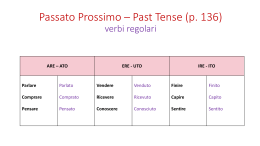
Il Passato Prossimo The Past Perfect Tense Passato Prossimo • Describes recent past events • It is a compound tense: formed by using a past participle of the verb, and an auxiliary verb. • The auxiliary verb is usually avere, but for some verbs it is essere. • Often used with certain expressions of time: ieri, domenica scorsa, un’ora fa… Forming the Past Participle Based on the infinitive of the verb: • -are verbs: formed by using -ato i.e. parlare parlato; giocare giocato • -ere verbs: formed by using -uto i.e. vendere venduto; accadere accaduto • -ire verbs: formed by using -ito i.e. sentire sentito; fuggire fuggito Try forming the past participle: • • • • • • • • • • Ascoltare Chiamare Partire Uscire Ripetere Tenere Capire Studiare Finire Piacere • • • • • • • • • • Ascoltato Chiamato Partito Uscito Ripetuto Tenuto Capito Studiato Finito Piaciuto ‘Avere’ Verbs • • • • Most Italian Verbs use Avere as auxiliary: Ho, hai, ha; abbiamo, avete, hanno Transitive verbs (they take an object) i.e. accetare, aiutare, bollire, cambiare, comprare, dare, fare, lasciare, mangiare, parlare, raccontare, ricordare, scordare, studiare… • Participles stay the same, regardless of gender: i.e. Marco ha mangiato. Maria ha mangiato. ‘Essere’ Verbs • • • • Some Italian Verbs use Essere as auxiliary: Sono, sei, è; siamo, siete, sono Intransitive verbs; no object, often motion. i.e. accadere, andare, arrivare, crescere, diventare, entrare, essere, mancare, morire, nascere, partire, piovere, restare, rimanere, scendere, stare, tornare, uscire, venire… • Participles must agree with noun: i.e. Marco è entrato. Maria è entrata. Irregular Participles • Some Italian Verbs have them. Yay! • Too many to list here, but a few important ones you might need: • Bere bevuto • Dire detto • Fare fatto • Leggere letto • Vedere visto • Morire morto Irregular Participles Noi mangiamo. Noi abbiamo mangiato Pratichiamo! Loro comprano. Loro hanno comprato Pratichiamo! Io pago. Io ho pagato Pratichiamo! Lui scrive. Lui ha scrivuto. Pratichiamo! Loro vendono la casa. Loro hanno venduto la casa. Pratichiamo! Lei fa un vaso. Lei ha fatta un vaso. Pratichiamo! Lui macina il caffè. Lui ha macinato il caffè. Pratichiamo! Lui beve l’acqua . Lui ha bevuto l’acqua. Pratichiamo! Loro arrivano . Loro sono arrivati. Pratichiamo! Noi andiamo . Noi siamo andati. Pratichiamo! Lui resta a casa. Lui è restato a casa. Pratichiamo! Lei torna a casa. Lei è tornata a casa. Pratichiamo! Lei nasce il bambino . É nato il bambino. Some past tense time expressions: • • • • • • • • • • • ieri ieri mattina scorso L’anno scorso La settimana scorsa due giorni fa molto tempo fa poco tempo fa già mai ormai yesterday yesterday morning last, past last year last week two days ago a long time ago recently, not long ago already ever (never) by now
Scaricare