.60 0.65 1.95 1.00 44 24 59 30 63 30 0.49 0.53 0.58 0.45 0.80 0.55 1.21 0.67 3.68 1.22 6.90 2.12 3.00 1.50 3.20 2.70 2.80 1.40 3.50 2.20 2.20 1.70 1.50 1.40 3.60 2.25 2.30 1.80 1.60 1.50 55 52 56 54 56 54 0.0011 9.5 00 ATEX 6036 4 0.0023 14.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 0.0029 16.0 00 ATEX 6037 4 ❊ I'n = In · cos ϕ 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); Altura de eje 56 estamos a su disposición (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); Altezza d'asse 56: su richiesta (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 94 3000/1500 1500/750 1500/1000 1000/500 2 ▼ J = PD 4 95 GB Self-braking motors Speed Rated data at F Moteurs freins Vitesse Données nominales à D Selbstbremsende Motoren Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Velocidad Datos nominales E I 4. Motores con freno 1 4.5 Motori autofrenanti Dati nominali a 3000 1500 1000 750 démarrage direct 400 V 50 Hz Direkteinschaltung arranque directo avviamento diretto rpm GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Motor type Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass Braking torque LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse Couple de freinage LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse Bremsmoment LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Coppia frenante Certificato LCIE Classe T Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] IIB EEx-d EEx-de♦ IIC EEx-d EEx-de♦ Velocità Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] cos ϕ Par de frenado J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] Nm IIB - IIC EEx-d EEx-de♦ F F F F F F F F 63 63 63 71 80 80 80 80 BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF A2 A2 A2 B2 A2 A2 A2 B2 F F F F F F F F 63 63 63 71 80 80 80 80 CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF A2 A2 A2 B2 A2 A2 A2 B2 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 2850 2780 2840 2820 2945 2920 2925 2885 0.40 0.56 0.70 0.95 0.95 1.20 1.80 2.30 54 53 63 65 74 80 79 81 0.89 0.88 0.89 0.90 0.79 0.85 0.77 0.86 0.40 0.61 0.84 1.24 1.20 1.80 2.40 3.60 5.3 4.0 5.7 5.0 10.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 2.6 2.2 3.0 2.3 5.0 4.0 4.0 2.8 2.8 2.4 3.3 2.4 5.4 4.3 4.4 3.0 62 62 62 64 66 66 66 66 0.0008 0.0008 0.0008 0.0012 0.0015 0.0015 0.0017 0.0017 9,5 9.5 9.5 11.5 12.0 18.5 18.5 18.5 4 4 4 4 16 16 16 16 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 F F F F F F F F 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF A4 A4 B4 B4 A4 A4 B4 C4 F F F F F F F F 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 80 CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF A4 A4 B4 B4 A4 A4 B4 C4 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 1435 1405 1425 1430 1450 1445 1415 1430 0.55 0.65 0.75 1.15 1.30 1.45 1.85 2.70 54 60 65 66 64 78 80 77 0.58 0.73 0.77 0.70 0.67 0.70 0.82 0.76 0.80 1.20 1.60 2.40 2.40 3.60 5.00 7.30 4.5 3.9 4.6 4.8 6.3 5.7 4.7 4.9 4.7 3.0 2.8 2.6 4.4 3.3 2.2 2.6 4.9 3.2 3.0 2.8 4.6 3.6 2.4 2.8 55 55 56 56 56 56 56 56 0.0008 0.0008 0.0012 0.0012 0.0025 0.0025 0.0025 0.0031 9.5 9.5 11.0 11.0 16.0 16.0 16.0 18.0 4 4 4 4 16 16 16 16 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF B6 C6 C6 A6 A6 C6 F F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 80 CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF B6 C6 C6 A6 A6 C6 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.25 0.37 0.55 930 925 890 950 930 920 0.55 0.90 0.90 0.90 1.10 1.75 50 49 53 60 65 68 0.61 0.60 0.77 0.62 0.74 0.70 1.20 1.90 2.70 2.50 3.80 5.60 2.7 2.3 2.5 4.0 3.0 3.8 1.6 1.5 1.4 2.4 1.6 2.2 1.7 1.6 1.5 2.6 1;8 2.4 52 52 52 54 54 54 0.0012 0.0013 0.0013 0.0025 0.0025 0.0025 11.0 11.5 11.5 16.0 16.0 18.0 4 4 4 16 16 16 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF BTVF B8 C8 C8 B8 C8 F F F F F 63 71 71 80 80 CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF CTVF B8 C8 C8 B8 C8 0.075 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 660 675 660 690 705 0.35 0.60 1.05 1.05 1.40 47 45 50 57 64 0.57 0.63 0.50 0.60 0.59 1.10 1.70 2.60 3.40 5.00 2.0 2.5 2.2 2.6 3.0 1.3 2.2 1.8 1.7 2.2 1.3 2.3 1.9 1.8 2.3 44 46 46 48 48 0.0012 0.0013 0.0013 0.0025 0.0030 9.0 10.0 10.0 16.0 18.0 4 4 4 16 18 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 ♦ Contact us for further information Nous consulter Kontaktieren Sie uns. 96 Velocità direct on line start ❊ I'n = In · 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); Estamos a su disposición (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); Su richiesta (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 2 ▼ J = PD 4 97 GB Motors driven by inverter Self-ventilated motor (IC 411) Pole GB Pôles F Pole D Polos E Poli I F Moteurs alimentés par inverseur Moteur autoventilé (IC 411) D Umrichter- Motoren Eigenbelüfteter Motor (IC 411) Motores para inverter Motor autoventilado (IC 411) Motori per inverter Motore autoventilato (IC 411) E 4. I 4.6 400 V, 50 Hz [Hz] 5 ÷ 50 range 1 ÷ 10 2 4 [Hz] 10 ÷ 50 range 1 ÷ 5 [Hz] 5 ÷ 50 ÷ 87 range 1 ÷ 10 ÷ 17 Mains connection Quadratic torque Constant torque Constant torque Constant torque Constant torque LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Alimentation de secteur Couple quadratique Couple constant Couple constant Couple constant Couple constant LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Netzeinspeisung Quadratisches Gegenmoment Konstantes Gegenmoment Konstantes Gegenmoment Konstantes Gegenmoment Konstantes Gegenmoment LCIE Konformitäts Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Alimentación desde la red Par cuadrático Par constante Par constante Par constante Par constante Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Alimentazione da rete Coppia quadratica Coppia costante Coppia costante Coppia costante Coppia costante Certificati LCIE Classe T IIC EEx-d EEx-de Pn kW] In [A] Pn [kW] Mn [Nm] Pn [kW] Mn [Nm] Pn [kW] Mn [Nm] 3000 [1/min] 63 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV A2 A2 A2 B2 C2 A2 A2 B2 F F F F F F F F 63 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV A2 A2 A2 B2 C2 A2 A2 b2 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.55 0.75 1.10 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.30 1.90 1.80 2.40 3.60 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.55 0.75 1.10 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.30 1.90 1.80 2.40 3.60 98 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV BTV A4 A4 B4 B4 A4 B4 C4 F F F F F F F 63 63 71 71 80 80 80 CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV CTV A4 A4 B4 B4 A4 B4 C4 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 0.80 1.20 1.60 2.40 3.60 5.00 7.30 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.10 0.80 1.20 1.60 2.40 3.60 5.00 7.30 Pn [kW] Mn [Nm] Pn [kW] Mn [Nm] IIB- IIC EEx-d EEx-de 0.13 0.26 0.27 0.28 0.43 0.50 0.65 0.70 0.22 0.43 0.44 0.46 0.75 0.85 1.10 1.15 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0.18 0.20 0.35 0.37 0.60 0.75 1.75 0.60 0.66 1.10 1.20 2.00 2.50 5.80 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 3000 [1/min] 0.11 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.52 0.55 0.70 1.00 0.36 0.60 0.80 1.30 1.80 1.80 1.67 3.40 0.08 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.92 0.28 0.60 0.80 1.30 1.70 1.80 1.45 3.00 1500 [1/min] F F F F F F F [Hz] 100 range 20 Motor type IIB EEx-d EEx-de F F F F F F F F [Hz] 87 range 17 0.15 0.28 0.29 0.31 0.50 0.55 0.80 1.05 0.28 0.54 0.56 0.60 1.00 1.10 1.45 2.00 1500 [1/min] 0.12 0.18 0.22 0.33 0.50 0.70 0.70 0.80 1.20 1.50 2.15 3.24 4.75 4.60 0.12 0.16 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.45 0.43 0.80 1.10 1.30 1.50 1.62 3.00 2.90 0.20 0.23 0.35 0.43 0.63 0.81 1.61 0.75 0.87 1.30 1.60 2.37 3.10 6.20 99 GB Single speed motors Speed Rated data at F Moteurs monophasés Vitesse D Einphasenmotoren Drehzahl Betriebsdaten bei Velocidad Datos nominales 4. E Motores monofásico 1 4.7 Motori monofase I Données nominales à Velocità Dati nominali a démarrage direct 230 V 50 Hz arranque directo avviamento diretto GB tours/min F U/min D rev/min E giri/min I Rated output Speed Current Efficiency Power factor Torque Starting current Starting torque Maximum torque Sound pressure Moment of inertia Mass LCIE Certificates Class T Moteur type Puissance Vitesse Intensité Rendement Facteur de puissance Couple Intensité démarrage Couple démarrage Couple maximal Pression sonore Moment d'inertie Masse LCIE Certificat Classe T Motor Typ Leistung Drehzahl Strom Wirkungsgrad Leistungsfaktor Moment Anlaufstrom Anlaufmoment Kippmoment Gerauschwerte Trägheitsmoment Masse LCIE Konformitäts-Bescheinigung Klasse T Tipo de motor Potencia Velocidad proporcionada Corriente Rendimiento Factor de potencia Par Corriente de Par de arranque arranque Par máximo Presión acústica Momento de inercia Peso Certificados LCIE Clase T Tipo motore Potenza resa Corrente Rendimento Fattore potenza Coppia Corrente avviamento Coppia avviamento Coppia massima Pressione sonora Momento d'inerzia Massa Certificato LCIE Classe T IIC EEx-d Velocità Pn [kW] n [1/min] In❊ [A] η [%] cos ϕ Mn [Nm] Ia/In Ma/Mn Mm/Mn Lp [dB(A)] J▼ [kgm2] m [kg] IIB - IIC EEx-d F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 63 71 80 80 BM BM BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV A2◆ B2◆ A2 B2 B2 C2 B2 B2 F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 63 71 80 80 CM CM CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV A2◆ B2◆ A2 B2 B2 C2 B2 B2 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.75 2640 2840 2800 2865 2830 2780 2930 2910 0.80 0.90 1.60 2.35 2.60 3.50 6.20 6.80 45 50 40 49 54 56 62 68 0.80 0.86 0.82 0.70 0.77 0.81 0.62 0.72 0.20 0.27 0.41 0.60 0.84 1.27 1.79 2.46 2.80 3.00 4.10 4.60 4.30 4.30 5.50 5.00 1.00 1.10 3.60 3.50 3.20 2.50 4.50 3.30 1.10 1.15 3.80 3.70 3.30 2.70 5.00 3.80 52 52 62 62 62 64 66 66 0.0012 0.0013 0.0008 0.0010 0.0010 0.0013 0.0016 0.0016 4.5 5.0 8.0 8.0 9.5 10.0 16.0 16.0 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 6 6 6 4 6 4 F F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 71 80 80 80 80 BM BM BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV A4◆ B4◆ B4 C4 C4 A4 B4 B4 C4 F F F F F F F F F 56 56 63 63 71 80 80 80 80 CM CM CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV A4◆ B4◆ B4 C4 C4 A4 B4 B4 C4 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.75 1410 1390 1415 1430 1410 1460 1445 1430 1390 0.72 0.95 1.70 2.10 3.30 2.80 3.40 5.60 6.40 44 49 47 54 48 61 65 61 66 0.84 0.79 0.70 0.68 0.68 0.68 0.74 0.70 0.76 0.41 0.56 0.81 1.20 1.69 1.64 2.45 3.67 5.16 2.70 2.70 3.50 3.80 3.30 4.30 4.30 4.10 2.80 1.10 1.30 2.20 2.20 1.80 2.20 2.20 2.40 1.53 1.15 1.35 2.40 2.30 2.00 2.40 2.40 2.60 1.60 50 50 55 55 56 56 56 56 56 0.0012 0.0012 0.0012 0.0013 0.0013 0.0024 0.0024 0.0024 0.0030 4.5 5.0 8.5 10.0 10.0 14.0 14.0 14.0 14.5 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6035 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 4 4 6 6 4 6 6 6 4 F F F F F F 63 63 71 80 80 80 BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV BMV B6 C6 C6 A6 B6 C6 F F F F F F 63 63 71 80 80 80 CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV CMV B6 C6 C6 A6 B6 C6 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.18 0.25 0.37 950 925 935 965 950 945 1.20 1.45 1.60 2.20 2.50 4.50 39 41 44 47 51 62 0.93 0.93 0.99 0.81 0.85 0.60 1.01 1.24 1.53 1.78 2.51 3.74 3.00 2.50 3.50 3.00 2.60 2.90 0.70 0.65 0.65 0.66 0.60 2.10 0.70 0.65 0.80 0.70 0.60 2.20 52 54 54 56 56 56 0.0012 0.0013 0.0013 0.0024 0.0024 0.0030 8.5 10.0 10.0 14.0 14.0 16.0 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6036 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 00 ATEX 6037 6 6 4 6 6 4 Unventilated motors Short Long Long ❊ I'n = In · 400 (I'n = current at U' Volt); U' (I'n = intensité à U' Volt); (I'n = Strom mit U' Volt); Non ventilés Court unbelüftet Kurz Lang No ventilados Corto Largo (I'n = corriente de U' Voltios); Non ventilati Corto Lungo (I'n = corrente a U' Volt); 100 3000 1500 1000 Direkteinschaltung rpm Motor type IIB EEx-d ◆ direct on line start 2 ▼ J = PD 4 101 GB F D 5. Overall dimensions 5.1 5.2 5.3 E Ventilated motors Unventilated motors Self-braking motors I 5. Dimensions 5.1 5.2 5.3 Moteurs ventilés Moteurs non ventilés Moteurs freins 5. Abmessungen 5.1 5.2 5.3 Motoren belüftet Motoren unbelüftet Selbstbremsende Motoren 5. Dimensiones de espacio máximo 5.1 5.2 5.3 Motore ventilados Motores no ventilados Motores con freno 5. Dimensioni d'ingombro 5.1 5.2 5.3 Motori ventilati Motori non ventilati Motori autofrenanti 103 GB Ventilated motors F 63÷80 IM B3 IM B5 IM B35 Motoren belüftet Motore ventilados 5.1 Motori ventilati LM L LR LQ LP LRA r q HC HD AD RA C BC øTLP B EA CA HA E H øAC IM B3 AA A AB BB LM L LR LQ LP LRA T r øM E H q HD øTLB AD RA øAC øP IM B5 øN EA LA LM L LR LQ LRA T r HC q EA HA CA B AA A AB FA øDA TTS / v GF BB GC F øD 104 øTLP LA C BC TTP / u GD E øM øAC IM B35 HD øTLB AD RA H LP GA I 5. øP E Moteurs ventilés øN D Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 A AA AB ø AC B BB BC C CA E EA H HA HC L 100 100 112 112 125 125 30 30 36 36 35 35 126 126 138 138 155 155 132 132 132 132 162 162 80 80 90 90 100 100 100 100 110 110 124 124 10 10 10 10 12 12 40 55 45 60 50 70 141 141 126 126 126 126 23 23 30 30 40 40 63 63 71 71 80 80 5 5 6 6 8 8 135 135 143 143 165 165 284 299 291 306 316 336 LM 307 322 314 329 339 359 LP LRA øq r ø TLP 173 188 173 188 202 222 50 50 50 50 50 50 118 118 118 118 146 146 23 23 23 23 23 23 7 7 7 7 9 9 Terminal box - Boîte à bornes - Klemmkasten - Caja de bornes - Morsettiera EEx-d ➊ Type IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 63 63 71 71 80 80 152 152 152 152 166 166 164 164 164 164 174 174 215 215 223 223 246 246 227 227 235 235 254 254 120 120 120 120 120 120 135 135 135 135 135 135 140 140 140 140 140 140 143 143 143 143 143 143 175 175 175 175 186 186 174 174 174 174 184 184 Type IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 63 63 71 71 80 80 122 122 122 122 137 137 153 153 153 153 166 166 185 185 196 196 217 217 216 216 225 225 246 246 110 110 110 110 110 110 100 100 100 100 100 100 110 110 110 110 110 110 107 107 107 107 107 107 132 132 132 132 145 145 160 160 160 160 172 172 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP65 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP65 IIB/IIC IP55 237 237 245 245 267 267 255 255 263 263 285 285 145 145 145 145 145 145 120 120 120 120 120 120 175 175 175 175 175 175 182 182 182 182 193 193 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 EEx-d ➌ B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 EEx-de ➌ IIB/IIC IP55 Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 AD IIB/IIC IP65 174 174 174 174 187 187 HD 192 192 192 192 205 205 LQ IIB/IIC IP65 190 190 190 190 190 190 LR RA IIB/IIC IP65 210 210 210 210 233 233 Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 øD F ø DAmax FA 11 11 14 14 19 19 4 4 5 5 6 6 GA GC GD GF ø TTP ø TTS u v 12.5 12.5 16.0 16.0 21.5 21.5 4 4 5 5 6 6 M4 M4 M5 M5 M6 M6 10 10 12 12 15 15 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type LA øM øN øP T ø TLB 63 B5 B35 71 B5 B35 80 B5 B35 8 8 10 115 130 165 95 110 130 140 160 200 3.0 3.5 3.5 9 9 11 ➊ Single phase Monophasés Einphasen Monofásico Monofase ➌ Three phase Triphasés Drehstrom Trifásico Trifase LR: Without cable gland Sans presse étoupe Ohne Kabelpresse Sin prensacables Senza pressacavo 105 GB Ventilated motors F 63÷80 IM B14 IM B34 Motoren belüftet Motore ventilados 5.1 Motori ventilati LM LR L LQ LP LRA AD RA q E H øM øAC IM B14 HD øTTB RA AD r T EA LM L LR LQ LRA LP r HD E C EA CA HA TLP B A AB BC øDA TTS / v GF FA GC øD 106 TTP / u GD BB F AA H HC q øM øAC IM B34 øTTB T GA I 5. øP øN E Moteurs ventilés øP øN D Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 A AA AB ø AC B BB BC C CA E EA H HA HC L LM LP LRA øq r ø TLP 100 112 125 30 36 35 126 138 155 132 132 162 80 90 100 100 110 124 10 10 12 40 45 50 141 126 126 23 30 40 63 71 80 5 6 8 135 143 165 284 291 316 307 314 339 173 173 202 50 50 50 118 118 146 23 23 23 7 7 9 Terminal box - Boîte à bornes - Klemmkasten - Caja de bornes - Morsettiera EEx-d ➊ Type IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 152 152 166 164 164 174 215 223 246 227 235 254 120 120 120 135 135 135 140 140 140 143 143 143 175 175 186 174 174 184 Type IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 122 122 137 153 153 166 185 196 217 216 225 246 110 110 110 100 100 100 110 110 110 107 107 107 132 132 145 160 160 172 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP65 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP55 IIB/IIC IP65 IIB/IIC IP55 237 245 267 255 263 285 145 145 145 120 120 120 175 175 175 182 182 193 EEx-d ➌ EEx-de ➌ IIB/IIC IP55 Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 AD IIB/IIC IP65 174 174 187 HD 192 192 205 LQ IIB/IIC IP65 190 190 190 LR RA IIB/IIC IP65 210 210 233 Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 øD F ø DAmax FA 11 14 19 4 5 6 GA GC GD GF ø TTP ø TTS u v 12.5 16.0 21.5 4 5 6 M4 M5 M6 10 12 15 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type øM øN øP T ø TTB 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 75 85 100 60 70 80 90 105 120 2.5 2.5 3.0 M5 M6 M6 ➊ Single phase Monophasés Einphasen Monofásico Monofase ➌ Three phase Triphasés Drehstrom Trifásico Trifase LR: Without cable gland Sans presse étoupe Ohne Kabelpresse Sin prensacables Senza pressacavo 107 GB Unventilated motors F 56÷80 IM B3 IM B5 IM B35 Motoren unbelüftet Motores no ventilados 5.2 Motori non ventilati L LX øAC LW JA AN TTA/8 PADS BOSSAGES BESCHLÄGE BULLONES BORCHIE BN E LP E L LP JB AD AD øAC HC IM B3 H HA øTLP B C BC AA CA A AB BB L LP E AD IM B5 øP øTLB T AN øN øM ø AC H LA L E LP AD T AN øTLB IM B35 HC øM ø AC H LA øTLP B C BC F øD 108 TTP / u GD BB GA I 5. øP E øN D Moteurs non ventilés HA CA AA A AB Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 56 B3 56 B5 63 B3 63 B5 71 B3 71 B5 80 B3 80 B5 - 56 ▲ 56 B35 63 ▲ 63 B35 71 ▲ 71 B35 80 ▲ 80 B35 A AA AB ø AC AD AN BN B BB BC C CA E 90 90 100 100 112 112 125 125 ----30 30 36 36 35 35 110 110 126 126 138 138 155 155 108 108 132 132 132 132 162 162 85 85 74 74 74 74 112 112 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° --45° --45° --45° --- 71 71 80 80 90 90 100 100 95 95 100 100 110 110 124 124 12 12 10 10 10 10 12 12 36 36 40 55 45 60 50 70 46 46 105 105 90 90 108 108 20 20 23 23 30 30 40 40 JA JB LW LX ø TLP TTA 232 242 ------------- 155 165 200 215 200 215 214 234 175 185 ------------- 65 --94 --101 --118 --- 105 --132 --139 --162 --- 6 6 7 7 7 7 9 9 M5 --M6 --M6 --M6 --- Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 56 B3 56 B5 63 B3 63 B5 71 B3 71 B5 80 B3 80 B5 H - 56 ▲ 56 B35 63 ▲ 63 B35 71 ▲ 71 B35 80 ▲ 80 B35 HA 56 56 63 63 71 71 80 80 HC L 3 3 5 5 6 6 8 8 113 113 129 129 137 137 163 163 7 --15 --15 --15 --- 7 --21 --21 --21 --- 212 222 248 263 255 270 298 318 ø D F GA GD ø TTP u 9 9 11 11 14 14 19 19 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 10.2 10.2 12.5 12.5 16.0 16.0 21.5 21.5 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 M3 M3 M4 M4 M5 M5 M6 M6 9 9 10 10 12 12 15 15 ø TLB LP Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 56 B3 56 B5 63 B3 63 B5 71 B3 71 B5 80 B3 80 B5 - 56 ▲ 56 B35 63 ▲ 63 B35 71 ▲ 71 B35 80 ▲ 80 B35 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type LA øM øN øP T 56 B5 B35 63 B5 B35 71 B5 B35 80 B5 B35 7 8 8 10 100 115 130 165 80 95 110 130 120 140 160 200 3.0 3.0 3.5 3.5 AD = With cable gland Avec presse-étoupe Mit Kabelpresse Con prensacables Con pressacavo Short Court Kurz Corto Corto Long Long Lang Largo Lungo 7 9 9 11 ▲= Pads Bossages Beschläge Bullones Borchie 109 GB Unventilated motors F 56÷80 IM B14 IM B34 Motoren unbelüftet Motores no ventilados 5.2 Motori non ventilati L LP E AC øTTB IM B14 øP AN øN øM H AD T L LP E AD AC øM H HD IM B34 øTTB AN HA T C øTLP B F øD 110 BB TTP / u GD BC GA I 5. øP E Moteurs non ventilés øN D AA CA A AB Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 56 63 71 80 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 A AA AB ø AC AD AN BN B BB BC C CA E 90 100 112 125 --30 36 35 110 126 138 155 108 132 132 162 85 74 74 112 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 45° 71 80 90 100 95 100 110 124 12 10 10 12 36 40 45 50 46 105 90 108 20 23 30 40 JA JB LW LX ø TLP 227 ------- 150 200 200 214 170 ------- --------- --------- 6 7 7 9 Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 56 63 71 80 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 H 56 63 71 80 HA 3 5 6 8 HC L 113 129 137 163 7 15 15 15 7 21 21 21 207 248 255 298 LP Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 56 63 71 80 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 ø D F GA GD ø TTP u 9 11 14 19 3 4 5 6 10.2 12.5 16.0 21.5 3 4 5 6 M3 M4 M5 M6 9 10 12 15 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type øM øN øP T TTB 56 63 71 80 65 75 85 100 50 60 70 80 85 90 105 120 2.5 2.5 2.5 3.0 M5 M5 M6 M6 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 B14 B34 AD = With cable gland Avec presse-étoupe Mit Kabelpresse Con prensacables Con pressacavo Short Court Kurz Corto Corto Long Long Lang Largo Lungo 111 GB Self-braking motors F 63÷80 IM B3 IM B5 IM B35 Selbstbremsende Motoren Motores con freno 5.3 Motori autofrenanti LM L LR LQ LP LRA r q HC HD AD RA C BC øTLP B EA CA HA E H øAC IM B3 AA A AB BB LM L LR LQ LP LRA T r øM E H q HD øTLB AD RA øAC øP IM B5 øN EA LA LM L LR LQ LRA T r HC q EA HA CA B AA A AB FA øDA TTS / v GF BB GC F øD 112 øTLP LA C BC TTP / u GD E øM øAC IM B35 HD øTLB AD RA H LP GA I 5. øP E Moteurs freins øN D Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 A AA 100 100 112 112 125 125 AB 30 30 36 36 35 35 ø AC 126 126 138 138 155 155 132 132 132 132 162 162 B 80 80 90 90 100 100 BB 100 100 110 110 124 124 BC 10 10 10 10 12 12 C 40 55 45 60 50 70 ▲ E EA H ♦ CA HA 165 165 150 150 176 176 189 189 174 174 196 196 23 23 30 30 40 40 63 63 71 71 80 80 5 5 6 6 8 8 HC 135 135 143 143 165 165 L LM ♦ ▲ ♦ ▲ 309 324 316 331 366 386 333 348 340 355 386 406 332 347 339 354 389 409 356 371 363 378 409 429 Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura Struttura Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 r ø TLP ▲ LRA IIB øq ♦ LP 197 212 197 212 252 272 221 236 221 236 272 292 50 50 50 50 50 50 118 118 118 118 146 146 23 23 23 23 23 23 7 7 7 7 9 9 Terminal box - Boîte à bornes - Klemmkasten - Caja de bornes - Morsettiera Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 152 152 152 152 166 166 164 164 164 164 174 174 215 215 223 223 246 246 227 227 235 235 254 254 120 120 120 120 120 120 144 144 144 144 144 144 140 140 140 140 140 140 144 144 144 144 144 144 175 175 175 175 186 186 174 174 174 174 184 184 Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 63 63 71 71 80 80 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 B3 B5 B35 øD ø DAmax F FA GA GC GD GF TTP TTS u v 11 11 14 14 19 19 4 4 5 5 6 6 12.5 12.5 16.0 16.0 21.5 21.5 4 4 5 5 6 6 M4 M4 M5 M5 M6 M6 10 10 12 12 15 15 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type LA øM øN øP T ø TLB 63 B5 B35 71 B5 B35 80 B5 B35 8 8 10 115 130 165 95 110 130 140 160 200 3.0 3.5 3.5 9 9 11 ♦ Frame size Hauteur d’axe Größe Tamaño Altezza d’asse Pole Pôles Polig Polos Poli Power Puissance Leistung Potencia Potenza ▲ Frame size Hauteur d’axe Größe Tamaño Altezza d’asse 63/71 2; 4 ≤ 0.18 [kW] 80 2; 4 6 8 ≤ 0.75 [kW] ≤ 0.37 [kW] ≤ 0.25 [kW] Pole Pôles Polig Polos Poli Power Puissance Leistung Potencia Potenza 63/71 2; 4 6; 8 > 0.18 [kW] > 0.075 [kW] 80 2; 4 6 8 > 0.75 [kW] > 0.37 [kW] > 0.25 [kW] 113 GB Self-braking motors F 63÷80 IM B14 IM B34 Selbstbremsende Motoren Motores con freno 5.3 Motori autofrenanti LM LR L LQ LP LRA AD RA q E H øM øAC IM B14 HD øTTB RA AD r T EA LM L LR LQ LRA LP r HD E C EA CA HA TLP B A AB BC øDA TTS / v GF FA GC øD 114 TTP / u GD BB F AA H HC q øM øAC IM B34 øTTB T GA I 5. øP øN E Moteurs freins øP øN D Overall dimensions [mm] GB Dimensions [mm] F Abmessungen [mm] D Dimensiones de espacio máximo [mm] E Dimensioni d'ingombro [mm] I Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 A AA 100 112 125 AB 30 36 35 126 138 155 ø AC 132 132 162 B 80 90 100 BB 100 110 124 BC 10 10 12 C 40 45 50 ▲ E EA H ♦ CA HA 165 150 176 189 174 196 23 30 40 63 71 80 5 6 8 HC 135 143 165 L LM ♦ ▲ ♦ ▲ 309 316 366 333 340 386 332 347 389 356 371 409 Structure - Structure - Gehäuse - Estructura - Struttura Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 r ø TLP ▲ LRA IIB øq ♦ LP 197 197 252 221 221 272 50 50 50 118 118 146 23 23 23 7 7 9 Terminal box - Boîte à bornes - Klemmkasten - Caja de bornes - Morsettiera Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 IIB IP55 AD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 HD IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LQ IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 LR IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 IIB IP55 RA IIB IP65 IIC IP55/65 152 152 166 164 164 174 215 223 246 227 235 254 120 120 120 144 144 144 140 140 140 144 144 144 175 175 186 174 174 184 Shaft - Arbre - Welle - Eje - Albero Type 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 øD ø DAmax F FA GA GC GD GF TTP TTS u v 11 14 19 4 5 6 12.5 16.0 21.5 4 5 6 M4 M5 M6 10 12 15 Flanges - Brides - Flansch - Bridas - Flange Type øM øN øP T ø TTB 63 B14 B34 71 B14 B34 80 B14 B34 75 85 100 60 70 80 90 105 120 2.5 2.5 3.0 M5 M6 M6 ♦ Frame size Hauteur d’axe Größe Tamaño Altezza d’asse Pole Pôles Polig Polos Poli Power Puissance Leistung Potencia Potenza ▲ Frame size Hauteur d’axe Größe Tamaño Altezza d’asse 63/71 2; 4 ≤ 0.18 [kW] 80 2; 4 6 8 ≤ 0.75 [kW] ≤ 0.37 [kW] ≤ 0.25 [kW] Pole Pôles Polig Polos Poli Power Puissance Leistung Potencia Potenza 63/71 2; 4 6; 8 > 0.18 [kW] > 0.075 [kW] 80 2; 4 6 8 > 0.75 [kW] > 0.37 [kW] > 0.25 [kW] 115 GB F D 6. Spare parts 6.1 6.2 E Spare parts for ventilated three-phase motors Spare parts for unventilated three-phase motors I 6. Pièces détachées 6.1 6.2 Pièces detachées moteurs triphasés ventilés Pièces detachées moteurs triphasés non ventilés 6. Ersatzteilliste 6.1 6.2 Ersatzteile für Drehstrommotoren belüftet Ersatzteile für Drehstrommotoren unbelüftet 6. Piezas de repuesto 6.1 6.2 Piezas de repuesto motores trifásicos ventilados Piezas de repuesto motores trifásicos no ventilados 6. Parti di ricambio 6.1 6.2 Parti di ricambio motori trifase ventilati Parti di ricambio motori trifase non ventilati 117 GB Spare parts for ventilated three-phase motors F D E I Pièces detachées moteurs triphasés ventilés 6. Ersatzteile für Drehstrommotoren belüftet Piezas de repuesto motores trifásicos ventilados 6.1 Parti di ricambio motori trifase ventilati 3 20 9 10 11 7 6 31 30 4 6 F63 F71 12 22 18 3 20 17 9 10 16 25 26 27 11 7 6 29 31 30 F80 12 22 18 17 16 25 26 27 29 32 Brake Frein Bremse Freno Freno 33 118 34 35 6 4 GB F D E I GB 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 Bearing, driving end, Terminal box Terminal box cover Terminal holder plate Rotor Stator Frame Endshield, non-driving end 16 17 18 20 22 25 26 27 Fan cover Shaft Dust seal, driving end Endshield, driving end Flange insert Bearing, non-driving end Dust seal, non driving-end Fan 29 30 31 (32) (33) (34) (35) Feet/Sliding block Cone Cone + cable tightening flange Brake feather key Spacer-rim Brake disk Brake Roulement avant Boîte à bornes Couvercle boîte à bornes Plaque a bornes Rotor Stator Carcasse Flasque arrière 16 17 18 20 22 25 26 27 Capot de ventilateur Arbre Bague avant d’étanchéité Flasque avant Bride rapportée Roulement arrière Bague arrière d’étanchéité Ventilateur 29 30 31 (32) (33) (34) (35) Patin Cône Bride de serrage cône + cable Clavette de frein Couronne-entretoise Garniture de frein Frein Kugellager A-Seite Klemmbrett Klemmkastendeckel Klemmkastenplatte Rotor Stator Motorgehäuse Lagerschild B-Seite 16 17 18 20 22 25 26 27 Lüfterhaube Welle Dichtring A-Seite Lagerschild A-Seite Flansch Antriebsseite Kugellager B-Seite Dichtring B-Seite Lüfterrad 29 30 31 (32) (33) (34) (35) Motorfuß Konus Befestigungsflansch Konus + Kabel Bremskeil Kranz-Distanzstück Bremsdichtung Bremse Cojinete delantero Caja de bornes Cubierta caja de bornes Placa porta bornes Rotor Estator Armazón Escudo trasero 16 17 18 20 22 25 26 27 Casquete cubre ventilador Eje Anillo de retención delantero. Escudo delantero Brida de acoplamiento Cojinete trasero Anillo de retención trasero. Ventilador 29 30 31 (32) (33) (34) (35) Pies Cono Brida de sujeción cono + cable Lengüeta del freno Corona-distancial Junta de frenado Freno Cuscinetto anteriore Morsettiera Coprimorsettiera Piastra porta morsetti Rotore Statore Carcassa Scudo posteriore 16 17 18 20 22 25 26 27 Calotta copriventola Albero Anello di tenuta anteriore Scudo anteriore Flangia riportata Cuscinetto posteriore Anello di tenuta posteriore Ventola 29 30 31 (32) (33) (34) (35) Piede/Piastra d’appoggio Cono Flangia di serraggio cono + cavo Linguetta del freno Corona-distanziale Guarnizione frenante Freno F 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 D 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 E 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 I 3 4 6 7 9 10 11 12 119 GB Spare parts for unventilated three-phase motors F D E I Pièces detachées moteurs triphasés non ventilés 6. Ersatzteile für Drehstrommotoren unbelüftet Piezas de repuesto motores trifásicos no ventilados 6.2 Parti di ricambio motori trifase non ventilati 9 10 11 30 31 12 F56 22 18 18 3 20 29 17 9 10 25 11 12 7 25 15 15 31 F63 F71 F80 22 120 3 29 17 30 7 GB F D E I GB 3 7 9 10 11 12 15 17 Bearing, driving end, Terminal holder plate Rotor Stator Frame Endshield, non-driving end Rear outside cover Shaft 18 20 22 25 29 30 31 Dust seal, driving end Endshield, driving end Flange insert Bearing, non-driving end Sliding block Cone Cone + cable tightening flange Roulement avant Plaque a bornes Rotor Stator Carcasse Flasque arrière Couvercle arrière Arbre 18 20 22 25 29 30 31 Bague avant d’étanchéité Flasque avant Bride rapportée Roulement arrière Patin Cône Bride de serrage cône + cable Kugellager A-Seite Klemmbrett Rotor Stator Motorgehäuse Lagerschild B-Seite Anschlußkastendeckel Welle 18 20 22 25 29 30 31 Dichtring A-Seite Lagerschild A-Seite Flansch Antriebsseite Kugellager B-Seite Motorfuß Konus Befestigungsflansch Konus + Kabel Cojinete delantero Placa porta bornes Rotor Estator Armazón Escudo trasero Casquillo externo trasero Eje 18 20 22 25 29 30 31 Anillo de retención delantero Escudo delantero Brida de acoplamiento Cojinete trasero Pies Cono Brida de sujeción cono + cable Cuscinetto anteriore Piastra porta morsetti Rotore Statore Carcassa Scudo posteriore Fondello esterno posteriore Albero 18 20 22 25 29 30 31 Anello di tenuta anteriore Scudo anteriore Flangia riportata Cuscinetto posteriore Piede/Piastra d’appoggio Cono Flangia di serraggio cono + cavo F 3 7 9 10 11 12 15 17 D 3 7 9 10 11 12 15 17 E 3 7 9 10 11 12 15 17 I 3 7 9 10 11 12 15 17 121 Sales programme Programme Verkaufsprogramm Programa de venta Programma di vendita Flameproof-Explosion proof motors EEx-d, EEx-de •low or medium voltage •frame size 56 ÷ 500 •power 0.06 ÷ 800 kW •threephase, 1 or 2 speed, singlephase •ventilated, unventilated •group I, IIA, IIB, IIC •category 2G, 2D, 2GD •temperature class T3, T4, T5, T6 •maximum surface temperature [°C] T150, 135, 125, 100, 85, 70 •with brake Moteurs antidéflagrants EEx-d, EEx-de •basse ou moyenne tension •hauteur d’axe 56 ÷ 500 •puissance 0.06 ÷ 800 kW •triphasés, à 1 ou 2 vitesses, monophasés •ventilés, non ventilés •groupe I, IIA, IIB, IIC •catégorie 2G, 2D, 2GD •classes de température T3, T4, T5, T6 •température superficielle maximum [°C] T150, 135, 125, 100, 85, 70 •avec frein Explosionsgeschützte Motoren EEx-d, EEx-de •Nieder- oder Mittelpannung •Baugrößen 56 ÷ 500 •Leistung 0.06 ÷ 800 kW •Drehstrommotoren, 1 oder 2 Geschwindigkeiten, Einphasenmotoren •mit Lüftung, ohne Lüftung •Gruppe I, IIA, IIB, IIC •Kategorie 2G, 2D, 2GD •Temperaturklassen T3, T4, T5, T6 •maximale Oberflächentemperatur [°C] T150, 135, 125, 100, 85, 70 •mit Bremse Motores antideflagrantes EEx-d, EEx-de •bajo o medio voltaje •tamaños 56 ÷ 500 •potencia 0.06 ÷ 800 kW •trifásicos, 1 o 2 velocidades, monofásicos •autoventilados o no •grupo I, IIA, IIB, IIC •categoría 2G, 2D, 2GD •clase temperatura T3, T4, T5, T6 •màxima temperatura superficial [°C] T150, 135, 125, 100, 85, 70 •con freno Motori antideflagranti EEx-d, EEx-de •bassa o media tensione •altezza d'asse 56 ÷ 500 •potenze 0.06 ÷ 800 kW •trifase, 1 o 2 velocità, monofase •ventilato, non ventilato •gruppo I, IIA, IIB, IIC •categoria 2G, 2D, 2GD •classi di temperatura T3, T4, T5, T6 •massima temperatura superficiale [°C] T150, 135, 125, 100, 85, 70 •con freno Increased safety motors EEx-e •frame size 63 ÷ 132 •power 0.12 ÷ 7.5 kW •threephase, 1 or 2 speed •group II •category 2G •temperature class T3 Moteurs à sécurité augmentée EEx-e •hauteur d’axe 63 ÷ 132 •puissance 0.12 ÷ 7.5 kW •triphasés, à 1 ou 2 vitesses •groupe II •catégorie 2G •classes de température T3 Motoren für erhöhte Sicherheit EEx-e •Baugrößen 63 ÷ 132 •Leistung 0.12 ÷ 7.5 kW •Drehstrommotoren, 1 oder 2 Geschwindigkeiten •Gruppe II •Kategorie 2G •Temperaturklassen T3 Motores de seguridad aumentada EEx-e •tamaños 63 ÷ 132 •potencia 0.12 ÷ 7.5 kW •trifásicos, 1 o 2 velocidades •grupo II •categoría 2G •clase temperatura T3 Motori a sicurezza aumentata EEx-e •altezza d'asse 63 ÷ 132 •potenze 0.12 ÷ 7.5 kW •trifase, 1 o 2 velocità •gruppo II •categoria 2G •classe di temperatura T3 Non sparking motors EEx-nA •low or medium voltage •frame size 63 ÷ 500 •power 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •threephase, 1 or 2 speed •group II •category 3G •temperature class T3 Moteurs anti-étincelles EEx-nA •basse ou moyenne tension •hauteur d’axe 63 ÷ 500 •puissance 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •triphasés, à 1 ou 2 vitesses •groupe II •catégorie 3G •classes de température T3 Funkenfreie Motoren EEx-nA •Nieder- oder Mittelspannung •Baugrößen 63 ÷ 500 •Leistung 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •Drehstrommotoren, 1 oder 2 Geshcwindigkeiten •Gruppe II •Kategorie 3G •Temperaturklassen T3 Motores no sparking EEx-nA •bajo o medio voltaje •tamaños 63 ÷ 500 •potencia 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •trifásicos, 1 o 2 velocidades •grupo II •categoría 3G •clase temperatura T3 Motori non sparking EEx-nA •bassa o media tensione •altezza d'asse 63 ÷ 500 •potenze 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •trifase, 1 o 2 velocità •gruppo II •categoria 3G •classe di temperatura T3 Totally enclosed fan cooled IEC motors •low or medium voltage •frame size 63 ÷ 500 •power 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •threephase, 1 or 2 speed •protection IP 55 •temperature class T3 Moteurs fermés IP 55 CEI/IEC avec ventilation extérieure •basse ou moyenne tension •hauteur d’axe 63 ÷ 500 •puissance 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •triphasés, à 1 ou 2 vitesses •protection IP 55 •classes de température T3 Geschlossene Motoren mit Fremdbelüftung nach IEC •Nieder- oder Mittelspannung •Baugrößen 63 ÷ 500 •Leistung 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •Drehstrommotoren, 1 oder 2 Geshcwindigkeiten •Schutzart IP55 •Temperaturklassen T3 Motores cerrados con ventilación exterior IP55 •bajo o medio voltaje •tamaños 63 ÷ 500 •potencia 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •trifásicos, 1 o 2 velocidades •protección IP55 •clase temperatura T3 Motori chiusi con ventilazione esterna CEI/IEC •bassa o media tensione •altezza d'asse 63 ÷ 500 •potenze 0.12 ÷ 800 kW •trifase, 1 o 2 velocità •protezione IP 55 •classe di temperatura T3 Centrifugal flameproof electric pumps for printing machines EEx-d - EEx-de •group IIB, IIC •output over 300 l/min •head up to 15 m •stem length 170 ÷ 550 mm •special applications •detachable motor from the pump unit Electropompes centrifuges antidéflagrantes pour machines d'impression EEx-d - EEx-de •groupe IIB, IIC •debit supérieur à 300 l/min •hauteur de refoulement jusqu’à 15 m •corps immerge 170 ÷ 550 mm •applications spéciales •moteur détacable de l’unitè pompe Explosionsgeschützte Zentrifugal-Elektropumpen für Druckmaschinen EEx-d - EEx-de •Gruppe IIB, IIC •Leistung bis 300 l/min •Bis zu 15 m Förderhöhe •Eintauchtiefe 170 ÷ 550 mm •Sonderanwendungen •Motor vom Pumpenkörper abnehmbar Electrobombas centrífugas antideflagrantes para máquinas de impresión EEx-d - EEx-de •grupo IIB, IIC •capacidad: más 300 l/min •altura: hasta 15 m •cuerpos sumergidos 170 ÷ 550 mm •aplicaciones especiales •motor separable del cuerpo bomba Elettropompe centrifughe antideflagranti per macchine da stampa EEx-d - EEx-de •gruppo IIB, IIC •portate oltre 300 l/min •prevalenze: fino a 15 m •corpi immersi 170 ÷ 550 mm •applicazioni speciali •motore separabile dal corpo pompa Centrifugal electric pumps for machine tools •self-priming •output over 300 l/min •head up to 30 m •stem length 90 ÷ 550 mm •special applications Electropompes centrifuges pour machines-outils •auto-amorçage •debit supérieur à 300 l/min •hauteur de refoulement jusqu'à 30 m •corps immerge 90 ÷ 550 mm •applications spéciales Elektropumpen für Werkzeugmaschinen •selbstansaugend •Leistung mehr als 300 l/min •Bis zu 30 m Förderhöhe •Eintauchtiefe 90 ÷ 550 mm •Sonderanwendungen Electrobombas centrífugas para máquinas herramientas •autocebantes •capacidad: más 300 l/min •altura: hasta 30 m •cuerpos sumergidos 90 ÷ 550 mm •aplicaciones especiales Elettropompe centrifughe per macchine utensili •autoadescanti •portate oltre 300 l/min •prevalenze fino a 30 m •corpi immersi 90 ÷ 550 mm •applicazioni speciali Descriptions and/or technical features listed in this catalogue may not be considered as binding. Cemp reserves the right to make alterations at any time without prior notice. Dans le souci d'améliorer continuellement nos produits, certaines données de notre catalogue peuvent être modifiées par la Cemp sans préavis. Die Beschreibung und/oder technische Eigenschaften, die in diesem Katalog angegeben sind, dürfen nicht als verbindlich angesehen werden. Cemp behält sich das Recht vor, ohne Mitteilung Abweichungen und Änderungen jederzeit vorzunehmen. Las descripciones y las características técnicas del presente catálogo no son vinculantes. Cemp se reserva el derecho y la facultad de aportar variaciones en cualquier momento, sin aviso previo. Le descrizioni e/o caratteristiche tecniche del presente catalogo non sono impegnative. Cemp si riserva il diritto e la facoltà di apportare modifiche in qualsiasi momento, senza preavviso. Cemp SpA Via Piemonte, 16 I 20030 SENAGO (MI) Tel. +39 02 99 01 08 04 Fax +39 02 99 89 177 e-mail: [email protected] www.cemp.it Cemp France SA 6 et 8, avenue Victor Hugo F 27320 NONANCOURT Tél. +33 (0)820 031 310 Fax +33 (0)820 031 816 e-mail: [email protected] www.cemp-international.com Cemp International GmbH Am Mollnhof 2 D 94036 PASSAU Tel. +49 (0)851 96 68 68 28 Fax +49 (0)851 96 68 68 29 e-mail: [email protected] www.cemp-international.com Cemp Great Britain - Service Center 41 Half House Lane - BRIGHOUSE West Yorkshire - HD6 2PH Tel. +44 (0)7929 002 038 Fax +44 (0)1484 722 122 e-mail: [email protected] www.cemp-international.com
Scaricare