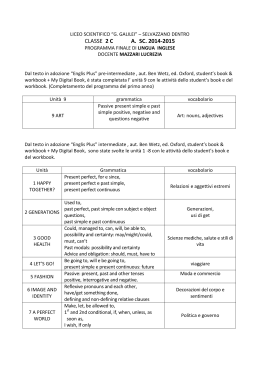
PAST SIMPLE O PRESENT PERFECT? Definizione Il Past simple e il Present perfect non sono intercambiabili. Il Past simple si usa con azioni finite ed espressioni di tempo passato. Il Present perfect si usa quando un’azione avvenuta nel passato ha conseguenze importanti nel presente, o quando non è chiaramente espresso il momento in cui l’azione è avvenuta. _____(past simple)_____l_________________ past now future Present perfect _________---------------------------I___________ past now Come si formano Present perfect: HAVE/HAS + PARTICIPIO PASSATO Past simple: per i verbi regolari si forma aggiungendo -ed all’infinito senza to, mentre quelli irregolari hanno una forma propria. AFFERMATIVA I have written a book. I wrote a book. NEGATIVA I haven’t written a book. I didn’t write a book. INTERROGATIVA Have you written a book? Did you write a book? INTERROGATIVA-NEGATIVA Haven’t you written a book? Didn’t you write a book? Quando si usano -1 • Per eventi conclusi che hanno conseguenze visibili nel presente: I’ve been to the hairdresser. Do you like my new hair colour? ⇩ Si vedono i capelli appena tinti. • Per eventi nel passato che non hanno rapporto con il presente: I went to the hairdresser only once last year. ⇩ Non c’è nessun rapporto con il presente. Quando si usano -2 • Per eventi ed esperienze fatte in un passato indefinito: We’ve visited so many museums. ⇩ Non è specificato quando. • Per eventi nel passato accaduti in un momento preciso: We visited an interesting museum last week end. ⇩ È chiaramente indicato quando. Quando si usano -3 • Per eventi accaduti in un periodo di tempo non ancora concluso nel momento in cui si parla, es. today, this morning….: This morning I’ve called all the hotels on the list. ⇩ È ancora mattina. • Per eventi nel passato accaduti quando quella parte della giornata è già conclusa, es. this morning, this afternoon, today (quando è sera): This morning I called all the hotels on the list. ⇩ Non è più mattina. Quando si usano -4 • Per dare notizie di eventi recenti: There has been a car accident. ⇩ C’è appena stato un incidente. • Per fornire ulteriori dettagli alle notizie annunciate con il Present perfect: There has been a car accident, one of the cars didn’t stop at the traffic lights. ⇩ I dettagli sono al Past simple. Quando si usano -5 • Per parlare di azioni o stati iniziati nel passato che continuano nel presente: Paul has worked for the same company for ten years. ⇩ Ci lavora ancora. • Per dare informazioni dettagliate su esperienze compiute nel passato: Paul started working when he was 20 years old. ⇩ I dettagli sono espressi con il Past simple. Altri usi Nell’inglese americano (AE) si tende a usare il Past simple e il Present perfect indistintamente quando si parla di situazioni che hanno rilevanza nel presente. Nell’inglese britannico (BE) la differenza è più marcata: I just finished my homework. (AE) I’ve just finished my homework. (BE) Did you go to the Picasso exhibit? (AE) si usa se la mostra è ancora in corso, o è già finita. (BE) si usa solo se la mostra è finita. Have you been to the Picasso exhibit? (BE e AE), si usa solo se la mostra è ancora in corso. Per esercitarsi Inserisci il Past simple o Present perfect dei verbi tra parentesi alla forma affermativa, interrogativa o negativa. She.…………………to school since Monday. (not go) He………………..………to work yesterday. (walk) …………………………….the book yet? (you finish) She ………………………..Japanese food. (never eat) Last week………………….a great film on TV.(we watch) …………………………….the film? (you like) I..……………………a good time at the party. (not have) They……………..……………. here? (always live) IT’S TELLY TIME! Mettiti alla prova! Cerca di riconoscere il Present perfect e il Past simple in un contesto reale! How I Met Your Mother - Our First Song http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6eHX7N2KmuI
Scarica