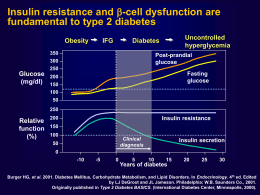
Nuovi approcci alla terapia personalizzata del paziente con diabete di tipo 2 Riccardo C. Bonadonna Dipartimento di Medicina Università di Verona e AOUI di Verona Presenter Disclosure Information Riccardo C. Bonadonna Research Support: None Speaker’s Bureau: Sanofi Aventis, MSD, BMS, Eli Lilly Ltd Board Member/Advisory Panel: MSD, Eli Lilly Ltd, Amgen, Sanofi Aventis Stock/Shareholder: None Consultant: None Employee: None Other: None The position statement of ADA and EASD • Individualisation of treatment is the cornerstone of success • Patient-centered care is…an approach to “providing care that is respectful of and responsive to individual preferences, needs, and values and ensuring that patient values guide all clinical decisions” Inzucchi SE et al.; Diabetologia 2012 Alcuni bisogni di questo paziente • Rieducazione nutrizionale • Rieducazione motoria • Tre cali: – Peso – Appetito – Glicemia post-prandiale • Limitare il rischio delle ipoglicemie • Limitare il numero di iniezioni Dipendenza psicofisica A classification of GLP-1 RAs Comparison of prandial vs. non-prandial GLP-1 receptor agonists Parameters Prandial GLP-1 Ras Non-prandial GLP-1 Ras (short-acting, exendin-4 derived) (short-acting, GLP-1 derived*) Exenatide, Lixisenatide Albiglutide*, Dulaglutide*, Exenatide-LAR, Liraglutide* 2-5h 12h-several days Fasting blood glucose levels Modest reduction Strong reduction Post-prandial glucose levels Strong reduction Modest reduction Modest stimulation Strong stimulation Post-prandial insulin secretion Reduction Modest stimulation Glucagon secretion Reduction Reduction Deceleration No effect Reduction Reduction No effect or small increase (0-2 bpm) Moderate increase (2-5 bpm) 1-5kg 2-5kg 20-50%, attenuates slowly (weeksmany months) 20-40%, attenuates quickly (~4-8 weeks) Compounds Half-life Effects Fasting insulin secretion Gastric emptying rate Blood pressure Heart rate Body weight reduction Induction of nausea Meier J et al.; Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012 Lixisenatide prolongs gastric emptying time and blunts aftermeal glucose excursions in patients with type 2 diabetes 300 Time (min) 250 Placebo Lixisenatide ¶ P=0.003 Lixisenatide vs Placebo ¶ 200 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 Change from baseline in gastric emptying t 1/2 Lorenz M et al.; Regulat Pept, 2013 Lixisenatide decreases the absolute amounts of insulin and glucagon released after breakfast in patients with type 2 diabetes Post-breakfast AUC (h.pmol/L) 1200 1000 800 Placebo Lixisenatide ¶ P=0.004 Lixisenatide vs Placebo Post-breakfast change AUC (h.pmol/L) Placebo 14 12 Lixisenatide ¶ P=0.007 Lixisenatide vs Placebo 10 ¶ 600 400 200 0 Insulin AUC 8 6 ¶ 4 2 0 Delta Glucagon AUC Lorenz M et al.; Regulat Pept, 2013 Domanda • Exenatide e lixisenatide sono due farmaci sovrapponibili? Lixisenatide vs Exenatide. The GetGoal-X study. Lixisenatide vs Exenatide in addition to: Metformin ≥ 1.5 g/day 1 wk 20 µg qd Lixisenatide 15 µg 1 wk 10 µg Key Inclusion Criteria: Type 2 DM HbA1c ≥7.0% – ≤10.0% Stratified by A1c (<8.0%/≥8.0%) All patients: background treatment at a stable dose Diet & lifestyle counselling every 3 months from D1 R 5 µg bid 4 wks 10 µg bid Single-blind Screening run-in W-3 W-1 W0 Exenatide Main double-blind treatment period W4 Rosenstock J et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 W12 Variable extension period W24 Primary endpoint 3 d F/U W44 End of treatment F/U Visit Lixisenatide has similar glucose lowering efficacy and somewhat less weight lowering efficacy compared to exenatide. The GetGoal-X study. Glucose control Body weight Rosenstock J et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 Lixisenatide causes nausea and hypoglycemia significantly less frequently than exenatide. The GetGoal-X Study. ¶ ¶ ¶ P < 0.05 or less for Lixisenatide vs Exenatide Rosenstock J et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 GetGoal program: Lixisenatide in patients uncontrolled on 1 or 2 OADs Placebo-controlled trials Basal insulin OADs Active comparator-controlled trial 2 OADs GetGoal-L Add-on to basal insulin ± MET 1 OAD GetGoal-S Diet and exercise Add-on to SU ± MET GetGoal-M Add-on to MET GetGoal-Mono Add-on to MET Add-on to pioglitazone ± MET GetGoal-M-Asia Add-on to MET± SU GetGoal-Mono Japan GetGoal-X Monotherapy Add-on to MET Add-on to basal insulin ± SU GetGoal-P GetGoal-F1 Monotherapy GetGoal-L-Asia GetGoal-Duo1 Add-on to insulin glargine +MET ±TZD Lixisenatide in aggiunta alla terapia con insulina basale: le evidenze Lixisenatide added to basal insulin. The GetGoal-L study. Lixisenatide vs Placebo in addition to: Basal insulin ± metformin 1 wk 20 µg Lixisenatide 15 µg 1 wk 10 µg Key Inclusion Criteria: Type 2 DM HbA1c ≥7.0% – ≤10.0% Stratified by A1c (<8.0%/≥8.0%) All patients: background treatment at a stable dose Diet & lifestyle counselling every 3 months from D1 R 10 µg 1 wk 15 µg 1 wk 20 µg Single-blind Screening run-in W-3 W-1 W0 Placebo Main double-blind treatment period W4 Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 W12 Variable extension period W24 Primary endpoint 3 d F/U W44 End of treatment F/U Visit Lixisenatide added on basal insulin (±metformin) reduces HbA1c, body weight and daily insulin dose. The GetGoal-L study Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 After-meal glucose excursion (mmol/L) Lixisenatide added on basal insulin (± metformin) reduces post-prandial glucose excursions. The GetGoal-L study 10 8 ¶ P<0.0001 Lixisenatide vs Placebo 6 Basal insulin (±metformin) + placebo (n=204) 4 2 ¶ 0 Basal insulin (±metformin) + lixisenatide (n=194) -2 -4 -6 Baseline Week 24 LOCF LS mean change Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 Lixisenatide added to basal insulin + metformin. The GetGoal-Duo study. Lixisenatide in addition to:: Basal insulin + metformin (±TZDs) 1 wk 20 µg Lixisenatide 15 µg 1 wk 10 µg Key Inclusion Criteria: Type 2 DM HbA1c ≥7.0% – ≤10.0% Stratified by A1c (<8.0%/≥8.0%) All patients: background treatment at a stable dose Diet & lifestyle counselling every 3 months from D1 R 10 µg 1 wk 15 µg 1 wk 20 µg Single-blind Screening run-in W-3 W-1 W0 Placebo Main double-blind treatment period W4 Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 W12 Variable extension period W24 Primary endpoint 3 d F/U W44 End of treatment F/U Visit Lixisenatide added on basal insulin + metformin reduces HbA1c, body weight and insulin doses. The GetGoal-Duo study Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 After-meal glucose excursion (mmol/L) Lixisenatide added on basal insulin + metformin reduces post-prandial glucose excursions. The GetGoal-Duo study 8 6 ¶ P<0.0001 Lixisenatide vs Placebo 4 Basal insulin + metformin (±TZDs) + placebo (n=211) 2 ¶ 0 Basal insulin + metformin (±TZDs) + lixisenatide (n=194) -2 -4 -6 Baseline Week 24 LOCF LS mean change Riddle MC et al.; Diabetes Care 2013 Conclusioni • Gli agonisti del GLP1-R sono ulteriormente classificabili in agonisti prandiali (breve durata d’azione, derivati da exendin-4) e non-prandiali (lunga durata d’azione) • Lixisenatide ed exenatide, i due GLP1-R prandiali, presentano sensibili differenze in effetti terapeutici e collaterali e in facilità d’uso • Lixisenatide, in virtù dei suoi spiccati effetti nel periodo post-prandiale, si presta a essere usata in combinazione/aggiunta all’insulina basale per raggiungere un controllo ottimale anche delle iperglicemie post-prandiali, con ulteriori effetti benefici su peso, appetito e pressione arteriosa Grazie per l’attenzione Human pancreas and incretin therapy Nondiabetic Controls DM DM on Incretins Nondiabetic Controls DM 2,5 DM on Incretins % Area 2 140 120 1,5 Weight (g) 100 1 80 60 40 0,5 20 0 0 Beta cell area Alpha cell area Pancreas weight Butler AE et al.; Diabetes (in press) Human pancreas and incretin therapy. Diabetic patients not on incretin therapy ID Code Age Diabetes duration Age at diabetes diagnosis BMI Rx Cause of Death 6028 33 17 16 30 Insulin Gunshot 6059 18 0.3 17 39 None CV 6108 57 2 55 30 Met ICH/Stroke 6110 20 0.2 20 40 None ICH/DKA 6109 48 - 48 33 None ICH/DKA 6114 42 2 40 31 Met Asphyxia 6124 62 3 59 34 Met ICH/Stroke 6127 44 10 34 30 Insulin ICH/Stroke 6133 45 20 25 40 Insulin CV 6139 37 1.5 35.5 45 None Seizure 6142 29 14 15 34 None Meningitis 6149 39 20 19 29 Insulin ICH/Stroke Butler AE et al.; Diabetes (in press)
Scarica