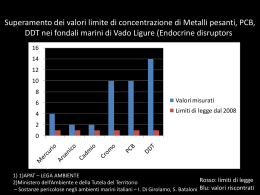
Group Leader Marina Marini, Associate Professor Department of Histology, Embryology and Cell Biology University of Bologna Via Belmeloro, 8 - 40126 BOLOGNA, ITALY tel (+39)051 2094 116 (office); 094 or 126 or 127 (lab); 100 (secretary) fax (+39)051 2094 110 e-mail: [email protected] Group members Simona di Tullio (post-doc fellow) tel. (+39)051 2094 094 email: [email protected] Provvidenza M. Abruzzo (PhD student) tel. (+39)051 2094 094 email: [email protected] Cosetta Marchionni (laboratory technician) tel. (+39)051 2094 094 email: [email protected] Key words (max 5) Oxidative stress, aging, ADP-ribosylation, physical exercise, neuromuscolar diseases Research projects • Physical exercise, hypoxia and oxidative stress To evaluate the biomolecular pathways activated by physical exercise and hypoxia, in the view that the oxidative stress they induce may have hormetic effects, and hence, at low doses, limit apoptosis and DNA damage. • Oxidative stress in skeletal muscle denervation To elucidate the pathogenetic role of oxidative stress in degenerative processes occurring in denervated muscles and the role of physical exercise in contrasting aging-related sarkopenia. • Oxidative stress in mental disorders A project under development. Collaborations Prof. Arsenio Veicsteinas and Prof. Michele Samaja University of Milan, Italy Prof. Rosanna Abbate University of Florence, Italy Prof. Luisa Gorza and Prof. Ugo Carraro University of Padua, Italy Prof. Giorgio Fanò University of Chieti, Italy Prof. M. Rosaria Faraone-Mennella University of Naples, Italy Dr. Alessandro Ghezzo Fondazione Don Gnocchi, Ancona, Italy Dr. Helmut Kern Wilhelminenspital. Vienna, Austria Publications (last 5 years) 1. Marini M., Lapalombella R., Canaider S., Farina A., Monti D., De Vescovi V., Morellini M., Bellizzi D., Dato S., De Benedictis G., Passarino G., Moresi R., Tesei S., Franceschi C. Heat shock response by EBVimmortalized B-lymphocytes from centenarians and control subjects: A model to study the relevance of stress response in longevity. Experimental Gerontology, 39, 83-90 (2004). 2. Fabbri F., Carloni S., Brigliadori G., Zoli W., Lapalombella R., Marini M. Sequential events of apoptosis involving docetaxel, a microtubule-interfering agent : a cytometric study BMC Cell Biology, 7:6 (2006) 3. Marini M., Lapalombella R., Margonato V., Ronchi R., Samaja M, Scapin C., Gorza L., Maraldi T., Carinci P.,Ventura C., Veicsteinas A. Mild exercise training, cardioprotection and stress gene profile. European Journal of Applied Physiology 99:503-510 (2007) 4. Tavolari S, Bonafé M, Marini M, Ferreri C, Bartolini G, Brighenti E, Manara S, Tomasi V, Laufer S, Guarnieri T. Licofelone, a dual COX/5-LOX inhibitor, induces apoptosis in HCA-7 colon cancer cells through the mitochondrial pathway independently from its ability to affect the arachidonic acid cascade. Carcinogenesis 29:371-380 (2008) 5. Marini M., Falcieri E., Margonato V., Treré D., Lapalombella R., di Tullio S., Marchionni C., Burattini S., Samaja M., Esposito F., Veicsteinas A. Partial persistance of exercise-induced myocardial angiogenesis following 4-wk detraining in the rat. Histochem Cell Biol 129(4): 479-487 (2008) 6. Lapalombella R., Kern H., Adami N., Biral D., Zampieri S., Scordari A., di Tullio S., Marini M. Persistance of regenerative myogenesis in spite of down-regulation of activity-dependent genes in long-term denervated rat muscle. Neurological Research 30 (2): 197-206 (2008) 7. Malagolini N., Chiricolo M., Marini M., Dall'Olio F. Exposure of alpha-2,6-sialylated lactosaminic chains marks apoptotic and necrotic death in different cell types. Glycobiology 19(2):172-181 (2009) 8. Romani R, De Medio GE, di Tullio S, Lapalombella R, Pirisinu I., Margonato V, Veicsteinas A, Marini M, Rosi G. Modulation of paraoxonase 1 and 3 expression after moderate exercise training in the rat Journal of Lipid Res (2009) e-pub 16 Dec 2008; PMID: 19091700. 9. Giusti B., Marini M. , Rossi L., Lapini I., Magi A., Capalbo A., Lapalombella R., di Tullio S., Samaja M., Esposito F., Margonato V., Boddi M., Abbate R., Veicsteinas A. Gene expression profiling in rat left ventricle after 10-week mild exercise training Conditionally Accepted now under revision. 10. Esposito F, Ronchi R, Milano G, Margonato V, Paracchino E, Di Tullio S, Marini M, Veicsteinas A, Samaja M. Long-term training in rats improves reversibly myocardial tolerance to ischemia- reperfusion via stress protein signaling Submitted 11. Squecco R., Kern H., Carraro U., Pond A., Adami N., Biral D., Vindigni V., Boncompagni S., Pietrangelo T., Bosco G., Fanò G., Marini M., Abruzzo P. M., Germinario E., Danieli-Betto D., Protasi F., Francini F., Zampieri S. Despite lost contractility, a sub-population of rat muscle fibers maintains an assessable excitation-contraction coupling mechanism after long-standing denervation Submitted 12. Faraone-Mennella M.R., Marini M, Ferone A., Cacace A., Liguoro A., Margonato V., Farina B., Veicsteinas A. Physical exercise activates the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation system in rat testes Submitted
Scaricare