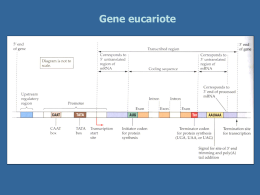
Celiac disease DQ2 or DQ8 HLA variants are necessary for onset and development of celiac disease Typical symptoms of CD: diarrhea abdominal distention delayed growth High risk for the disease: first degree of patients with CD (up to 12-15%) others disorders: -type 1 diabetes -Down syndrome -deficit IgA MALATTIA CELIACA GEMELLI MONOZIGOTI GEMELLI DIZIGOTI 80 % 20 % HLA TYPING MAY BE USEFUL a negative test for HLA DQ2-DQ8 has a high negative predictive value wich may have a role in those with borderline histology or serology a positive family history is another indication where HLA typing may be useful. Those who are HLA compatible for CD need follow up also if are initially negative, whereas those are HLA DQ2 and DQ8 negative may be discharged. wheat GLUTEN -gliadins -gliadins -gliadins Glutenins + α γ ω RUN Gliadin structure α-gliadin 290 aa C: N /translation="MVRVPVPQLQPQNPSQQQPQEQVPLVQQQQFPGQQQPFPPQQPY PQPQPFPSQQPYLQLQPFPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQPFRPQQPYPQSQPQY SQPQQPISQQQQQQQQQQQQKQQQQQQQQILQQILQQQLIPCRDVVLQQHSIAYGSSQ VLQQSTYQLVQQLCCQQLWQIPEQSRCQAIHNVVHAIILHQQQQQQQQQQQQPLSQVS FQQPQQQYPSGQGSFQPSQQNPQAQGSVQPQQLPQFEEIRNLALETLPAMCNVYIPPY CTIAPVGIFGTNYR - gliadin product="alpha-gliadin" ORIGIN 1 61 121 181 241 301 361 421 481 541 601 661 721 781 841 atggttagag gagcaagttc caacagccat ccatttccgc ctaccatatc cagtattcgc caacaaaaac ctaattccat gttttgcaac atccccgagc caacagcaac cagcctcaac caggcccagg gcgctagaga ccagttggca ttccagtgcc cattggtaca atccgcagcc agccgcaact cgcagccgca aaccacaaca aacaacaaca gcagggatgt aaagtactta agtcgcggtg aacaacaaca aacaatatcc gctctgtcca cgctacctgc tcttcggtac acaattgcag acaacaacaa gcaaccattt accatatccg accatttcga accaatttcg acaacaacaa tgtattgcaa ccagctggtg ccaagccatc acaacaacaa atcaggccag gcctcaacaa aatgtgcaat taactatcga ccacaaaatc tttccagggc ccatcacaac cagccgcaac ccacaacaac cagcagcagc cagatccttc caacacagca caacaattgt cacaatgttg caacaaccgt ggctccttcc ctgccccagt gtctatatcc tga catctcagca agcaacaacc aaccatatct taccatatcc catatccaca agcagcagca aacaaatttt tagcgtatgg gttgtcagca ttcatgctat tgagccaggt agccatctca ttgaggaaat ctccatattg acaaccacaa atttccacca gcagctgcaa gcagccgcaa atcgcaacca acaacaacaa gcaacaacaa aagctcacaa gctgtggcag tattctgcat ctccttccaa gcaaaaccca aaggaaccta caccattgct 33-mer large peptide LQLQPFPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQPF 1 LQLQPFPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQLPYPQPQPF 1 3 2 N - gliadin The trimolecular complex Peptide 1-domain 1-domain HLA 2-domain 2-domain Ig homology folds intestinal lumen toxic gluten (33 mer) lamina propria MICA (MHC class I- related chain A) NKG2D intestinal lumen toxic gluten Il-15 O C H2N NH2 O O- C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 C C H Gln COOH H2N H Glu COOH Linfocita T4 helper maturo Secrezione di Lymphocytes B Linfocita T4 helper Secrezione di IL1 da parte del macrofago IL2 Proliferazione dei linfociti B attivati plasmacellule SEROLOGICAL TESTS Tissue transglutaminase antibody [ELISA] Endomysial antibody [Indirect immunofluorescence] Antibodies against deamidated gliadin [ELISA] Schermo televisivo Endoscopio Telecamera Duodenal biopsy is necessary alwais? The advent of highly sensitive and specific serological markers has led to some protagonist proposing that celiac disase can be diagnosed without the need for a biopsy. However, this is an area of controversy. Sequence Specific Primers SSP Match esatto → Amplificazione (Allele specifico) Mismatch → Nessuna Amplificazione (Allele non specifico) GENOTYPES DQ2 → DQA1*0501 - DQB1*0201 DQ8 → DQA1*03 - DQB1*0302 Chromosome 6 Genomic sequence: 6,295 bases Aminoacids: 232 HLA SYSTEM Class II DP DQ Class III Class I DR B C E B1 A1 tel cent C4A TNXA TNXB C4B gene espresso RP1 gene non espresso RP2 CYP21P CYP21 30 kb A DQA1 gene map 5’ 3’ IVS1 (4kb) 1 2 3 4 chain chain 1 1 NH2 N2H 2 COOH 2 COOH There are 27 DQA1 nucleotide sequences currently reported in the HLA sequence database http://www.ebi.ac.uk/imgt/hla Specific PCR amplifications group 1 → DQA1*01 group 2 → DQA1*02, *04, *05 group 3 → DQA1*03 Sequencing-based typing (SBT) Chromosome 6 DQB1 gene Genomic sequence: 7,347 bases Aminoacids: 261 Chr6 Classe II DP DQ Classe III Classe I DR B C E B1 A1 tel cent C4A gene espresso gene non espresso RP1 TNXA RP2 CYP21P TNXB C4B CYP21 30 kb A DQB1 gene Seq. Leader 1-domain 5 5’ 1 1,5kb 2- domain transmembrane and tail 95 3’ 2,5kb 2 chain 3 chain 1 1 NH2 N2H 2 COOH 2 COOH 4 5 NEW THERAPEUTIC APPROACH 111 endopeptidase Flavobacterium meningosepticum pH pH pH pepsin C: Bacterial prolyl-endopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum removes gluten toxicity by cleaving it into small fragments Gli enzimi prolyl oligopeptidase hanno l’ottimo di pH tra 7 e 8 e così non possono funzionare a pH acido dello stomaco; inoltre esse sono efficientemente distrutte dalla pepsina secreta dallo stomaco. Queste proprietà implicano che la supplementazione orale con prolil oligopeptidasi non è ancora sufficiente a degradare il glutine prima che arrivi nella parte prossimale del duodeno. Aspergillus niger prolyl-endopeptidase pH pH compatible Resistant to degradation pH by pepsin C: The prolyl-endoprotease from Aspergillus niger (AN-PEP) is a member of the serine peptidase family, and this degrades gluten peptides rapidly. This AN-PEP is capable of accelerating the degradation of gluten in a gastrointestinal model that closely mimics in-vivo digestion. The pH optimum of the enzyme is compatible with that found in the stomach, and the enzyme is resistant to degradation by pepsin. Grazie per l’attenzione Piero Sammarco
Scarica