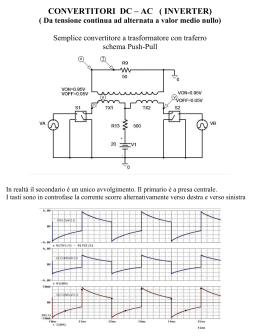
Inverter monofase Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte V0 i1 Vs/2 Q1 C1 D1 i0 Q1 Q2 ‐Vs/2 T0 i2 R Q2 Vs/2 Q1 i1 V0 Vs Vs/2 D2 i2 C2 Caso di carico resistivo Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte Valore efficace tensione in uscita V0 Q1 Q1 Q2 i1 V0 _ eff 2 = T0 T0 ⎡ T0 ⎤ 2 2 2 ⎥ 1 ⎢ 2 ⎛ Vs ⎞ ⎛ Vs ⎞ ⎢ = dt + ∫ ⎜ − ⎟ dt ⎥ = T0 ⎢ ∫ ⎜⎝ 2 ⎟⎠ 2⎠ ⎥ 0 0⎝ ⎢⎣ ⎥⎦ T0 2 Vs2 Vs dt = ∫ 4 2 T0 i2 Caso di carico resistivo 0 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita V0 a0 ∞ V0 = + ∑ ⎡ an cos ( nωt ) + bn sin ( nωt ) ⎤⎦ 2 n =0 ⎣ Simmetria a un quarto d’onda dispari: an=0 0 π ⎡ ⎤ 0 2 ⎢ ⎥ Vs Vs 2 bn = ⎢ ∫ − sin ( nωt ) d ( ωt ) + ∫ sin ( nωt ) d ( ωt ) ⎥ = π⎢ π 2 2 ⎥ 0 − ⎢⎣ 2 ⎥⎦ π⎫ ⎧ 0 2 Vs ⎪ ⎡ 1 1 ⎤ ⎡ ⎤ 2 ⎪ 4 Vs = ⎨ ⎢ cos nωt ⎥ π + ⎢ − cos nωt ⎥ ⎬ = π 2 ⎪⎣ n ⎦− ⎣ n ⎦ 0 ⎪ nπ 2 2 ⎩ ⎭ V0 = Q1 Q1 Q2 i1 T0 i2 Caso di carico resistivo ∞ ⎡ 4 Vs ⎤ ∑ ⎢⎣ nπ 2 sin ( nωt )⎥⎦ n =1,3,5 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita V0 = V0 ∞ ⎡ 4 Vs ⎤ sin n ω t ( ) ⎢ nπ 2 ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ n =1,3,5 ∑ Q1 Q2 i1 per Q1 T0 4 Vs 1 n = 1 ⇒ V01 = = 0.45Vs nπ 2 2 i2 Valore efficace della componente fondamentale Caso di carico resistivo Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte V0 Caso ohmico‐induttivo i0 i1 Vs/2 Q1 C1 D1 V0 Vs L i0 R i2 Q2 Vs/2 C2 i1 T0 D2 D1 Q1 D2 Q2 Q1 ON Q2 ON Q2 OFF Q1 OFF D1 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase a mezzo ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita V0 ∞ i0 ⎡ 4 Vs ⎤ V0 = ∑ ⎢ sin ( nωt ) ⎥ ⎦ n=1,3,5 ⎣ nπ 2 i1 T0 Corrente a regime in uscita i0 = ∞ ∑ n =1,3,5 nπ nωL θn = a tan R 2Vs R 2 + ( nωL ) 2 sin ( nωt − θn ) D1 Q1 D2 Q2 Q1 ON Q2 ON Q2 OFF Q1 OFF D1 Caso ohmico‐induttivo Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase ponte V0 Vs Q1 D1 Q1Q2 D3 Q3 V0 Q1Q2 i0 Q3Q4 ‐Vs T0 Vs L Q4 D4 R i0 Q2 E D2 D1D2 Q1Q2 D3D4 Q3Q4 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase ponte Valore efficace tensione in uscita V0 Vs Q1Q2 Q3Q4 ‐Vs V0 _ eff = 2 T0 T0 ⎡ T0 ⎤ 2 ⎥ 1 ⎢2 2 2 ⎢ ∫ (Vs ) dt + ∫ ( −Vs ) dt ⎥ = = T0 ⎢ ⎥ 0 0 ⎢⎣ ⎥⎦ Q1Q2 i0 T0 D1D2 Q1Q2 D3D4 Q3Q4 T0 2 2 V s ∫ dt = Vs 0 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita a0 ∞ V0 = + ∑ ⎡ an cos ( nωt ) + bn sin ( nωt ) ⎤⎦ 2 n =0 ⎣ Simmetria a un quarto d’onda dispari: an=0 0 π ⎡ ⎤ 0 2 ⎢ ⎥ Vs Vs 2 bn = ⎢ ∫ − sin ( nωt ) d ( ωt ) + ∫ sin ( nωt ) d ( ωt ) ⎥ = π⎢ π 2 2 ⎥ 0 − ⎢⎣ 2 ⎥⎦ π⎫ ⎧ 0 2 ⎪⎡ 1 1 ⎤ ⎡ ⎤ 2 ⎪ 4V = Vs ⎨ ⎢ cos nωt ⎥ + ⎢ − cos nωt ⎥ ⎬ = s π ⎪⎣ n ⎦− π ⎣ n ⎦ 0 ⎪ nπ 2 ⎩ ⎭ V0 = V0 Vs Q1Q2 Q1Q2 i0 Q3Q4 ‐Vs T0 D1D2 Q1Q2 D3D4 Q3Q4 ∞ ⎡4 ⎤ ∑ ⎢⎣ nπ Vs sin ( nωt )⎥⎦ n =1,3,5 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita V0 = ∞ ⎡4 ⎤ ∑ ⎣⎢ nπ Vs sin ( nωt )⎦⎥ n =1,3,5 V0 Vs Q1Q2 Q1Q2 i0 Q3Q4 ‐Vs T0 per n = 1 ⇒ V01 = 4 1 Vs = 0.9Vs nπ 2 Valore efficace della componente fondamentale D1D2 Q1Q2 D3D4 Q3Q4 Inverter PWM Inverter monofase Inverter monofase ponte Tensione istantanea in uscita V0 = ∞ ⎡4 ⎤ ∑ ⎣⎢ nπ Vs sin ( nωt )⎦⎥ n =1,3,5 V0 Vs Q1Q2 Q1Q2 i0 Q3Q4 ‐Vs T0 Corrente a regime in uscita i0 = ∞ 4Vs ∑ n =1,3,5 nπ θn = a tan R + ( nωL ) 2 2 sin ( nωt − θn ) D1D2 Q1Q2 D3D4 Q3Q4 nωL R Inverter PWM
Scaricare