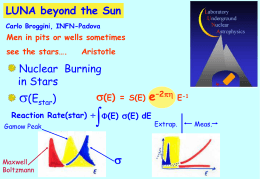
LUNA at LNGS Alessandra Guglielmetti Universita’ degli Studi di Milano and INFN, Milano, ITALY Outline: -Nuclear Fusion reactions in stars -Why going underground -The Luna Experiment -Future perspective Laboratory Underground Nuclear Astrophysics Hydrogen burning Produces energy for most of the life of the stars pp chain p + p d + e+ + n e d + p 3He + g 84.7 % 3He 13.8 % +3He a + 2p 3He +4He 7Be + g 0.02 % 13.78 % 7Be+e- 7Li 7Li + g +ne +p a+ a 7Be 8B + p 8B + g 2a + e++ ne 4p 4He + 2e+ + 2ne + 26.73 MeV Nuclear reactions in stars Sun: T= 1.5 107 K kT = 1 keV<< EC (0.5-2 MeV) Reaction 3He(3He,2p)4He E0 21 keV d(p,g)3He 6 keV 14N(p,g)15O 27 keV 3He(4He,g)7Be 22 keV Cross section and astrophysical S factor 1 (E) exp(- 31.29Z1Z 2 /E ) S(E) E Astrophysical Gamow energy region Gamow factor EG factor Cross section of the order of pb! S factor can be extrapolated to zero energy but if resonances are present? Sub-Thr resonance Extrapol. Mesurements Tail of a broad resonance Narrow resonance Non resonant process Danger in extrapolations! Sun Luminosity (irradiated energy per time) = 2 ·1039 MeV/s Q-value (energy for each reaction) = 26.73 MeV Reaction rate = 1038 s-1 Rlab= ··Ip··Nav/A Laboratory ~ 10 % IP ~ mA ~ g/cm2 pb < < nb event/month < Rlab < event/day Underground Laboratory Cross section measurement requirements Environmental radioactivity has to be considered underground shielding Rlab > Bcosm+ Benv + Bbeam induced Beam induced bck from impurities in beam & targets high purity 3MeV < Eg < 8MeV: 0.5 Counts/s 1,00E+00 HpGe 1,00E+00 GOING UNDERGROUND 1,00E-01 1,00E-02 1,00E-03 1,00E-01 1,00E-02 counts counts 3MeV < Eg < 8MeV 0.0002 Counts/s 1,00E-04 1,00E-03 1,00E-04 1,00E-05 1,00E-05 1,00E-06 1,00E-06 0 2000 4000 6000 Eg [keV] 8000 10000 0 2000 4000 Eg[keV] 6000 8000 10000 Laboratory for Underground Nuclear Astrophysics LUNA site LNGS (shielding 4000 m w.e.) LUNA 1 (1992-2001) 50 kV LUNA 2 (2000…) 400 kV Radiation LNGS/surface Muons Neutrons 10-6 10-3 Laboratory for Underground Nuclear Astrophysics 400 kV Accelerator : I max 500 A protons I Energy spread 70 eV E beam 50 – 400 keV max 250 A alphas Long term stability 5eV/h LUNA "non solar phase" 2006-ongoing (p,g) reactions on : Nitrogen, Oxygen, Neon, Sodium and Magnesium isotopes belonging to: CNO, NeNa and MgAl cycles of Hydrogen burning Important for second generation stars with temperature and mass higher than those of our Sun Seeds of the reactions already present Higher Coulomb barrier: these cycles are unimportant for energy generation but essential for nucleosynthesis of elements with A>20 D(4He,g)6Li 6Li detected in metal poor stars is unexpectedly large compared to BBN predictions. D(4He,g)6Li is the main reaction for 6Li production No direct measurements for Ecm<650 keV Theoretical calculations for the S-factor differ by more than one order of magnitude data taking concluded reaction CNO cycle In progress Ne-Na cycle BBN Q-value (MeV) Gamow energy (keV) 12.13 10-300 130 50 17O(p,g)18F 5.6 35-260 300 65 18O(p,g)19F 8.0 50-200 143 89 23Na(p,g)24Mg 11.7 100-200 240 138 22Ne(p,g)23Na 8.8 50-300 250 68 1.47 50-300 700(direct) 50(indirect) 50 15N(p,g)16O D(a,g)6Li Lowest meas. Energy (keV) In progress proposal approved by LNGS SC in 2007 LUNA limit LOI to LNGS for a new accelerator for He-burning key reactions 3.5 MeV accelerator Reaction rate Estimate At LUNA 12C(a,g)16 O The “Holy Grail” Reaction rate Estimate At LUNA 13C(a,n)16 O Reaction rate Estimate At LUNA 22Ne(a,n)25M g Recoil mass separator approach A+aC+g A Cn+ a detection A/C>1015 g A detection separation - low induced background - high detection efficiency - measurement of tot - low background g-ray spectra coincidence European Recoil-separator for Nuclear Astrophysics ion source tandem accelerator ion beam purification: velocity and momentum filter beam preparation g detection setup recoil focusing magnetic quadrupole multiplets ion beam emittance control 4He gas target recoils separation Wien filter (velocity) 60° magnet (momentum) Wien filter TOF/DE-E (velocity) detector ERNA experimental program Hydrogen burning and neutrino flux from 8B 3He(a,g)7Be measured in Bochum 7Be(p,g)8B Helium burning and synthesis of Oxygen and Fluorine 12C(a,g)16O measured in Bochum down to ~2 MeV CM 14N(a,g)18F(b+)18O 15N(a,g)19F LUNA COLLABORATION Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, INFN, ASSERGI: A.Formicola, C.Gustavino, M.Junker Forschungszentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Germany D. Bemmerer, M.Marta INFN, Padova, Italy C. Broggini, A. Caciolli, M. Erhard, R.Menegazzo, C. Rossi Alvarez Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary Z.Elekes, Zs.Fülöp, Gy. Gyurky, E.Somorjai Osservatorio Astronomico di Collurania, Teramo, and INFN, Napoli, Italy O. Straniero Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany C.Rolfs, F.Strieder, H.P.Trautvetter Seconda Università di Napoli, Caserta, and INFN, Napoli, Italy F.Terrasi Università di Genova and INFN, Genova, Italy F. Confortola, P.Corvisiero, H. Costantini, A. Lemut, P.Prati Università di Milano and INFN, Milano, Italy V. Capogrosso, A.Guglielmetti, C. Mazzocchi Università di Napoli ''Federico II'', and INFN, Napoli, Italy G.Imbriani,B. Limata, V.Roca Università di Torino and INFN, Torino, Italy G.Gervino ERNA COLLABORATION INFN, Napoli, Italy M. De Cesare, N. De Cesare, A. Di Leva, A. D'Onofrio, L. Gialanella, G. Imbriani, B. Limata, M. Romano, D. Schuermann, F.Terrasi, S. Cristallo, L. Piersanti INFN, Napoli, Italy M. Busso, R. Guandalini, M. Nucci, S. Palmerini. A. Salterelli Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany D. Rogalla, C.Rolfs, F.Strieder Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary University of Connecticut, USA CNRS Orsay, France University of Jerusalem, Israel
Scarica