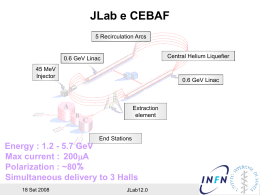
Commissione Scientifica Nazionale III Torino 16 Settembre 2013 L’esperimento JLAB12 : stato e prospettive M.Battaglieri & G.M.Urciuoli per conto della collaborazione JLAB12 INFN -GE, INFN-RM1 Italy 1 Sommario ✴ Jefferson Lab a 6 GeV e progressi verso l’ upgrade a 12 GeV ✴ Il programma di fisica a Jlab. ✴ JLAB12: la collaborazione italiana a Jlab 2 I parametri del CEBAF ✴ Fascio primario: Elettroni ✴ Energia del fascio: 4 GeV (iniziale) • 10 > λ > 0.1 fm transizione nucleone → quark stati eccitati barionici e mesonici 6 GeV nel passato 12 GeV prossimamente ✴100% Duty Factor (cw) Beam • esperimenti in coincidenza • Tre fasci simultanei di energia e intensità variabili indipendentemente e in modo complementare, esperimenti lunghi ✴ Polarizzazione (fascio e prodotti di reazione) • gradi di libertà di spin • correnti neutre deboli L > 106 x SLAC al tempo degli esperimenti originali DIS! La luminosità di JLab12 aumenterà di un fattore 10 x 3 Jefferson Lab nel passato (6 GeV) 4 The 12 GeV upgrade Il disegno e le performance del CEBAF hanno reso l’upgrade in energia “facile”. •Le cavità RF del CEBAF eccedono le specifiche di disegno di un 50% •Ottenuta di routine un’energia massima di fascio di 6 GeV (energia massima •nominale: 4 GeV) • ARCS puo’ fornire un fascio di elettroni sino a 24 GeV ✴ Upgrade dell’acceleratore ✴ Costruzione di nuovi apparati per Hall A, B e C ✴ Costuzione di una nuova sala sperimentale (Hall D) L’upgrade del CEBAF a 12 GeV (la più alta priorità del 2007 NSAC Long Range Plan) è quasi ultimato •Il progetto è “on cost and on schedule” e quasi completato •Le operazioni iniziali con il fascio inizieranno in Hall A nella prima metà del 2014 e l’acceleratore sarà completamente operativo entro giugno 2015 Il programma di ricerche a 12 GeV sta evolvendo rapidamente 5 CEBAF @12 GeV Add new hall Upgrade magnets and power supplies CHL-2 Enhance equipment in existing halls 6 Gli apparati per Jlab a 12 GeV Hall A – Spettrometri ad alta risoluzione e un nuovo rivelatore multipurpose a grande accettanza short range correlations, fattori di forma e nuovi esperimenti : SOLID, MOELLER, SBS Hall C – Super High Momentum Spectrometer (SHMS) Determinazione precisa delle proprietà dei q di valenza nei nucleoni e nei nuclei Hall D – Rivelatore GLUEx per esperimenti di fotoproduzione Hall B – Rivelatore a grande accettanza CLAS12 for misure a grande luminosità (1035cm-2s-1) Comprensione della struttura del nucleone via GPDs and TMDs e spettroscopia adronica 7 Le origini del confinamento attraverso lo studio dei mesoni ibridi Time schedule & Costi 18 maggio 2012: completato il programma a 6 GeV ! 16 mesi di installazione : maggio 2012 – settembre 2013 Commissioning Hall A inizia: febbraio 2014 Commissioning Hall D inizia: ottobre 2014 Commissioning Hall B/C inizia: gennaio/febbraio 2016 Completamento del progetto: marzo 2017 ✴12 GeV - Total project cost: 310M$ ✴~75% completed (~90% obligated) at June 2013 ✴Base equipment fully funded by DOE ✴JLAB12 (Italy) contributes to extra 8 equipment Missione scientifica di Jlab ✴Capire come gli adroni sono formati dai quark e dai gluoni ✴Capire le basi della QCD per la forza nucleone-nucleone ✴Esplorare i limiti della nostra comprensione della struttura nucleare • Alta precisione • Corte distanze • La transizione dalla descrizione nucleone-mesone alla descrizione da QCD ✴Per fare progressi in queste aree dobbiamo rispondere a una serie di ✴interrogativi: • Qual’è il meccanismo del confinamento? • Dove la dinamica dell’interazione q-q compie una transizione dal regime forte (confinamento) al regime perturbativo QCD (tipo QED) ? Esplorare nuova fisica attraverso test di alta precisione del Modello Standard 9 9 JLab12 science: today and in the 12 GeV era ✴Nucleon Structure • • EM, EW, and Flavor-Separated Form Factors Transverse Momentum Distributions (TMD) ✴Nuclear Structure and the Quark Structure of Nuclei • Hypernuclear Physics Quark Electro-Weak Couplings and Standard Model Tests ✴The Physics of Confinement – the Search for Hybrid Mesons 10 NUCLEON STRUCTURE from elastic form factors to TMDs & GPDs The Proton and Neutron are the “Hydrogen Atoms” of QCD What we “see” changes with spatial resolution >1 fm Nucleons 11 0.1 — 1 fm Constituent quarks and glue < 0.1 fm “bare” quarks and glue S=1/2 S=1/2 S=1/2 Q=1 Q=1 Q=1 NUCLEON STRUCTURE from elastic form factors to GPDs X. Ji, D. Müller, A. Radyushkin (19941997) Elastic Scattering transverse quark distribution in Coordinate space (charge and current densities) 12 Deep Exclusive Scattering fully-correlated quark distribution in both coordinate and momentum space (GPD&TMD) Deep Inelastic Scattering longitudinal quark distribution in momentum space (momentum and helicity distributions) JLab data on the EM form factors provide a testing ground for theories constructing nucleons from quarks and glue Before JLab and Recent non-JLab Data 13 JLab data on the EM form factors provide a testing ground for theories constructing nucleons from quarks and glue Today, including new JLab Data 14 JLab data on the EM form factors provide a testing ground for theories constructing nucleons from quarks and glue Today, including new JLab Data, compared to theory 15 Form Factors – Plans for 12 GeV 16 Today Form Factors – Plans for 12 GeV 17 JLab at 12 GeV SBS Spectrometer in Hall A • • • • High luminosity Moderate acceptance Forward angles Reconfigurable detectors ⇓ Form Factors at high Q2 Precision SIDIS JLab12 Responsibility •Front Tracker (GEM+SiD) •Readout Electronics (FT) BA, CT, GE, ISS, RM1 SiD 18 UVa U. of Glasgow JLab Norfolk State U. INFN Rutgers U. Carnegie Mellon U. College WM U. of New Hampshire SBS Tracker : • Based on the recent GEM technology and Silicon Microstrips • Large chamber, small dead area, minimum material budget, for high luminosity experiments Front Tracker GEM construction process Revision Foils from GEM CT Stretching Gluing the next frame with spacers GE Sanità/BA: Test and characterization by cosmics (Analysis example) Noise level ~ 10 ADC unit Electronics based on APV25 chip Radiation Tolerant Components in FEC VME64x compliant readout Modular Front Tracker GEM construction process Revision Stretching Foils from CERN Gluing Frame CT/Clean Room Integrate electronics, gas pipes, HV ...) Compressing (uniform gluing, remove air from glue and contact surfaces) GE Sanità/BA: Test and characterization by cosmics (Analysis example) Noise level ~ 10 ADC unit Electronics based on APV25 chip Radiation Tolerant Components in FEC VME64x compliant readout Modular Primi moduli GEM finali 40x50 cm2 Solenoid 2x2 small scintillators as telescope for trigger One big GEM in solenoid open space One big GEM beyond the magnet as reference tracking Basically all final components under test (big GEMs, electronics, gas system, cabling ...) Analysis in progress --Beam Profile BigGEM in solenoid X y Clean hits vs time x Small GEM, ref. y BigGEM as 2xGEM, ref. 21 Rivelatore a microstrisce di silicio: 105 mm Strip Pitch 50 µm DC PAD for bonding (200x40 µm2) Guard Ring PAD (500x90 µm2) 22 Circuiti stampati per il piano X e il piano Y Piano X Piano Y 23 Sistema completo con elettronica di lettura APV25 Backplane Kapton 24 25 SBS Tracker: summary • Participants: • • • • • • INFN/BA – gas system and test INFN/CT – GEM assembling, mechanics, test, analysis INFN/GE – electronics design INFN/ISS – design, test, analysis and coordination INFN/RM1 – Silicon tracker JLab, Glasgow, UvA, Ruthers, UNH, CMU – SBS collaboration • Funding: (prototyping and realization) 1 M$ • Status: most of the components procured or ordered; GEM assembling underway; characterization in progress. Silicon Microstrip prototype ready by the end of 2013. Silicon microstrip planes ready by the end of 2014. • Expected installation 2015 (delayed by JLab/HallA schedule) • Note: project delayed by ~ 1 year – due mainly to foil delivery and first quality check failures. Do not affect JLab plan! HCAL-J Design 24 Modules (360cm) HCAL-J based on COMPASS HCAL1 Each module: 15 cm x 15 cm Layered scintillator and iron Replicate with small design modifications 288 modules for JLab HCAL Integral WLS/ Light guide Acrylic with Coumarin-7 impregnated surface 5 mm thick 40 layers 20 mm iron / 5 mm scintillator Light Guide /WLS Existing HCAL1 in COMPASS Novel light guide for 1 in PMTS Steel casing Hole in downstream light guide 27 Hypernuclei at JLab Study -N Interaction potential Experimental requirements: - Excellent Energy Resolution - Detection at very forward angles (6°→septum magnets) - Excellent PId for kaon selection →RICH - High luminosity Experiment E94-107 Hypernuclear spectroscopy 9Be (e,e’k+) 9 Li reaction Λ Published Reactions Investigated: 9Be→9Li (3 spin doublets, information on Δ) Λ 12C→12B (evidence of excited core states → Λ sN contribution) 16O→16N (unmatched peak may indicate Λ large sΛ term) H →Λ,Σ0 (elementary process) Analisi dell’esperimento sulla produzione di ipernuclei a Jlab completamente in mano alla collaborazione italiana: - M. Iodice, F. Cusanno et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 052501 (2007) (ipernucleo 12ΛB) - F. Cusanno, G.M. Urciuoli et al., Phys Rev. Lett. 103 202501 (2009) (ipernucleo 16ΛN) - G.M. Urciuoli, F. Cusanno, S. Marrone et al. Sottomesso a PHYS REV C 28 RM1, ISS Thanks to energy resolution improvements a clear three peak structure appears in the excitation energy spectrum. Experiment E06-007 208Pb(e,e’p)207Tl and 209Bi(e,e’p)207Pb cross sections at true quasielastic kinematics (xB=1, q=1 GeV/c, ω=0.433 GeV/c ) and at both sides of q Never been done before for A>16 nucleus ★ ★ ★ RM1, ISS 29 Determine the spectroscopic factors dependence with Q2 Long range correlations: not needed! Relativistic effect in nuclei: needed! Lead (208Pb) Radius Experiment: PREX Elastic Scattering Parity Violating Asymmetry Hall A Collaboration Experiment E=1GeV, J=5o e on lead A neutron skin established at ~93 % CL 208Pb Neutron Radius RN = 5.78 + 0.16 - 0.18 fm Neutron Skin RN - RP = 0.33 + 0.16 - 0.18 fm PREX-II Approved by JLabPAC (Aug 2011) with high rating 30 RM1 Future equipment for PaVi experiments at JLab SOLID (PV e- - q scattering + SIDIS) - PV e-quark - High precision TMD 31
Scaricare