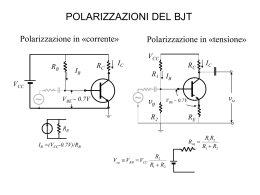
Goal: Study of a class A amplifier with biasing current which flows through the load Components to be used: A BJT BC142, resistors RB =10 K RC =RE =100 Trimmer T Setup: Consider the circuit shown in the figure in which VCC is equal to 15 V and Icmax = 20 mA. Please note that: • The voltage on the series RC+TC+RE can vary from VCESAT .0V to VCC . • The collector current can vary from 0 to Icmax (20mA). K and TC VCC RB RC IC IB TB TC The 2 trimmers fix the polarization of the device and must be set so that to guarantee, during operation, the condition of maximum useful power on the load (RC + TC). The following considerations can be made: The maximum load power corresponds to maximum excursion of voltage and current: K VC + VCE BJT VE -IE≈IC RE 1ˆ ˆ V I 2 PL The maximum excursions can be obtained if the operating point is where VCEQ VCC /2 and ICQ=Icmax/2 (in this case the static load line coincides with the dynamic load line). IC -1/(RC+TC+RE) IC ICmax ICmax IBQ ICQ VCC/2 t ICQ VCC VCE Î t V̂ In this context, you choose to find the biasing conditions: changing the base current IBQ (using the trimmer TB) and changing, by the resistance on the collector, the VCEQ (using the trimmer TC). In order to display the adjustment obtained with the two trimmers consider the simplifying assumption VCE VC (we neglect the voltage drop on RE compared VCE) and perform the following steps: 1. Connect the channel-1 probe and the channel-2 probe respectively to the collector and emitter of the BJT (the voltage of RE depends on IC). Select the XY mode (with DC coupling), to display the working point. Since, the signal on the Y axis is proportional to IC and the signal on the X axis represents VC VCE. 2. Adjust TB (IBQ ) so that ICQ=Icmax/2. 3. Adjust TC until VC VCEQ is equal to VCC/2. 4. If necessary, readjust TB. Oscilloscope Display Mode Y-T 1, 2 CH1=5.0V/ CH2=1.0V/ Mode X-Y VE=REIC REICmax REICmax/2 3 2 VCC/2 CH1=5.0V/ VCC VCVCEQ CH2=1.0V/ To evaluate the obtained biasing, by a capacitor of 680 nF apply a sinusoidal signal at the base (with frequency 1 kHz) and increase its amplitude, until the load line reaches the chosen limits (Icmax and VCC). Verified the load line conditions, return to normal mode. Quantities to be calculated and Measures to be done: 1. Before assembling the circuit, measure the real value of RE. 2. Fix the position of working point how it is described in the setup and display the waveforms of voltage. 3. Using the oscilloscope with AC coupling, measure the maximum voltage values of the sinusoidal signals at the collector and emitter. 4. Compute the power transferred to the load (series trimmer RC). 5. Estimate the power supplied to the amplifier. 6. Evaluate the efficiency of the power amplifier. Do not disassemble the circuit and pass the following experiment. Goal: Study of a class A amplifier with biasing current which does not flow through the load. Setup: To the previous circuit connect to the BJT collector a load RL = 1K by a capacitor from 22 F (negative terminal connected to the RL , the positive terminal connected to the circuit). VCC RB RC IC IB TB TC VC BJT VE -IE≈IC RL RE Considerations: Justify the slope change of the load line. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Goal: Study of a Class B amplifier with complementary symmetry Components to be used: BJT1 BC142(npn) and BJT2 BC143 (pnp). Resistor RL to be defined. +VCC BJT1 Setup: Consider the circuit shown in the figure where VCC=10V and assume Icmax=10 mA. In this type of amplifier if the signal is absent the current signal ICQ is null. Injecting at the input a sinusoidal signal: • for Vin> V the BJT1 is in conduction • for vin <V the BJT2 is in conduction RL BJT2 -VCC Quantities to be calculated and Measures to be done: Find the value of RL which is necessary to ensure the maximum output power. Before mounting the circuit, measure the real value of RL. Apply a sinusoidal signal at the input and increase its amplitude as far as it is possible (the output waveform must be a sinusoidal waveform). By the oscilloscope measure the output voltage and evaluate the effective power which is transferred to the load. Check for the presence of the crossover phenomenon. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Goal: Study and synthesis of the class AB amplifier. Components to be used: BJT1 BC142(npn) and BJT2 BC143 (pnp). Two diodes 1N4001. Two capacitors C1=1 F and C2 to be defined. Resistors RL and R1 to be defined. +VCC Setup: Take Icmax = 10mA, VCC = 20 V. Use the datasheet to deduce V and VBEon. R1 - C1 + IC + C2 Quantities to be calculated and Measures to be done: Choose the RL value which ensures the maximum output power. RL Choose the R1 value which ensure a current through R1 R1 equal to one tenth of the average value of IC, in conditions of maximum output power. The capacitor C2 must ensure an excursion of output voltage less than or equal to (Vcc/2)/20. Before mounting the circuit, measure the real value of RL At the input is applied a sinusoidal signal and using the oscilloscope display the output waveform, in particular: 1. Check the reduction of the crossover phenomenon 2. Apply a sinusoidal signal at the input and increase its amplitude as far as it is possible (the output waveform must be a sinusoidal waveform). By the oscilloscope measure the output voltage and evaluate the effective power which is transferred to the load. 3. Verify the variations of voltage on C2. Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe B a simmetria complementare Componenti da utilizzare: BJT1 BC107(npn) e BJT2 BC177 (pnp). Resistore RL da definire. Setup: Si consideri il circuito mostrato in figura in cui VCC=10V si assume ICmax=1 mA. In tale tipo di amplificatore in assenza di segnale la corrente ICQ è nulla. BJT complementari e alimentazione bilanciata, per cui la tensione sull’emettitore è nulla. Iniettando un segnale sinusoidale in ingresso: per vin > V il BJT 1è in conduzione per vin < V il BJT 2è in conduzione +VCC BJT1 RL BJT2 -VCC Si possono riportare le caratteristiche del BJT1 su gli assi relativi (IC1, VCE1) e le caratteristiche del BJT2 sul piano IC1 IC2 e VCE1: IC1max VCE1=VCE2+2VCC (VCE2 <0) IB1 Osservando la figura, si deduce che per massimizzare l’escursione del segnale sul carico tra –VCC a + VCC si deve scegliere: VCC RL 10 K IC max Q 2VCC VCC VCE1 IB2 Q IC2max IC2 Applicare un segnale sinusoidale in ingresso aumentarne l’ampiezza quanto possibile (la forma d’onda d’uscita non deve essere tagliata) Misure da effettuare: Prima di montare il circuito misurare il valore reale di RL Tramite oscilloscopio effettuare la misura della tensione d’uscita e valutare l’effettiva potenza ceduta al carico. Verificare l’eventuale presenza del fenomeno di “crossover”. Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe AB. Componenti da utilizzare: BJT1 BC107 e BJT2 BC177; 2 diodi 1N4001, 2Condensatori C1= C2=22 F; Resistori RL, R1da definire. Setup: Si consideri lo schema mostrato in figura. In tale circuito è utilizzata una sola batteria e ciò è ottenuto accoppiando il carico mediante un condensatore di capacità elevata. Durante il funzionamento, il condensatore si carica alla tensione VCC/2, e se la capacità è adeguata, la sua tensione rimane in pratica costante ed il condensatore si comporta come una batteria. Considerando ICmax =1mA, VCC =20 V. Da considerazioni analoghe a quelle fatte precedentemente si ottiene VCC VCC / 2 RL 10 K IC max Per il calcolo di R1 si impone una corrente IR1 =ICmax/10: VCC 2VBEon 2 R1 187 K 0.1IC max R1 82 K +VCC R1 - C1 + + C2 - RL R1 Misure da effettuare: Prima di montare il circuito misurare il valore reale di RL Si applichi in ingresso un segnale sinusoidale e mediante oscilloscopio visualizzare la forma d’onda in uscita. In particolare verificare l’eventuale riduzione del fenomeno di “crossover”, ed inoltre, aumentando l’ampiezza del segnale d’ingresso, verificare per quali valori si verifica il fenomeno di “clipping” e se tale fenomeno subentra simmetricamente. Effettuare la misura della tensione d’uscita e valutare l’effettiva potenza ceduta al carico. Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe A accordato Componenti da utilizzare: BJT BC107, Resistori R1 e RL da definire, Induttore L=1mH, Condensatori C da definire C1=C2=680nF Setup: Si consideri lo schema mostrato in figura. In tale circuito è utilizzata una sola batteria VCC=5V e si assume ICmax =2 mA. Si sceglie VCC VCC / 2 RL 1K IC max VCC L C RB C2 + Vin Per il calcolo di R1 si impone una corrente IR1 =ICmax/10: VCC 2VBEon 2 R1 187 K 0.1IC max C1 RL + Vout - R1 82 K Setup: Sono dati la tensione di polarizzazione VCC, il punto di lavoro del dispositivo (ICQ= 10 mA, VCEQ=5V). Tenendo presente le caratteristiche del dispositivo in ( VCEsat =1V, hFE =250 ,VBEQ =0.65V) definire i resistori con RB RC ed RL. In particolare RB ed RC devono garantire la polarizzazione ed RL deve massimizzare la potenza in uscita fornendo d’altra parte una segnale Vout esente da “clipping”. Effettuata la scelta dei componenti montare il circuito come mostrato in figura. Misure da effettuare: 1) Misurare mediante oscilloscopio il punto di lavoro verificando che le grandezze rilevate siano prossime a quelle calcolate. 2) Si applichi in ingresso un segnale e mediante l’oscilloscopio visualizzare la forma d’onda in uscita. In particolare aumentando l’ampiezza del segnale d’ingresso verificare per quali valori si verifica il fenomeno di “clipping” e se tale fenomeno subentra simmetricamente. Considerando ICQ =10 mA, VCEQ =5 V VCC VCEQ ICQ RC Vmax VCEQ VCEsat VCC RB I BQ VBEQ RC 4V RB Imax ICQ hFE VBEQ VCC VCEQ ICQ I CQ 10mA RB 15V 5V 10mA 1k Vmax Imax 400 RL hFE VCC VBEQ ICQ 360k VCC RB BJT + Vi -- C2 C1 RE RL + Vout -- Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe A Componenti da utilizzare: BJT BC141, Resistori RB RC e RL da definire Setup: Sono dati la tensione di polarizzazione VCC, il punto di lavoro del dispositivo (ICQ= 10 mA, VCEQ=5V). Tenendo presente le caratteristiche del dispositivo in ( VCEsat =1V, hFE =250 ,VBEQ =0.65V) definire i resistori con RB RC ed RL. In particolare RB ed RC devono garantire la polarizzazione ed RL deve massimizzare la potenza in uscita fornendo d’altra parte una segnale Vout esente da “clipping”. Effettuata la scelta dei componenti montare il circuito come mostrato in figura. Misure da effettuare: 3) Misurare mediante oscilloscopio il punto di lavoro verificando che le grandezze rilevate siano prossime a quelle calcolate. 4) Si applichi in ingresso un segnale e mediante l’oscilloscopio visualizzare la forma d’onda in uscita. In particolare aumentando l’ampiezza del segnale d’ingresso verificare per quali valori si verifica il fenomeno di “clipping” e se tale fenomeno subentra simmetricamente. Considerando ICQ =10 mA, VCEQ =5 V VCC VCEQ ICQ RC Vmax VCEQ VCEsat VCC RB I BQ VBEQ RC 4V Imax RB ICQ hFE VCC VCEQ ICQ I CQ 10mA VBEQ RB 15V 5V 10mA 1k Vmax Imax 400 RL hFE VCC VBEQ ICQ 360k VCC RB BJT + Vi -- 1.1.1 C2 C1 RE RL + Vout -- Amplificatore in Classe B Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe B Componenti da utilizzare: BJT BC107 e BC177 Resistore RL =100 Condensatore C=680nF Setup: Considerando Imax =0.4 A, Vmax =25 V, Vk =1V . Dato il carico RL=100 polarizzazione che permette di fornire al carico RL una PL=100mW . definire la minima tensioni di Verificare che le tensioni, correnti e potenze applicate ai singoli transistori siano minori di quelle consentite. Montare il circuito come mostrato in figura, con le tensioni di polarizzazioni ottenute. Effettuare la misura della tensione d’uscita e valutare l’effettiva potenza ceduta al carico. Misure da effettuare: Si applichi in ingresso un segnale e mediante l’oscilloscopio visualizzare la forma d’onda in uscita. In particolare verificare l’eventuale presenza del fenomeno di “crossover”, ed inoltre aumentando l’ampiezza del segnale d’ingresso verificare per quali valori si verifica il fenomeno di “clipping” e se tale fenomeno subentra simmetricamente. +VCC RL -VCC PL VCC VK 2 RL VCC VK PL 2 RL VTm 2 VCC VK ITm VCC VK RL PTm VCC ITm 2 10V 4.5V 100 1V 100mW 2 100 5.5V Vmax 0.045 A I m ax 5.5 0.045 A 79mW Obiettivo: Studio dell’amplificatore in classe AB Componenti da utilizzare: BJT BC107 e BC177; 2Condensatori C=680nF; Resistori RL =100 R1da definire. Setup: Considerando Imax =0.4 A, Vmax =25 V, Vk =1V. Dato il carico RL=100 definire la tensione e le resistenze R1 di polarizzazione in modo da fornire a RL una PL=100mW. Verificare che le tensioni, le correnti e le potenze applicate ai singoli transistori siano minori di quelle consentite. Montare il circuito come mostrato in figura, con la tensione ed i resistori di polarizzazione ottenuti. Misure da effettuare: Si applichi in ingresso un segnale e mediante l’oscilloscopio visualizzare la forma d’onda in uscita. In particolare verificare l’eventuale riduzione del fenomeno di “crossover”, ed inoltre, aumentando l’ampiezza del segnale d’ingresso, verificare per quali valori si verifica il fenomeno di “clipping” e se tale fenomeno subentra simmetricamente. Effettuare la misura della tensione d’uscita e valutare l’effettiva potenza ceduta al carico. 2 PL I m ax +VCC R1 I DC VCC RL R1 R1 VCC / 2 VK VCC 2 VK PL 2 RL 2 RL VCC / 2 VK 4.5 45mA RL 100 I m ax I DC 14.3mA I R1 1.43mA 10 2 VBE VCC I R1 2 R1 2 VBE 2 I R1 VTm VCC VK ITm VCC / 2 VK RL PTm VCC ITm 8.8V 2.86mA 10V 3K Vmax 4.5V 100 5.5 0.045 A 0.045 A I m ax 79mW 11V
Scarica