Anteprima Estratta dall' Appunto di
Informatica
Università : Università degli studi di Messina
Facoltà : Informatica
Indice di questo documento
L' Appunto
Le Domande d'esame
ABCtribe.com e' un sito di knowledge sharing per facilitare lo scambio di materiali ed informazioni per lo studio e la
formazione.Centinaia di migliaia di studenti usano ABCtribe quotidianamente per scambiare materiali, consigli e
opportunità Più gli utenti ne diffondono l'utilizzo maggiore e' il vantaggio che ne si può trarre :
1. Migliora i tuoi voti ed il tempo di studio gestendo tutti i materiali e le risorse condivise
2. Costruisci un network che ti aiuti nei tuoi studi e nella tua professione
3. Ottimizza con il tuo libretto elettronico il percorso di studi facendo in anticipo le scelte migliori per ogni esame
4. Possibilità di guadagno vendendo appunti, tesine, lezioni private, tesi, svolgendo lavori stagionali o part time.
www.ABCtribe.com
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 1]
L' Appunto
A partire dalla pagina successiva potete trovare l' Anteprima Estratta dall' Appunto.
Se desideri l'appunto completo clicca questo link.
Il numero di pagina tra le parentesi tonde si riferisce a tutto il documento contenente l'appunto.
Sull'appunto stesso in alcuni casi potrete trovare una altra numerazione delle pagine che si riferisce al solo
appunto.
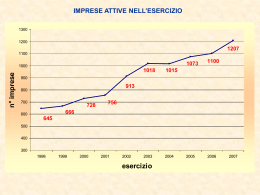
Grafico dei voti medi per questo
esame:
Grafico dei giorni medi per la
preparazione di questo esame:
Grafico Copyright © ABCtribe.com. Vietata la
riproduzione.
Grafico Copyright © ABCtribe.com. Vietata la
riproduzione.
Clicca qui per i grafici aggionati su Informatica >>
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 2]
1 Dots
The graphics objects
\psdot*[par](x1,y1)
\psdots*[par](x1,y1)(x2,y2)… (xn,yn)
put a dot at each coordinate.
What a “dot” is depends on the value of the
Default: *
dotstyle=style
parameter. This also determines the dots you get when showpoints=true.
Style
e.c
o
+
Ct
asterisk
oplus
AB
+
rib
x
Example
• • • • •
*
+
om
The dot styles are also pretty intuitive:
otimes
×
×
Style
Example
square
square*
+
+
+
diamond
♦ ♦ ♦ ♦ ♦
×
×
×
diamond*
◊
∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗
◊
◊
◊
triangle
⊕
⊕
⊕
⊕
⊕
triangle*
⊗
⊗
⊗
⊗
⊗
pentagon
|
◊
pentagon*
Except for diamond, the center of dot styles with a hollow center is
colored fillcolor.
Here are the parameters for changing the size and orientation of the dots:
dotsize=dim ‘num’
Default: 2pt 2
The diameter of a circle or disc is dim plus num times linewidth
(if the optional num is included). The size of the other dots styles
is similar (except for the size of the ¨| dot style, which is set by the
tbarsize parameter described on page ??).
dotscale=num1 ‘num2’
Default: 1
The dots are scaled horizontally by num1 and vertically by num2 .
If you only include num1, the arrows are scaled by num1 in both
directions.
1
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 3]
Default: 0
dotangle=angle
After setting the size and scaling the dots, the dots are rotated by
angle.
2 Arrowheads and such
New arrows:
Value
Example Name
T-bars and arrowheads.
T-bars and arrowheads, flush.
|<->|
|<*->|*
e.c
om
The size of these line terminators is controlled by the following parameters. In the description of the parameters, the width always refers to the
dimension perpendicular to the line, and length refers to a dimension in
the direction of the line.
Default: 1.5pt 2
arrowsize=dim ‘num’
rib
The width of arrowheads is dim plus num times linewidth (if the
optional ‘num’ is inclued). See the diagram below.
Default:
Ct
arrowlength=num
AB
Length of arrowheads, as a fraction of the width, as shown below.
Default:
arrowinset=num
Size of inset for arrowheads, as a fraction of the length, as shown
below.
arrowsize
=
dim num
width
=
num x linewidth + dim1
length
inset
=
=
arrowlength x width
length
inset
width
arrowinset x height
tbarsize=dim ‘num’
Default:
The width of a t-bar, square bracket or rounded bracket is dim
plus num times linewidth (if the optional ‘num’ is included).
bracketlength=num
Default:
The height of a square bracket is num times its width.
Arrowheads and such
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 4]
2
Default:
rbracketlength=num
The height of a round bracket is num times its width.
arrowscale=arrowscale=num1 ‘num2’
Default:
Imagine that arrows and such point down. This scales the width
of the arrows by num1 and the length (height) by num2 . If you
only include one number, the arrows are scaled the same in both
directions. Changing arrowscale can give you special effects not
possible by changing the parameters described above. E.g., you
can change the width of lines used to draw brackets.
The size of dots is controlled by the dotsize parameter.
om
3 Lines and polygons
\psdiamond*[par](x0,y0)(x1,y1)
e.c
\psdiamond draws a diamond centered at (x0,y0), and with the
half width and height equal to x1 and y1, respectively.
rib
2
0
1
2
3
4
AB
0
Ct
\psdiamond[framearc=.3,fillstyle=solid,
fillcolor=lightgray](2,1)(1.5,1)
1
The diamond is rotated about the center by
gangle=gangle
Default: 0
\pstriangle*[par](x0,y0)(x1,y1)
\pstriangle draws an isosceles triangle with the base centered at
(x0,y0), and with width (base) and height equal to x1 and y1,
respectively.
2
1
\pstriangle*[gangle=10](2,.5)(4,1)
0
0
1
2
3
4
Lines and polygons
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 5]
3
4 Framed boxes
\psdiabox*[par]{stuff }
\psdiabox draws a diamond.
Happy?
\psdiabox[shadow=true]{\Large\bf Happy?}
\pstribox*[par]{stuff }
\pstribox draws a triangle.
Begin
om
\pstribox[trimode=R,framesep=5pt]{\Large\bf Begin}
The triangle points in the direction:
Default: U
e.c
trimode=*U/D/R/L
AB
Ct
rib
If you include the optional *, then an equilateral triangle is drawn,
otherwise, you get the minimum-area isosceles triangle.
\pstribox[trimode=*U]{\Huge Begin}
Begin
5 Obsolete put commands
There is an obsolete command \Rput that has the same syntax as \uput
and that works almost the same way, except the refangle argument has
the syntax of \rput’s refpoint argument, and it gives the point in stuff that
should be aligned with (x,y). E.g.,
\qdisk(4,0){2pt}
\Rput[tl](4,0){$(x,y)$}
(x; y)
Here is the equivalence between \uput’s refangle abbreviations and
\Rput’s refpoint abbreviations:
Framed boxes
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 6]
4
\uput
r
u
l
d
ur
ul
dr
dl
\Rput
l
b
r
t
bl
br
tr
rl
Some people prefer \Rput’s convention for specifying the position of
stuff over \uput’s.
AB
Ct
rib
e.c
om
Once upon a time there was \psput instead of \nput. This feature is still
supported for backwards compatibility.
Obsolete put commands
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 7]
5
Questo documento e' un frammento dell'intero appunto utile come
anteprima. Se desideri l'appunto completo clicca questo link.
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 8]
Preparati con le domande di ABCtribe su Informatica.
1. Reti LAN e
Risposta:
Le reti LAN (Local Area Network) sono
[Clicca qui >> per continuare a leggere].
2. Funzio
Risposta:
Una funzione hash prende
[Clicca qui >> per continuare a leggere].
* Carica Appunti,Domande,Suggerimenti su : Informatica e guadagna punti >>
* Lezioni Private per Informatica >>
Avvertenze:
La maggior parte del materiale di ABCtribe.com è offerto/prodotto direttamente dagli studenti (appunti, riassunti,
dispense, esercitazioni, domande ecc.) ed è quindi da intendersi ad integrazione dei tradizionali metodi di studio e
non vuole sostituire o prevaricare le indicazioni istituzionali fornite dai docenti. Il presente file può essere utilizzato in
base alle tue necessità ma non deve essere modificato in alcuna sua parte, conservando in particolare tutti i
riferimenti all’autore ed a ABCtribe.com; non potrà essere in alcun modo pubblicato tramite alcun mezzo, senza
diverso accordo scritto con l’autore ed i responsabili del progetto ABCtribe.com. Per eventuali informazioni, dubbi o
controversie contattate la redazione all’indirizzo [email protected].
ABCtribe.com - [Pagina 9]
Scarica